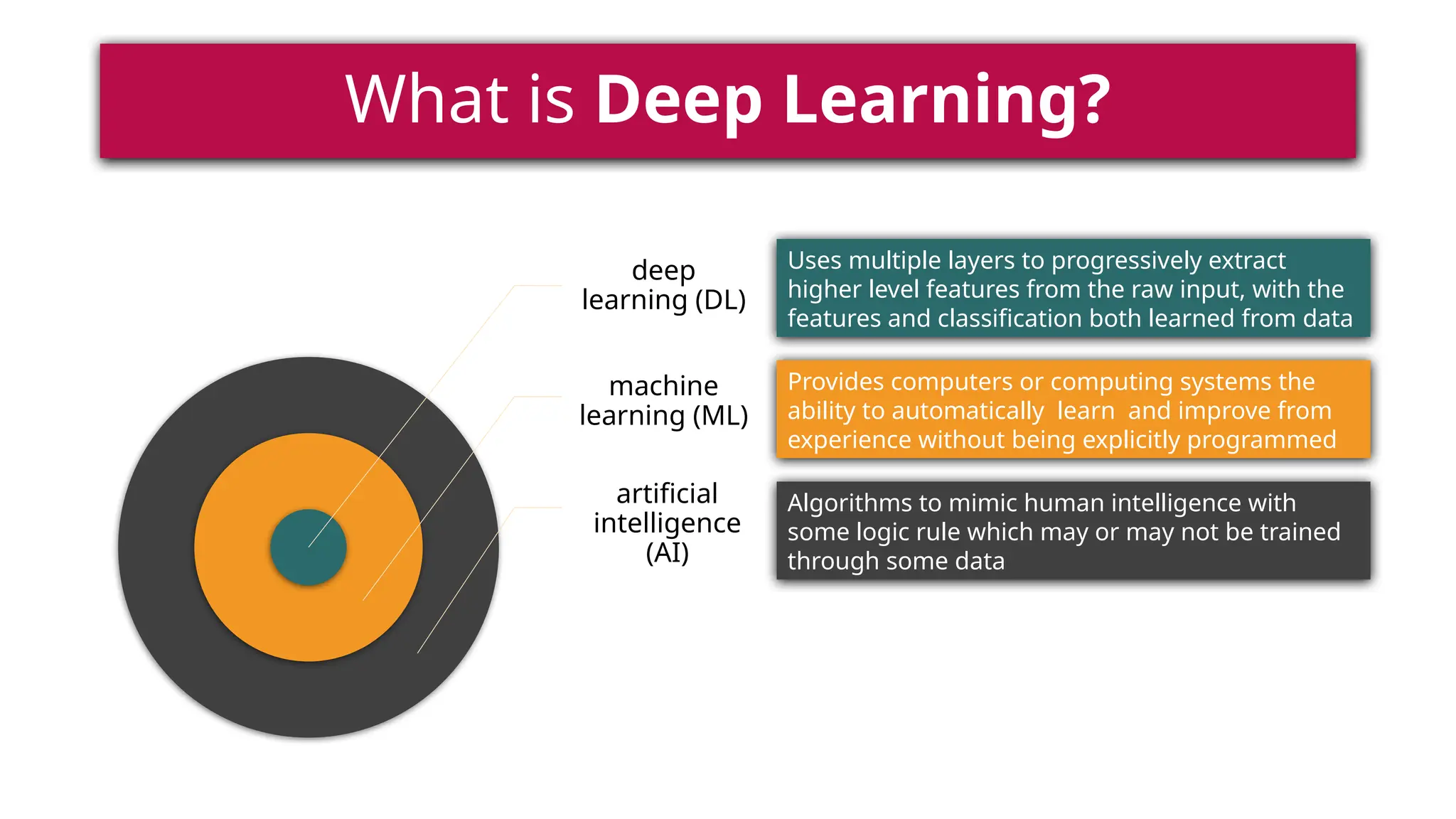
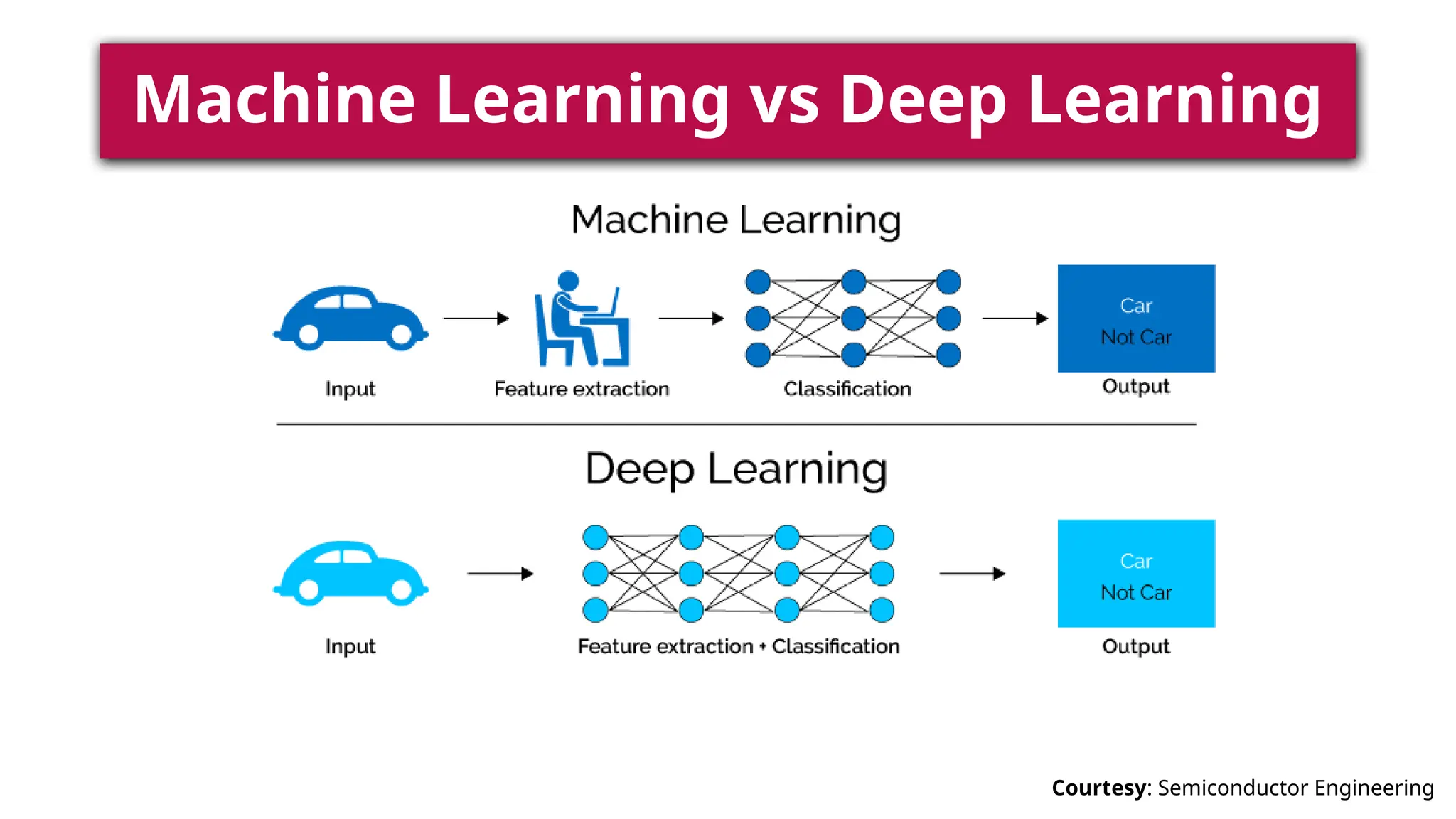
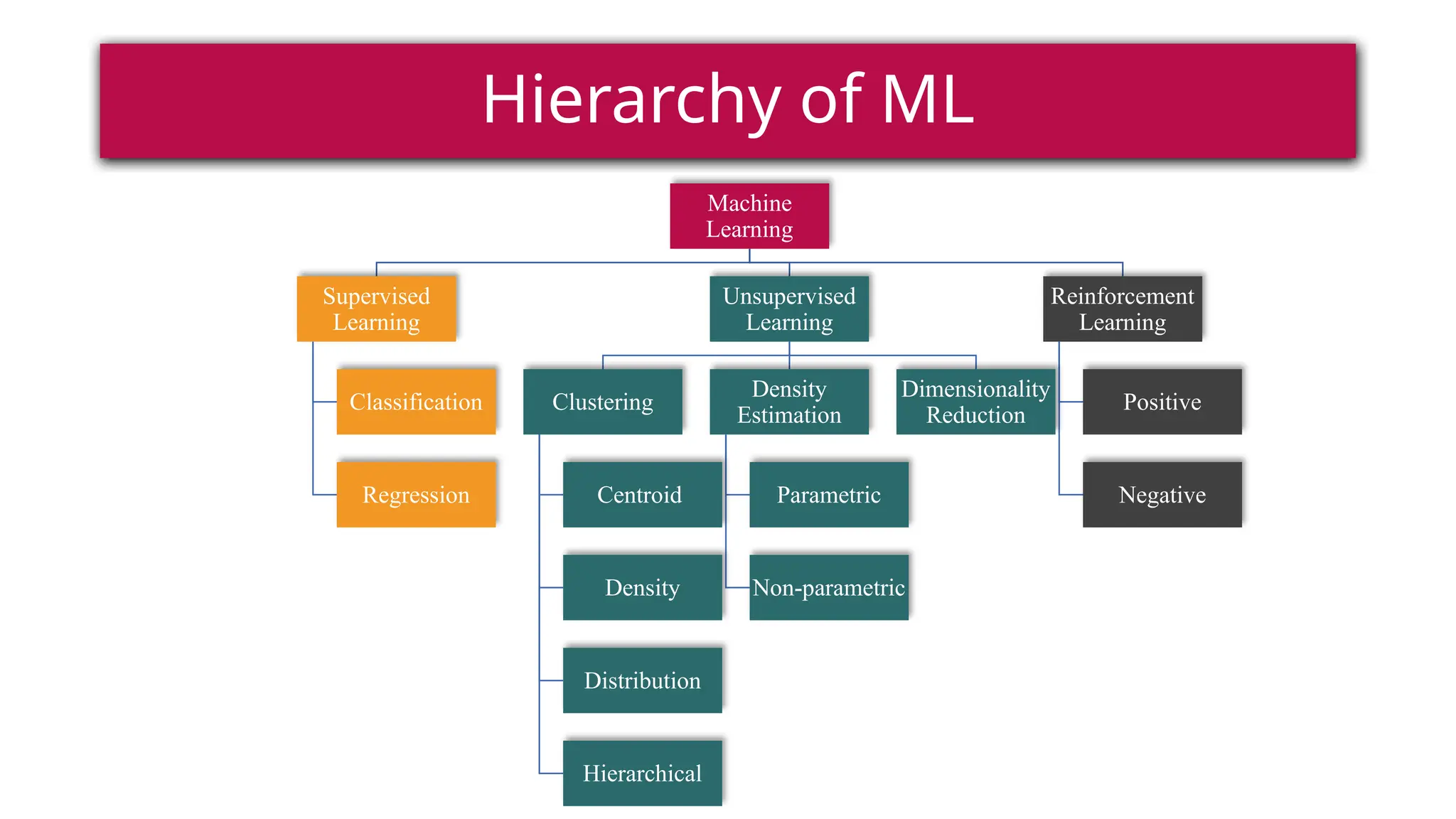
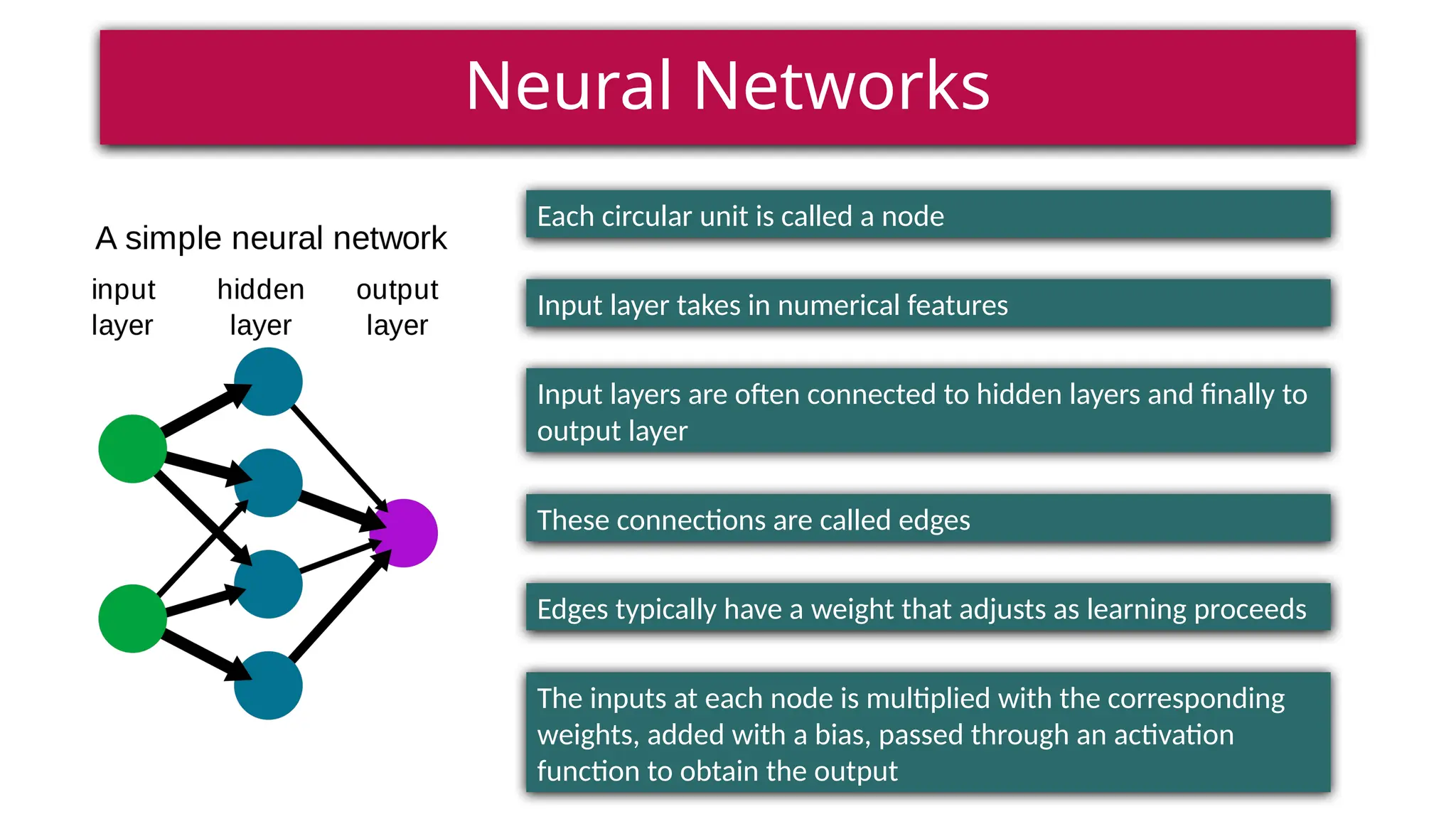
