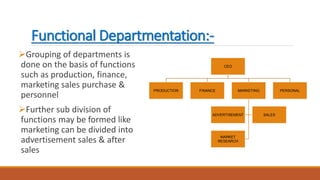
The document discusses departmentation, which is the process of dividing organizational activities into units or departments based on functions, products, regions, or customers. The key points are:
1) Departmentation aims to efficiently manage large undertakings by assigning work to those best suited and facilitating activities.
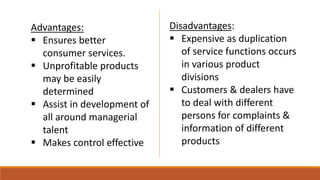
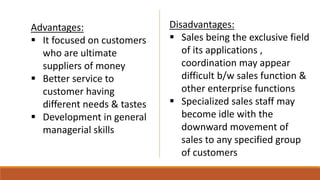
2) Common ways to departmentalize include by function, product, region, and customer, with advantages like specialization and control but disadvantages like lack of coordination.
3) Factors for effective departmentation include specialization, coordination, control, economy, and human considerations.