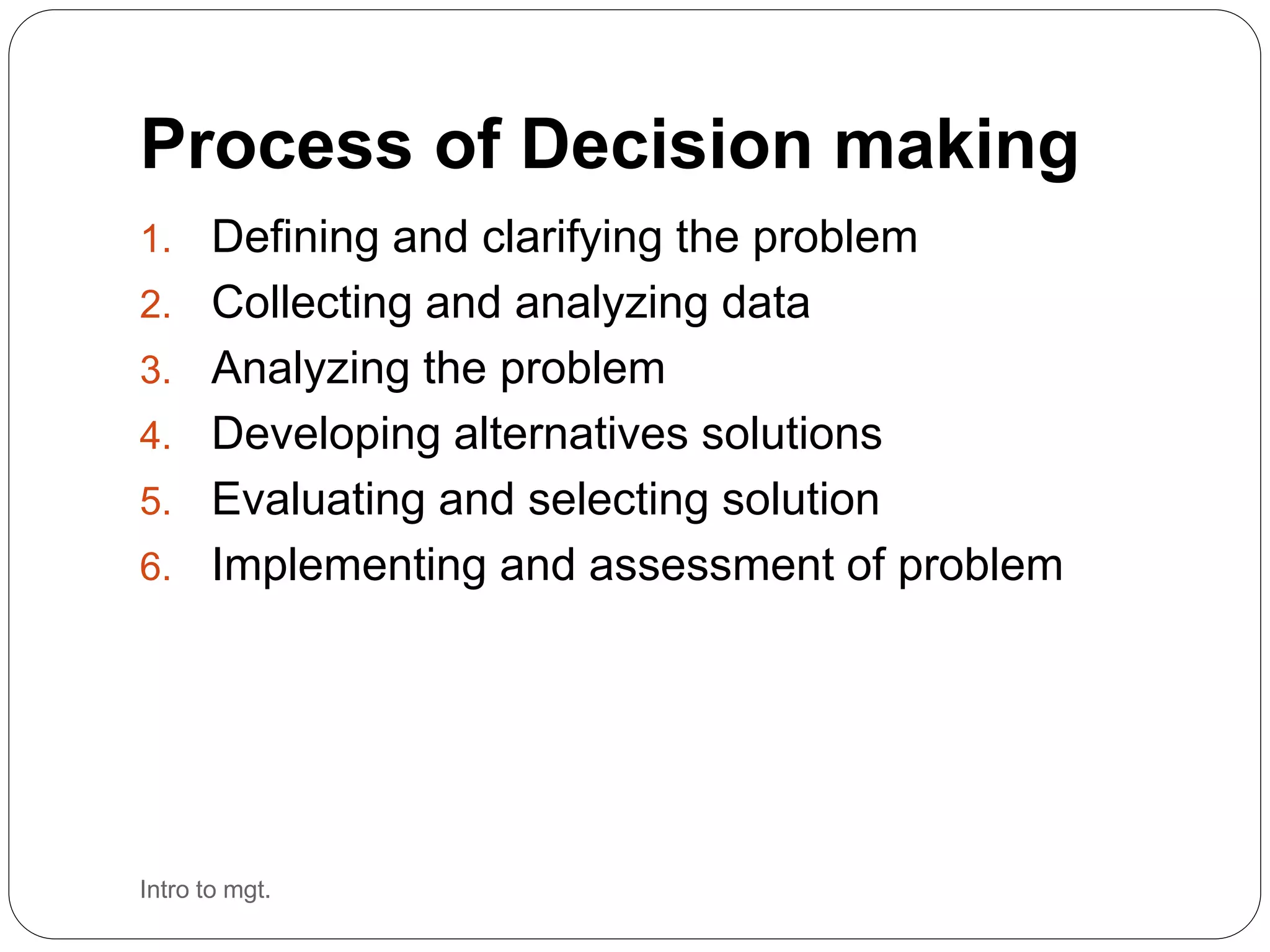
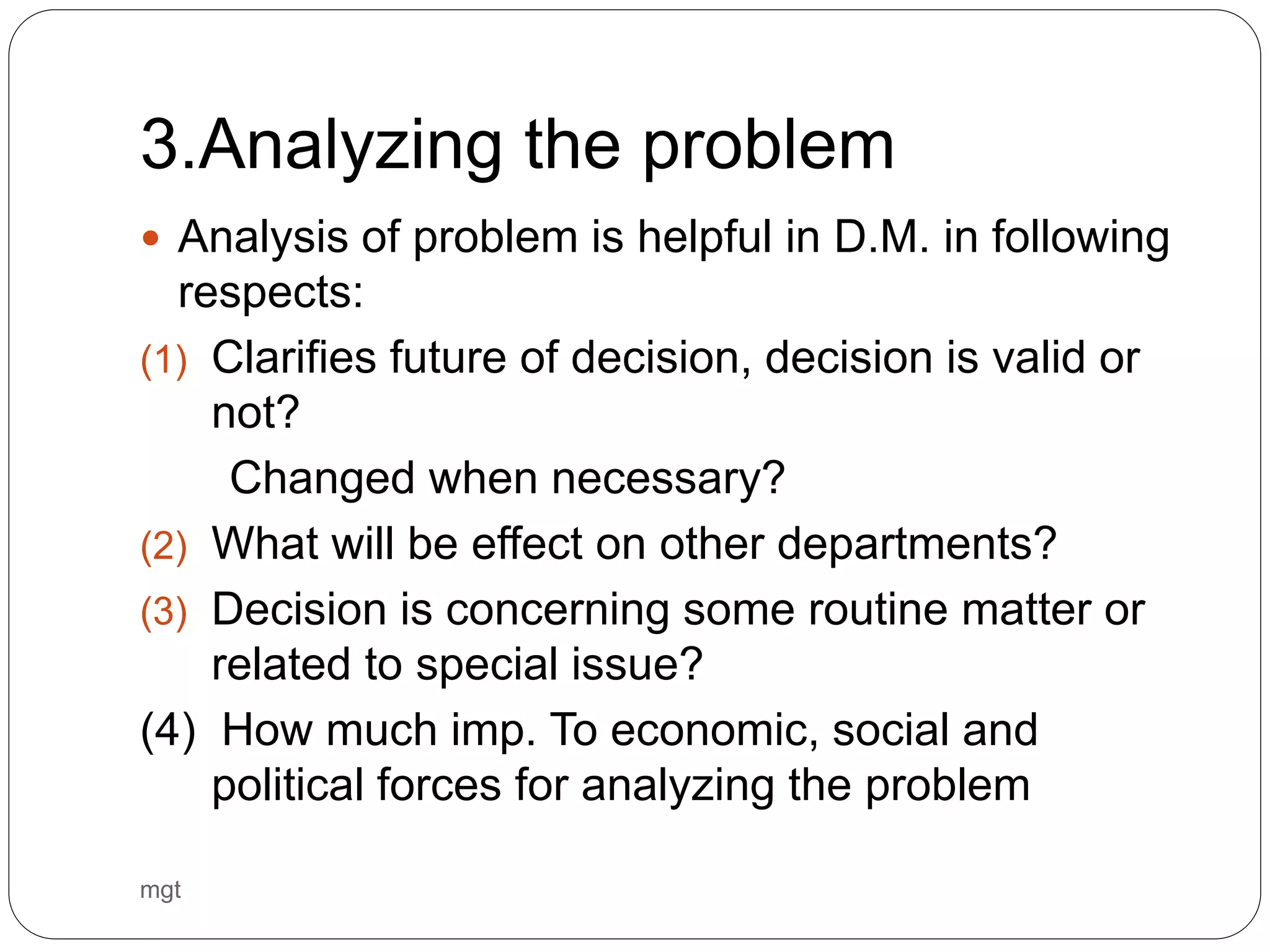
This document discusses decision making in business management. It outlines the decision making process which includes defining the problem, collecting and analyzing data, analyzing the problem, developing alternative solutions, evaluating and selecting a solution, and implementing and assessing the decision. It also discusses types of decisions like programmed vs non-programmed and strategic vs tactical. Potential impediments in decision making are identified as bad ideas, acting too fast, lack of information, and fear of failure. The document provides examples of business decisions at different stages.