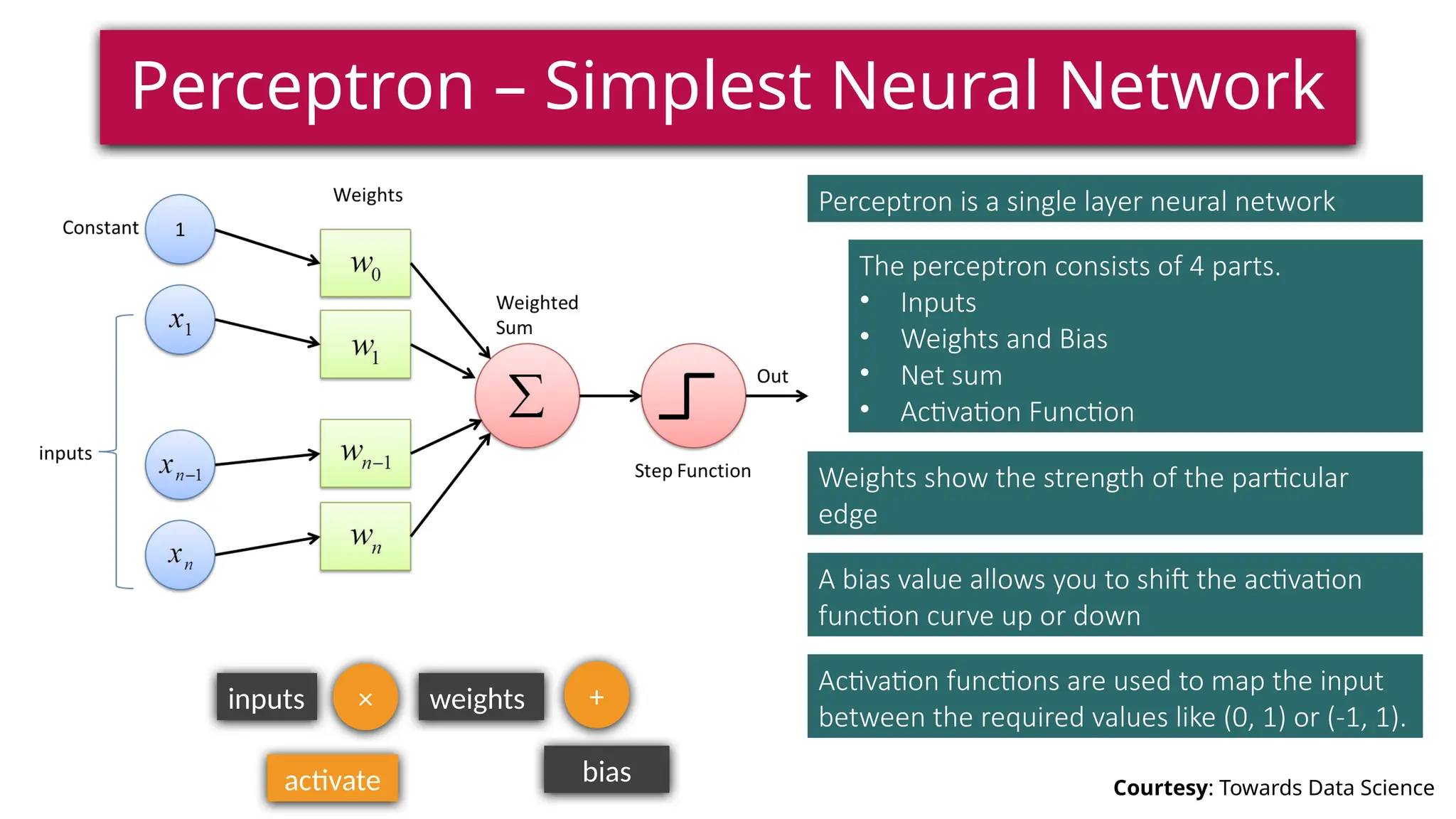
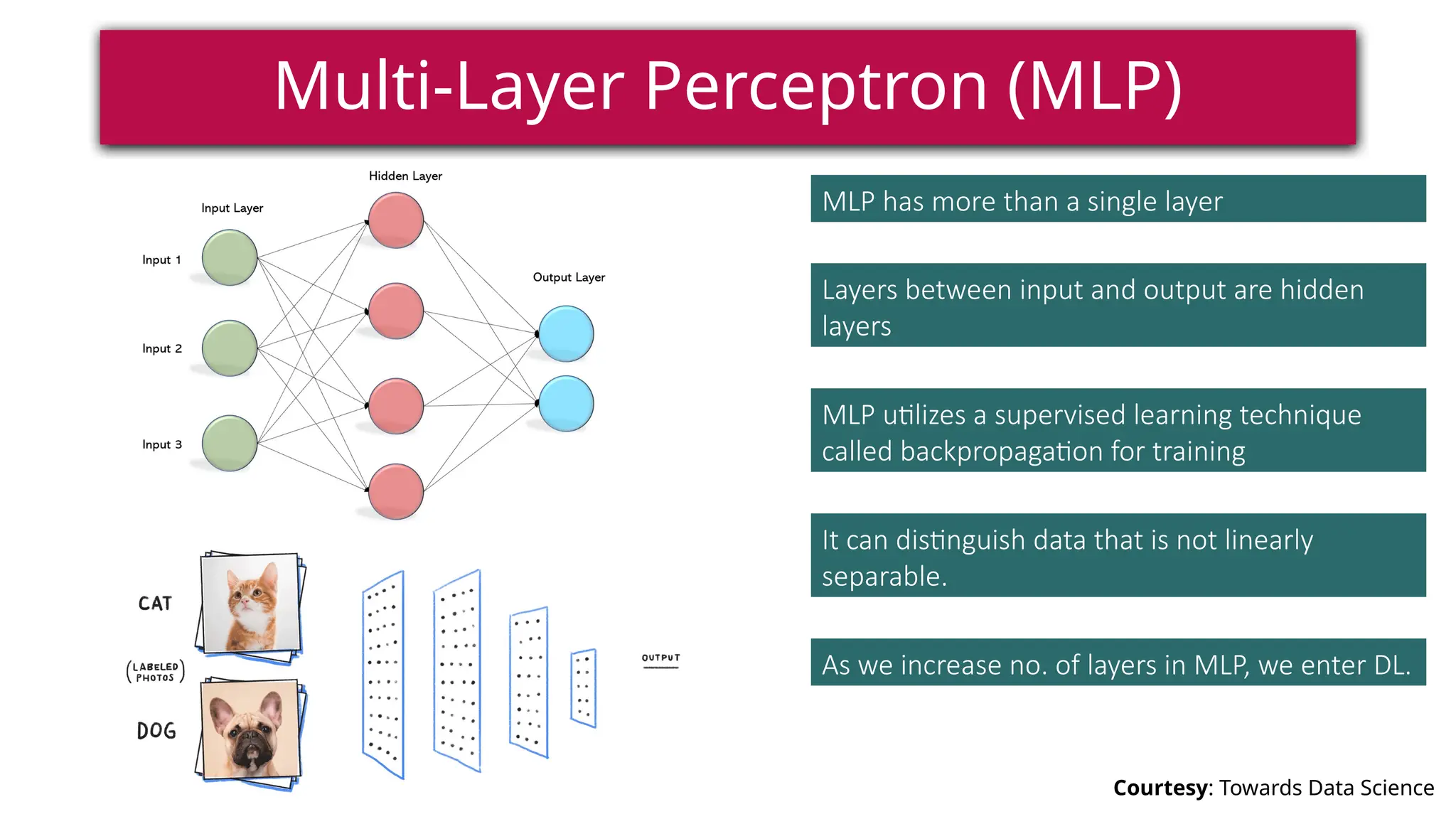
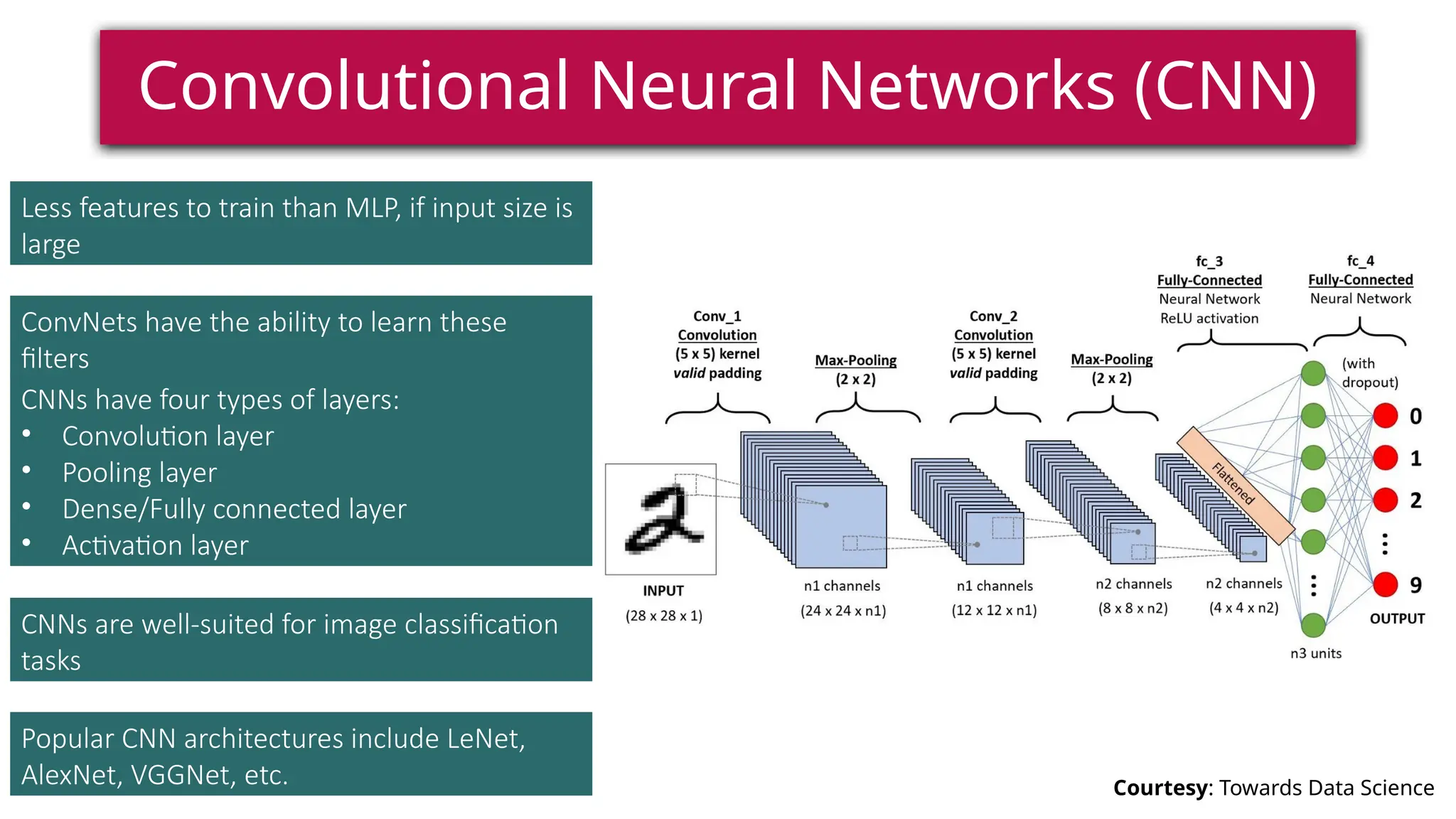
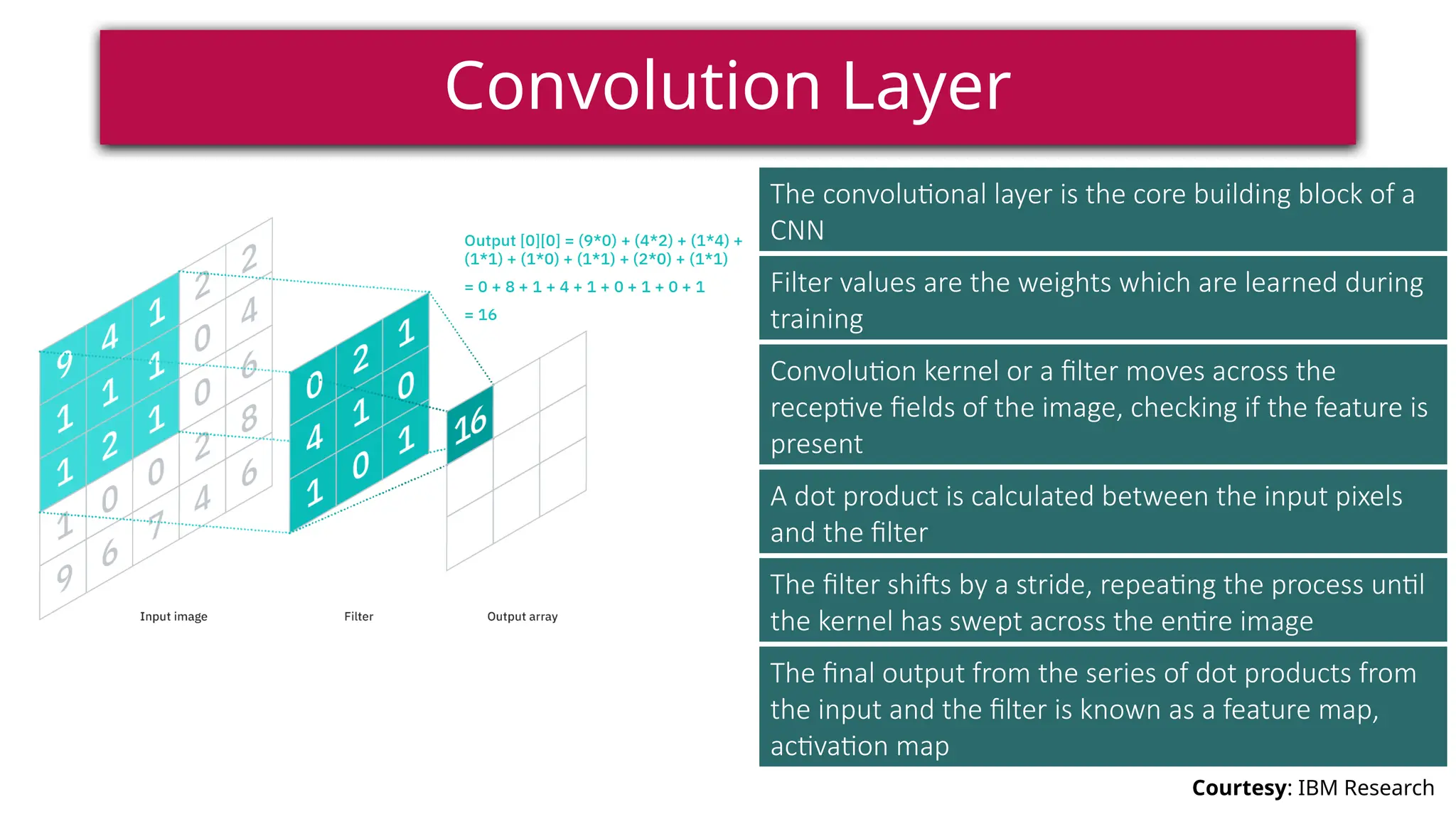
