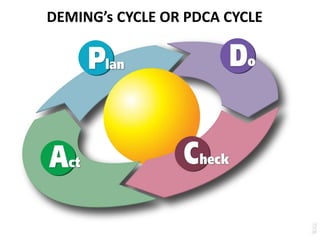
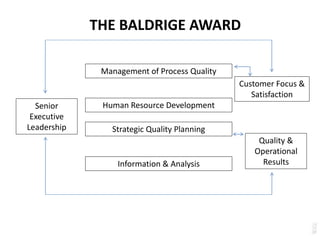
Quality refers to meeting customer requirements and needs. It is defined by characteristics like performance, reliability, durability, and conformance for products, and attributes like timeliness, courtesy, accuracy for services. Total quality management aims to integrate all organizational functions to achieve continuous quality improvement through prevention over inspection and customer satisfaction. It requires leadership commitment, employee involvement, and a long-term process focus. Quality gurus like Deming, Juran, and Crosby provided frameworks like the PDCA cycle and emphasis on goals, training, and management roles to implement quality programs.