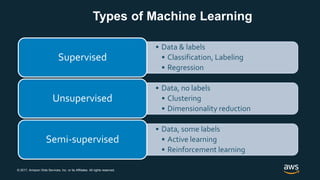
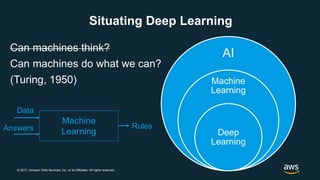
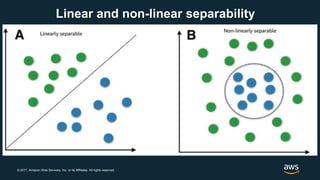
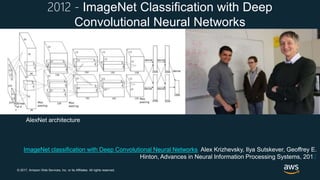
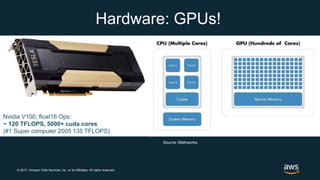
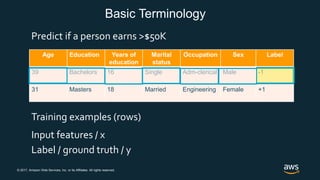
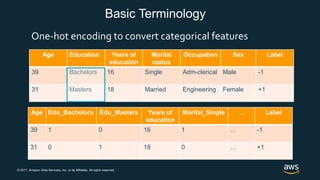
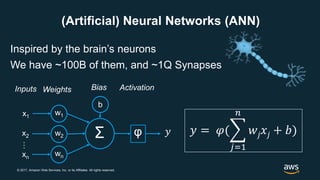
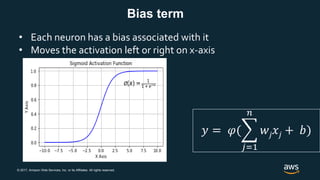
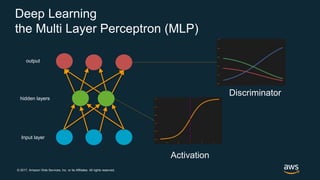
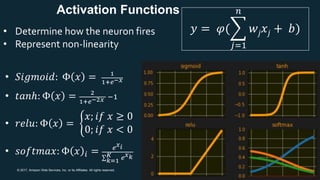
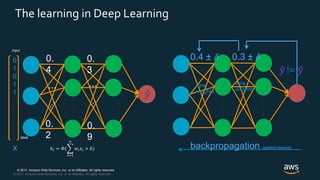
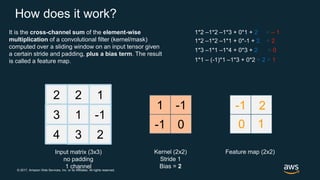
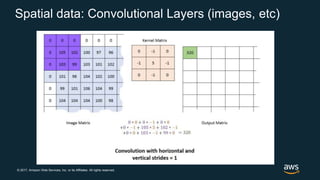
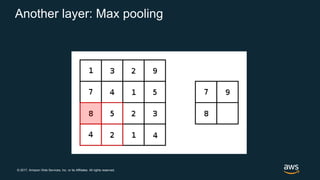
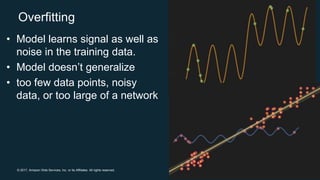
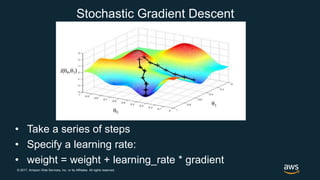
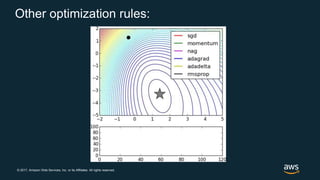
The document provides an overview of deep learning fundamentals. It discusses key concepts like neural networks, convolutional neural networks, activation functions, backpropagation, and optimization techniques like stochastic gradient descent. Examples are given of deep learning applications in areas like computer vision, natural language processing, and medical imaging. The document also traces the history and growth of deep learning since 2012, driven by advances in hardware, software frameworks, and large datasets.