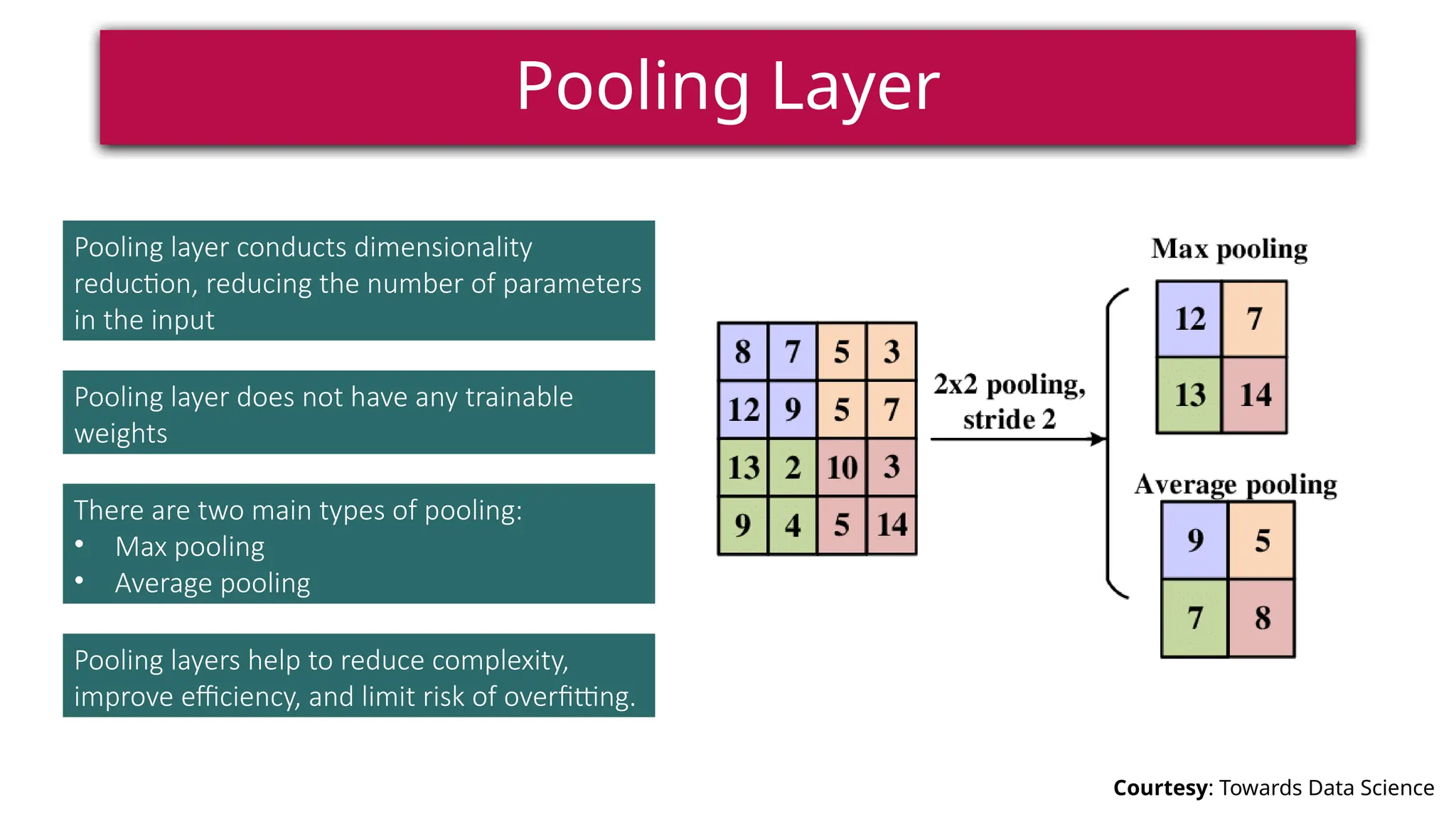
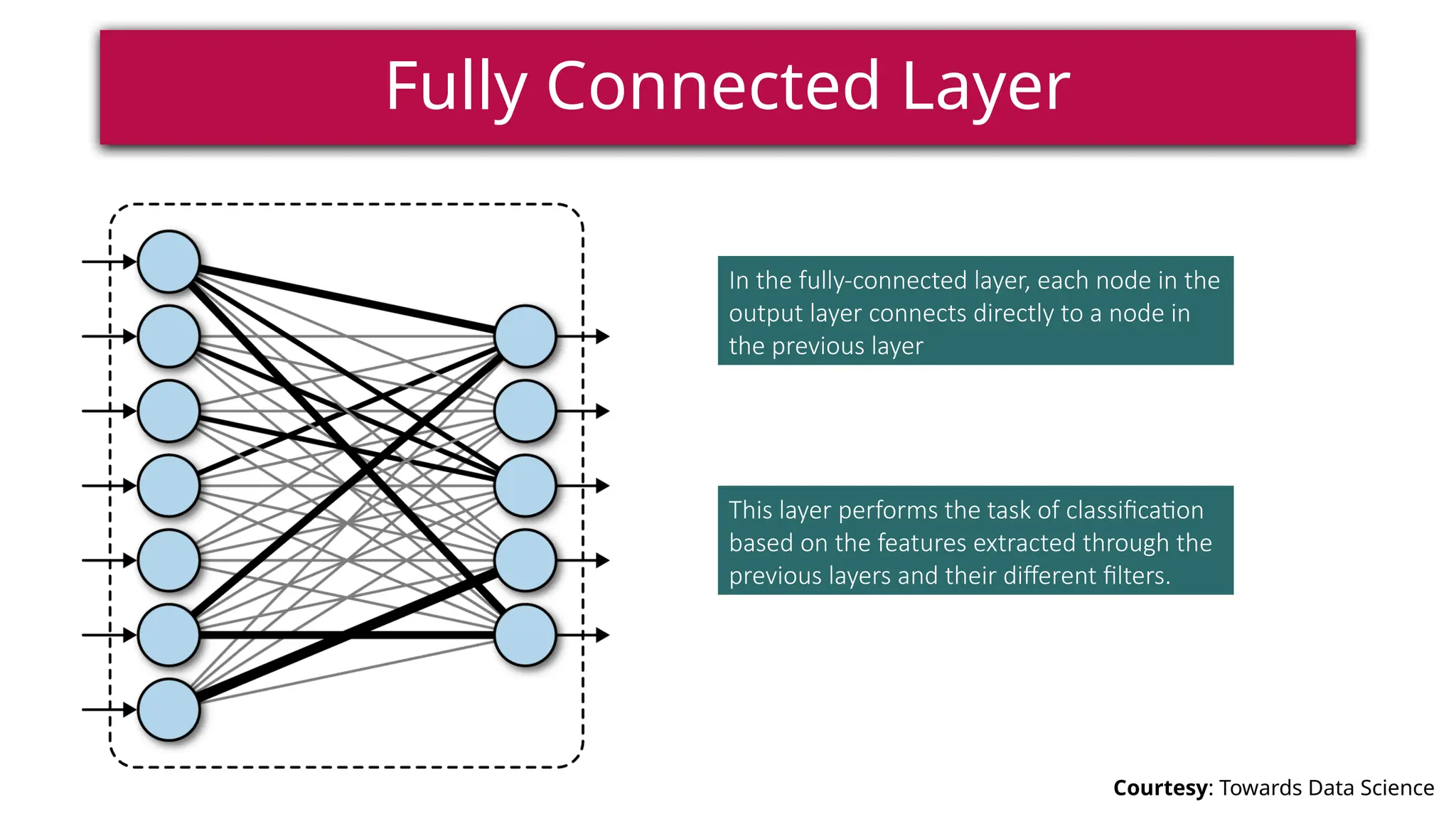
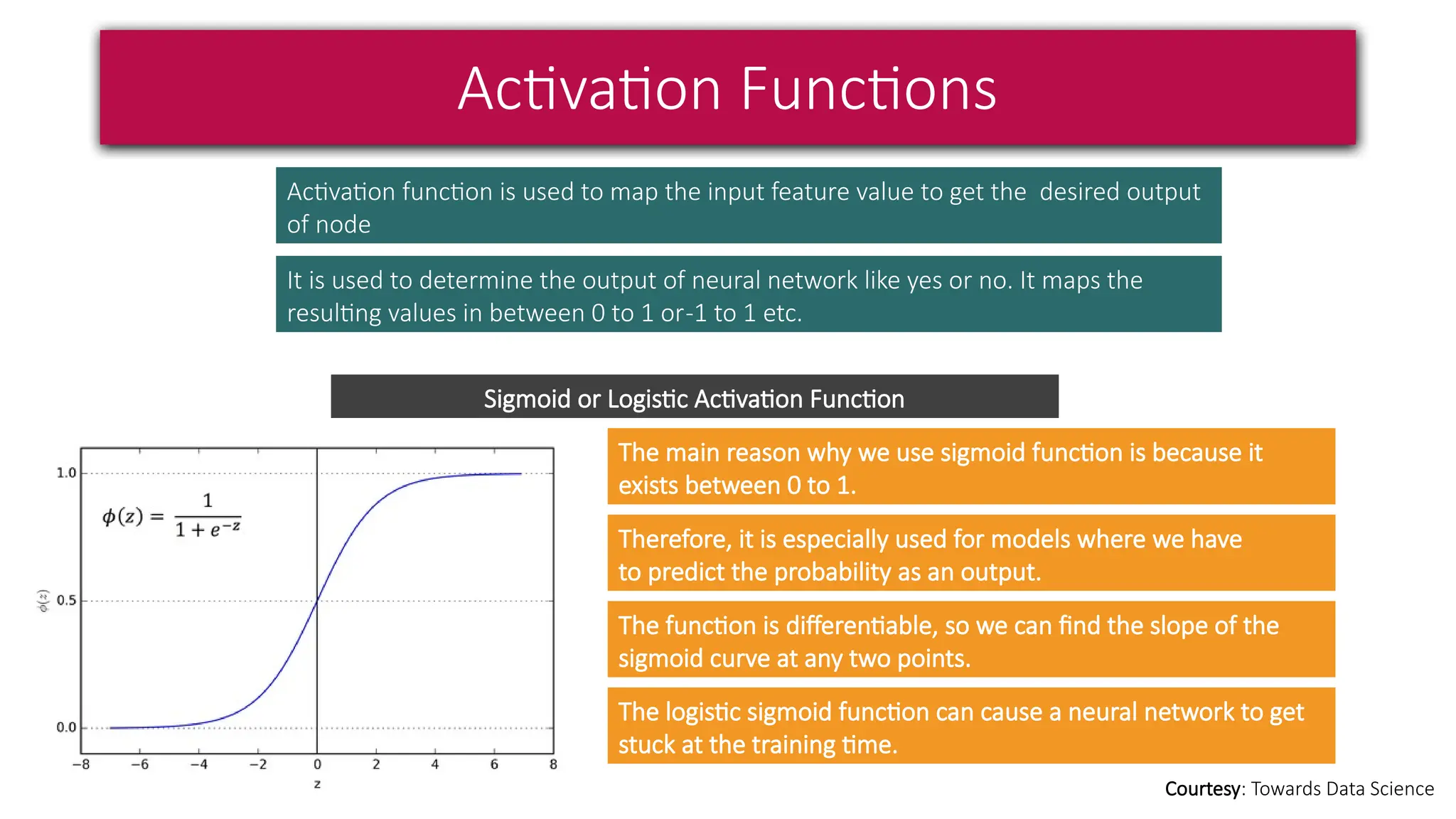
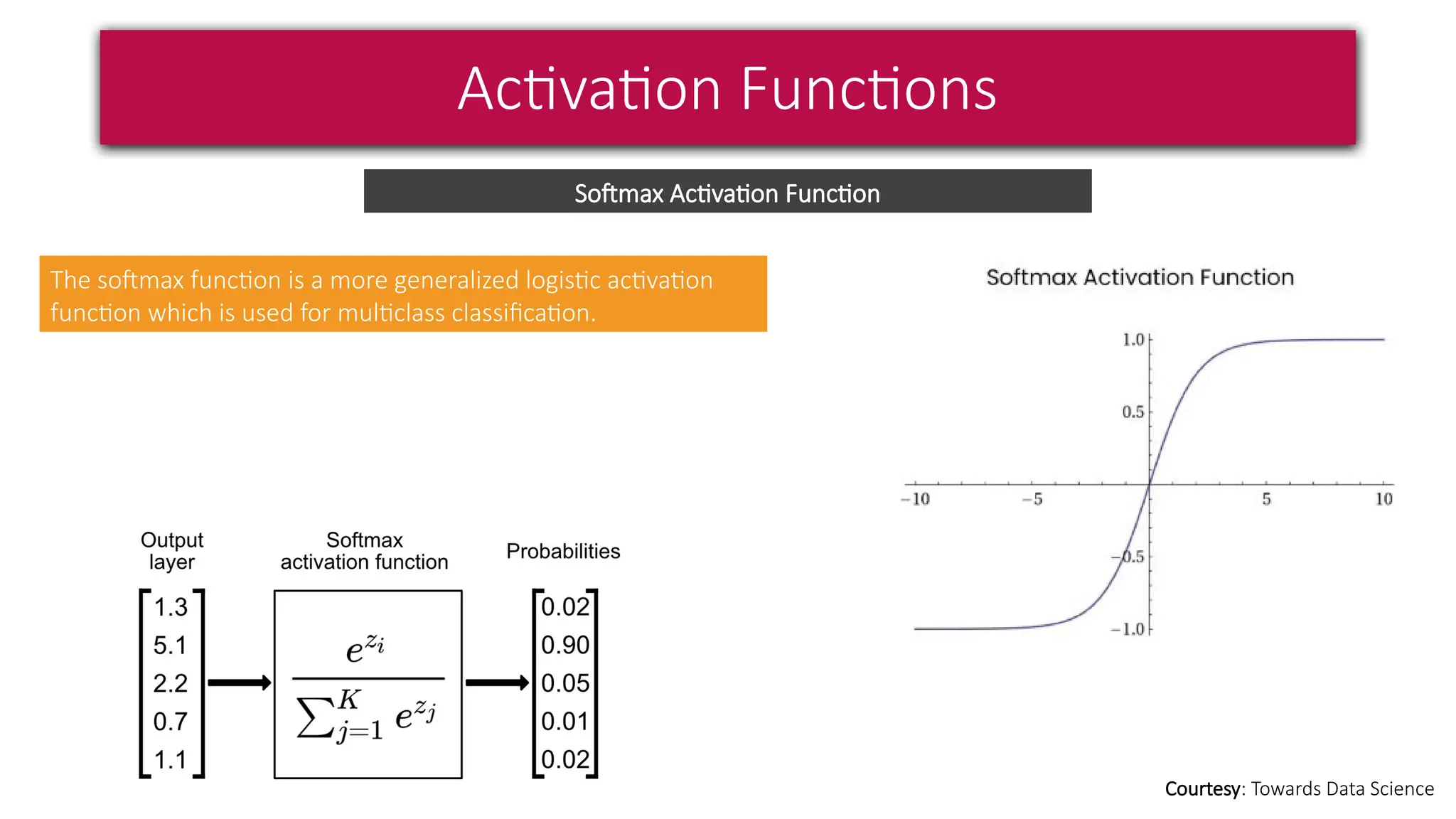
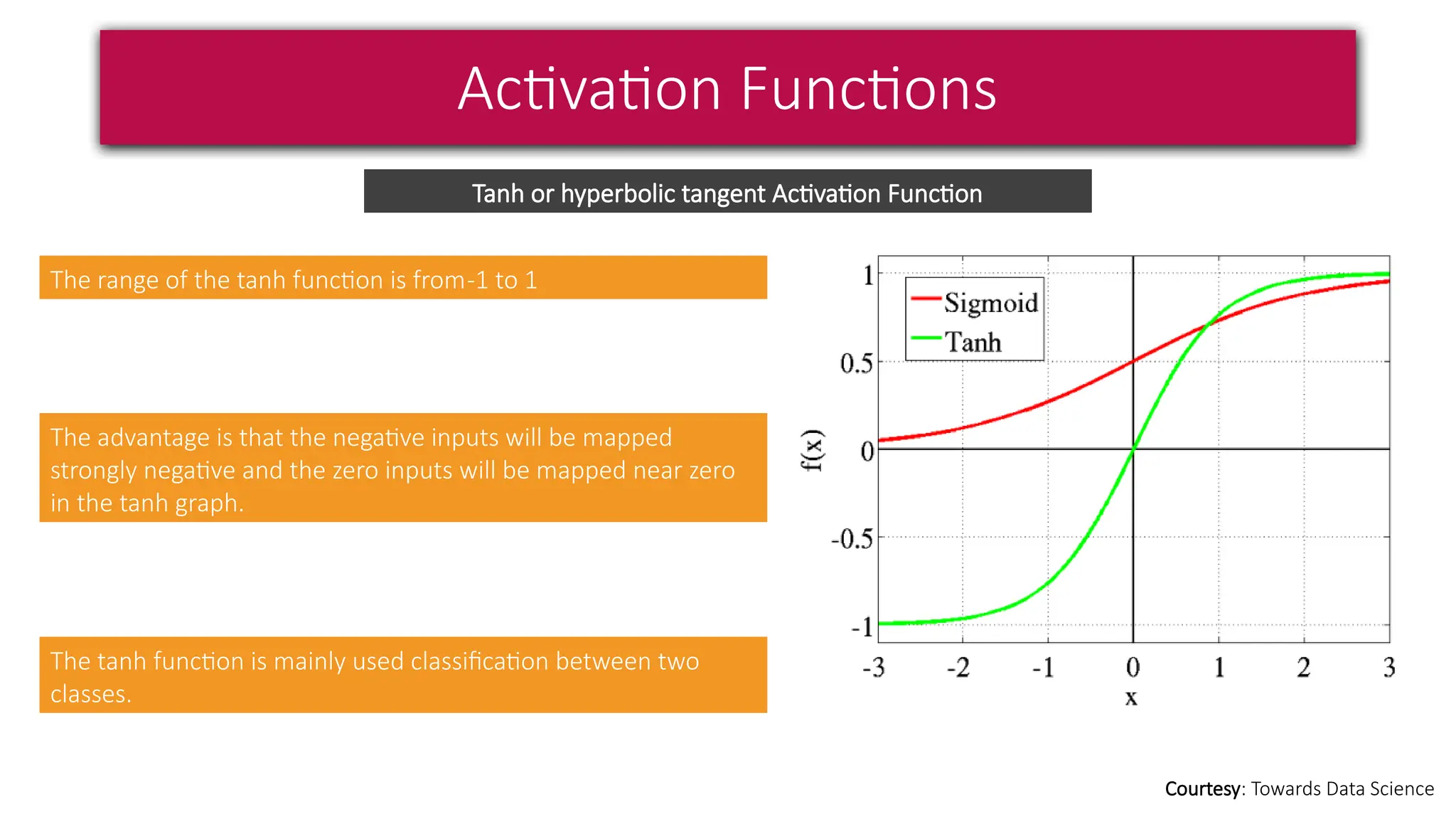
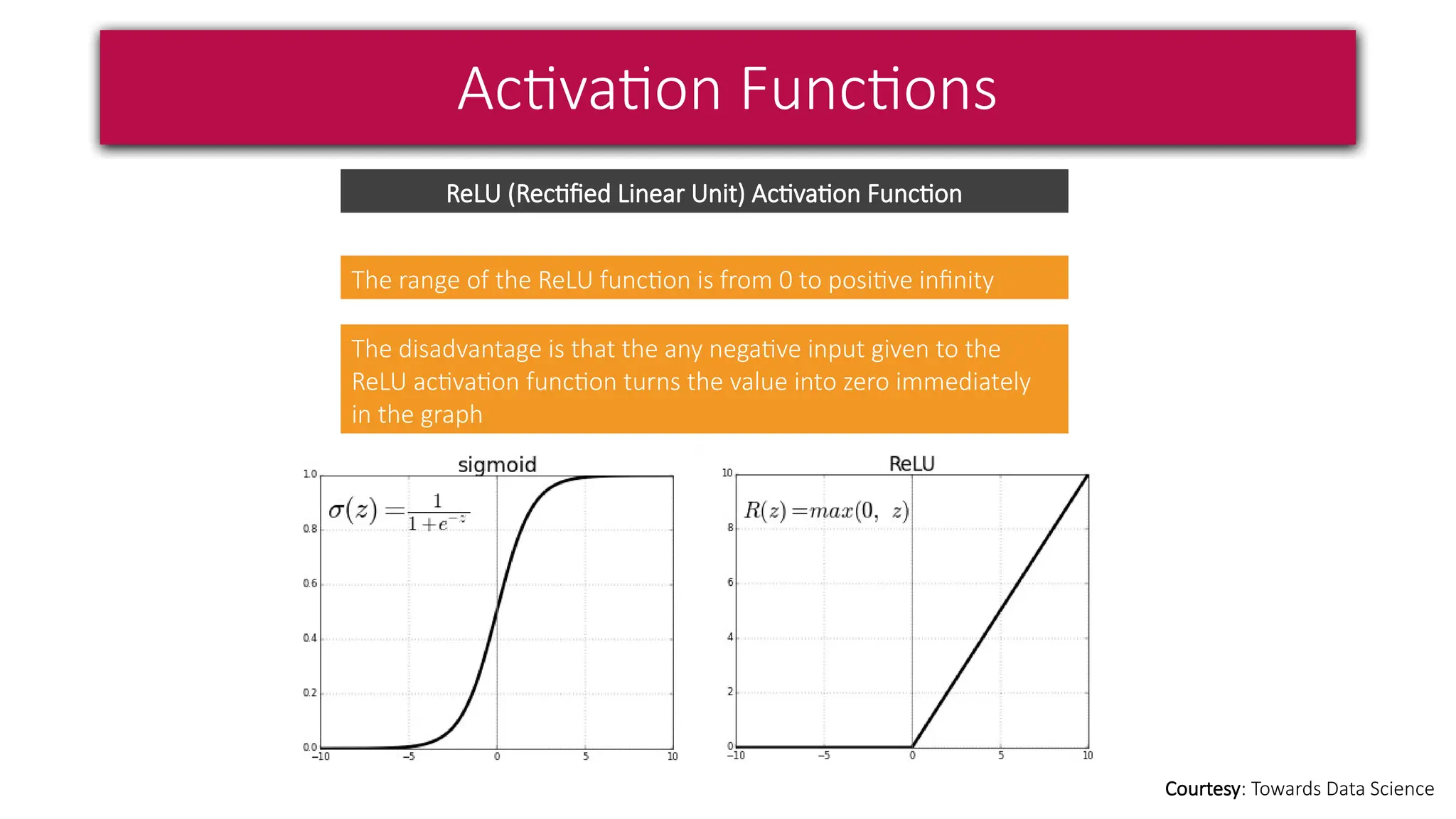
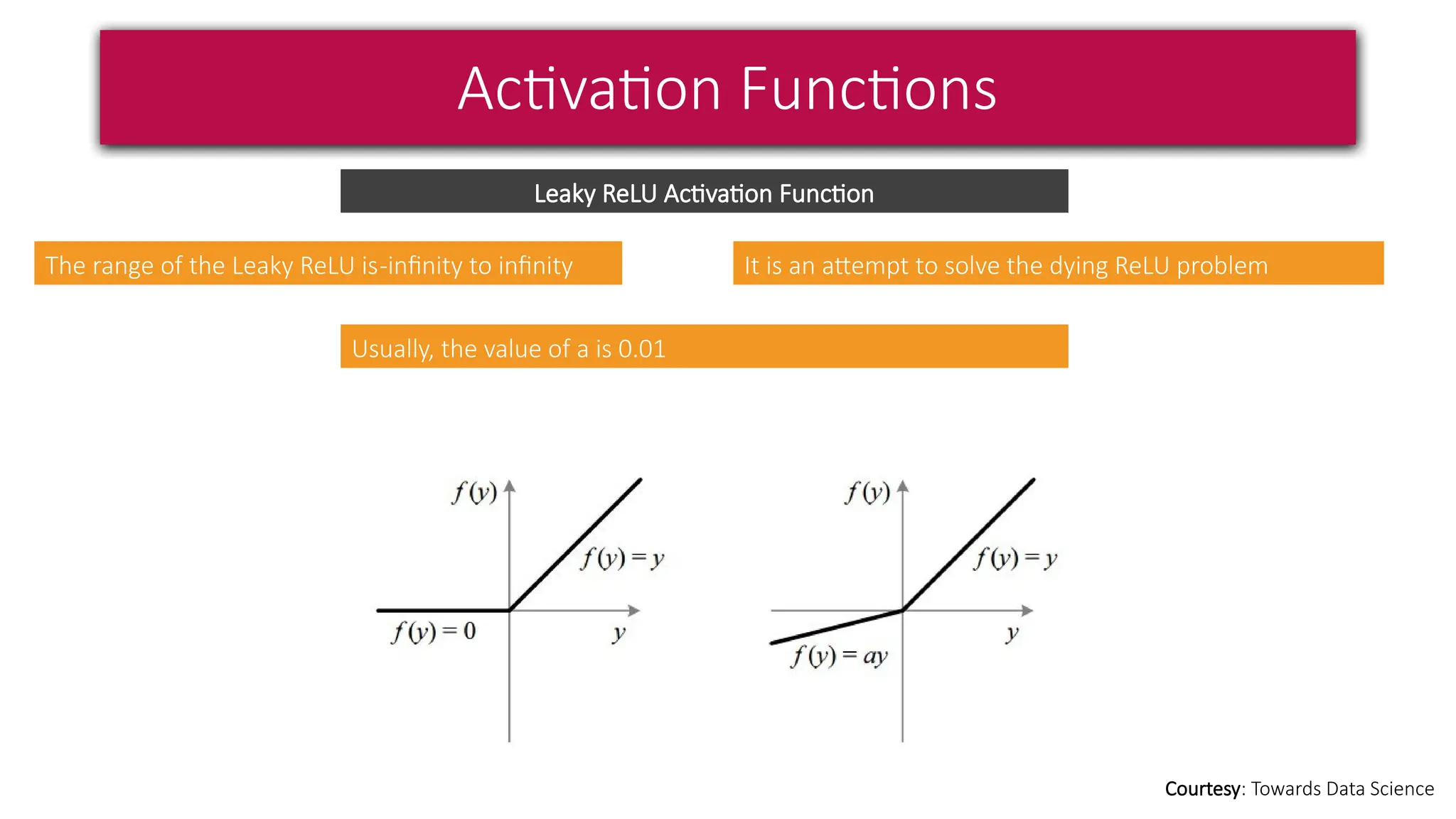
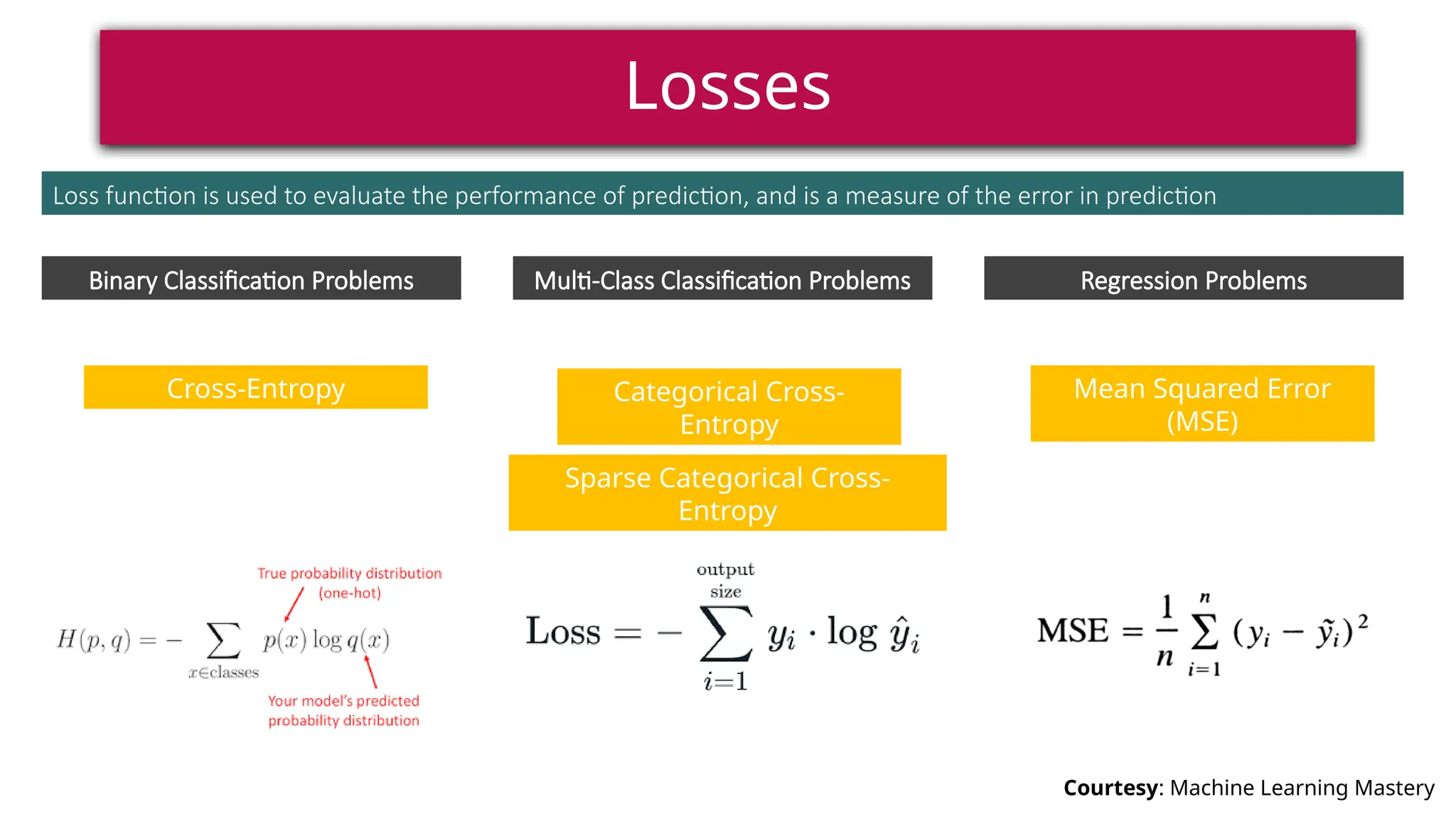
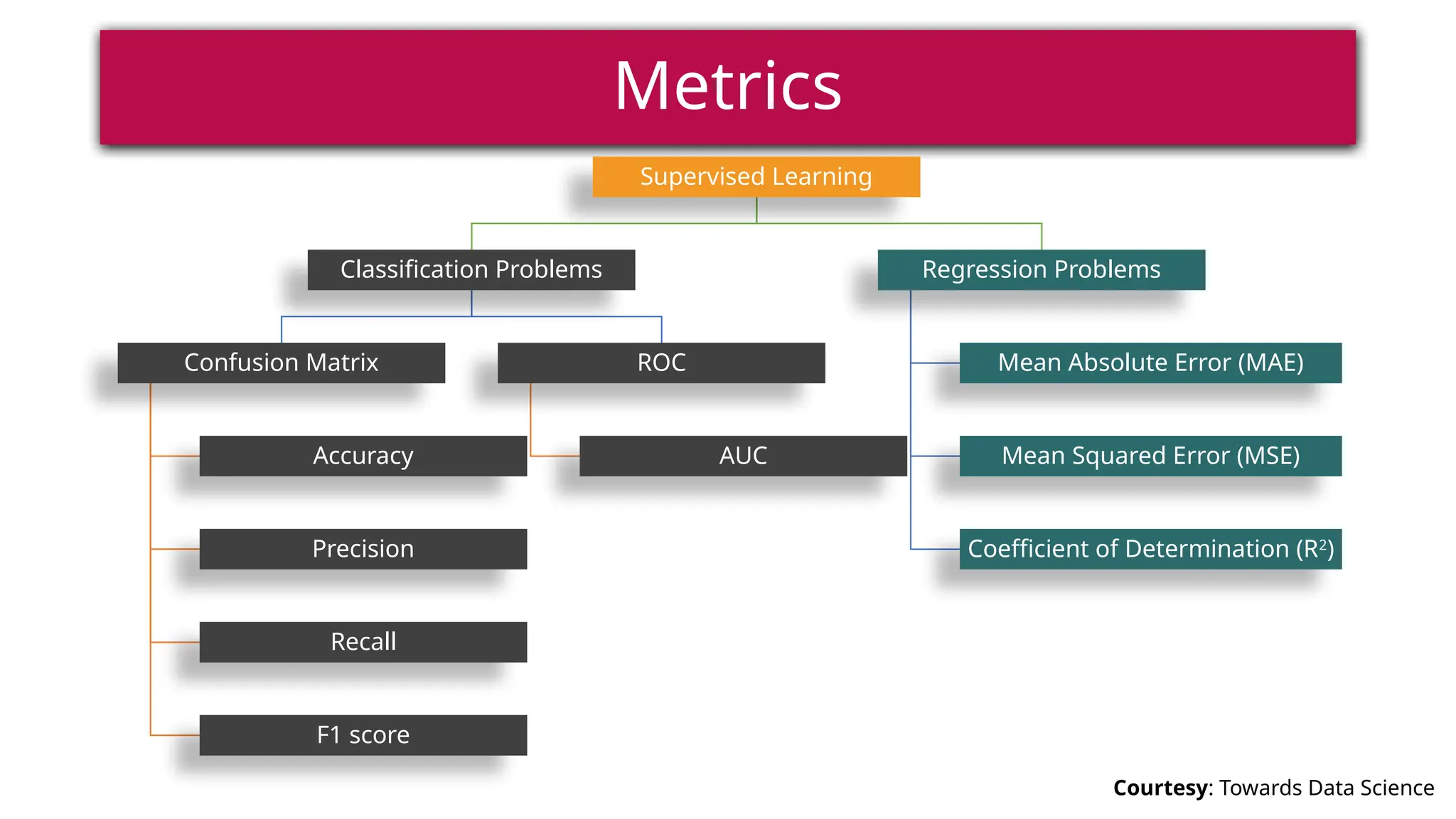
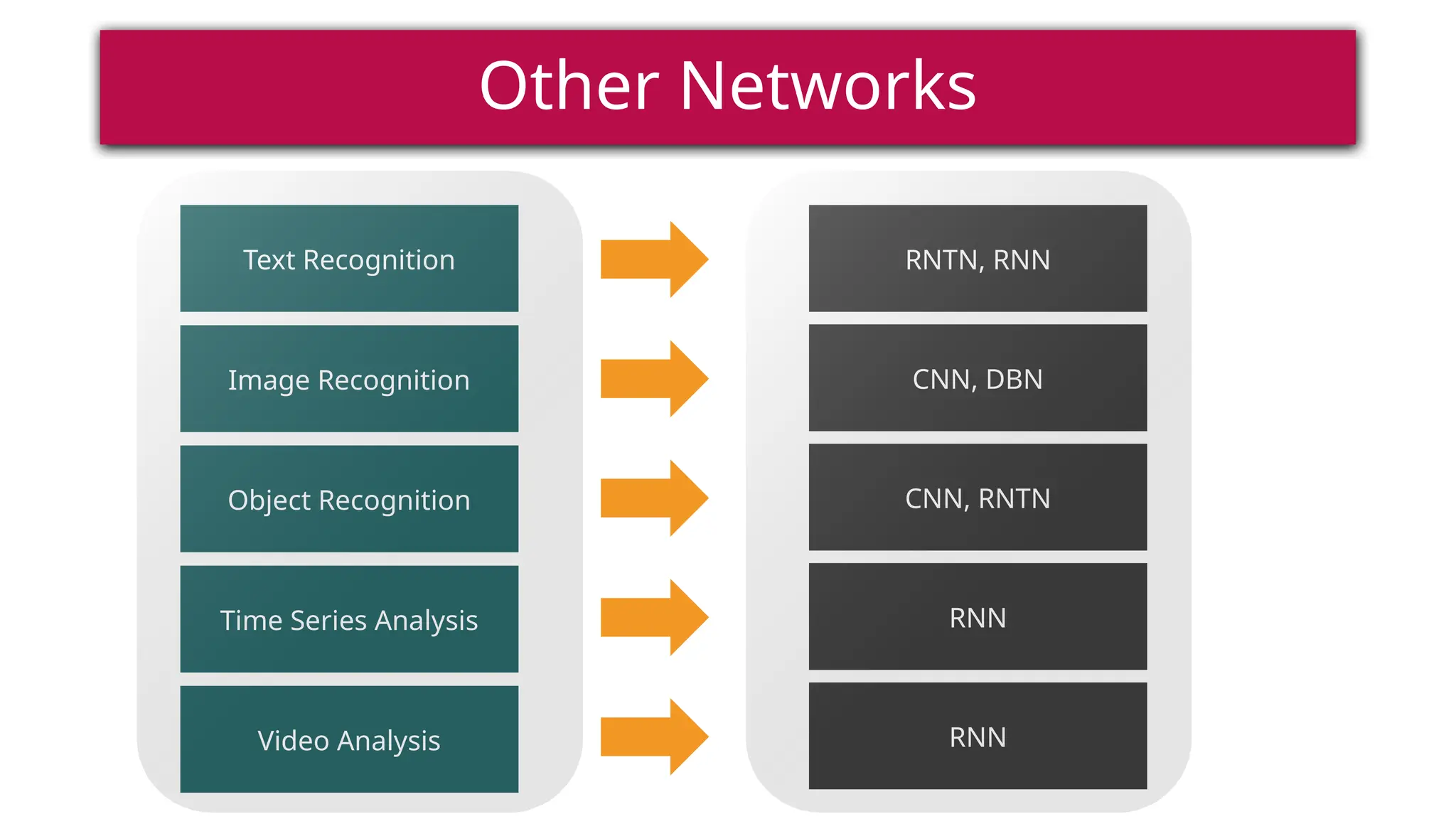
This document provides a comprehensive overview of deep learning, defining it as a subset of machine learning within artificial intelligence, employing multiple layers to extract features from input data. It discusses various neural network architectures like perceptrons, multi-layer perceptrons, and convolutional neural networks, detailing their components and functions in tasks such as image classification and medical diagnostics. The document also covers key concepts such as activation functions, loss functions, and performance metrics essential for training deep learning models.