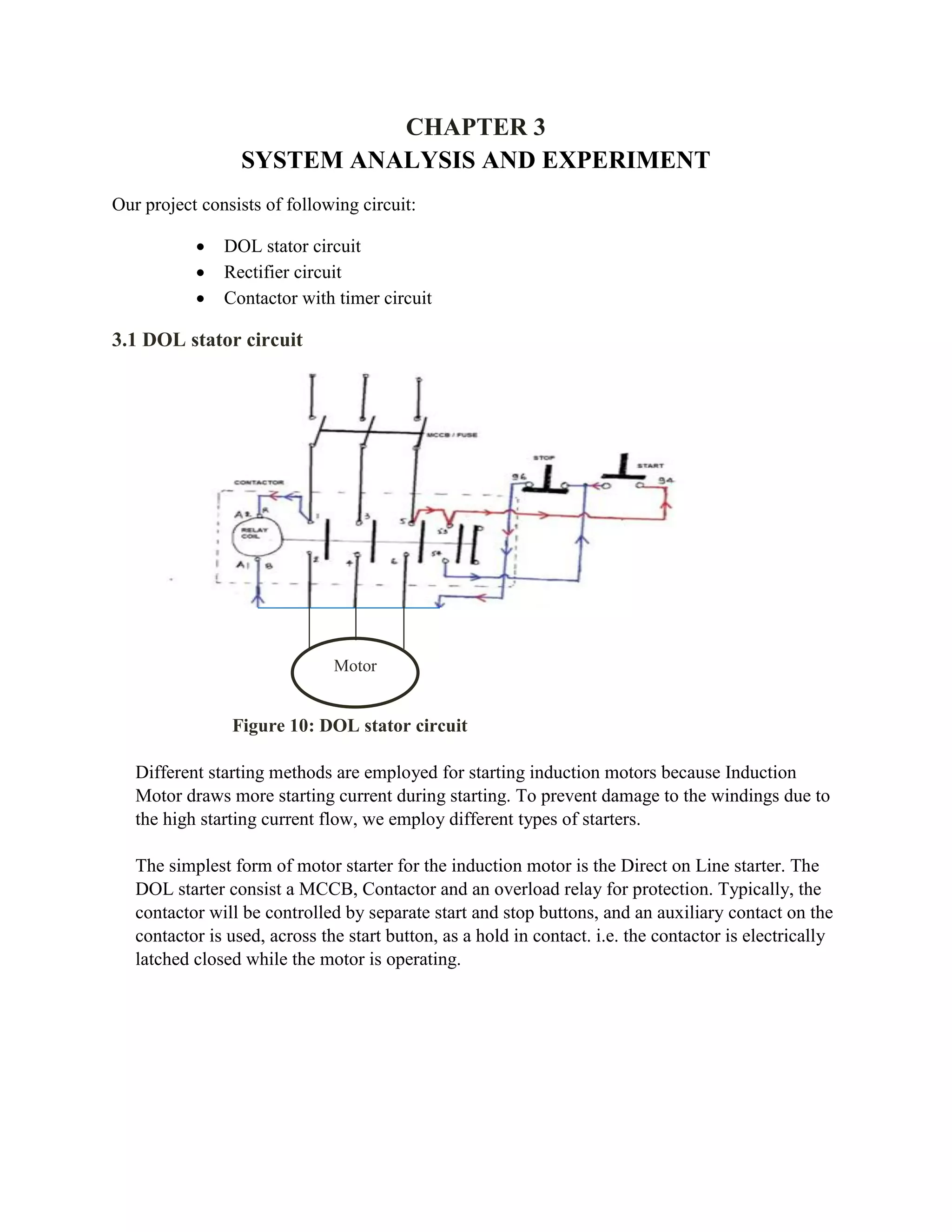
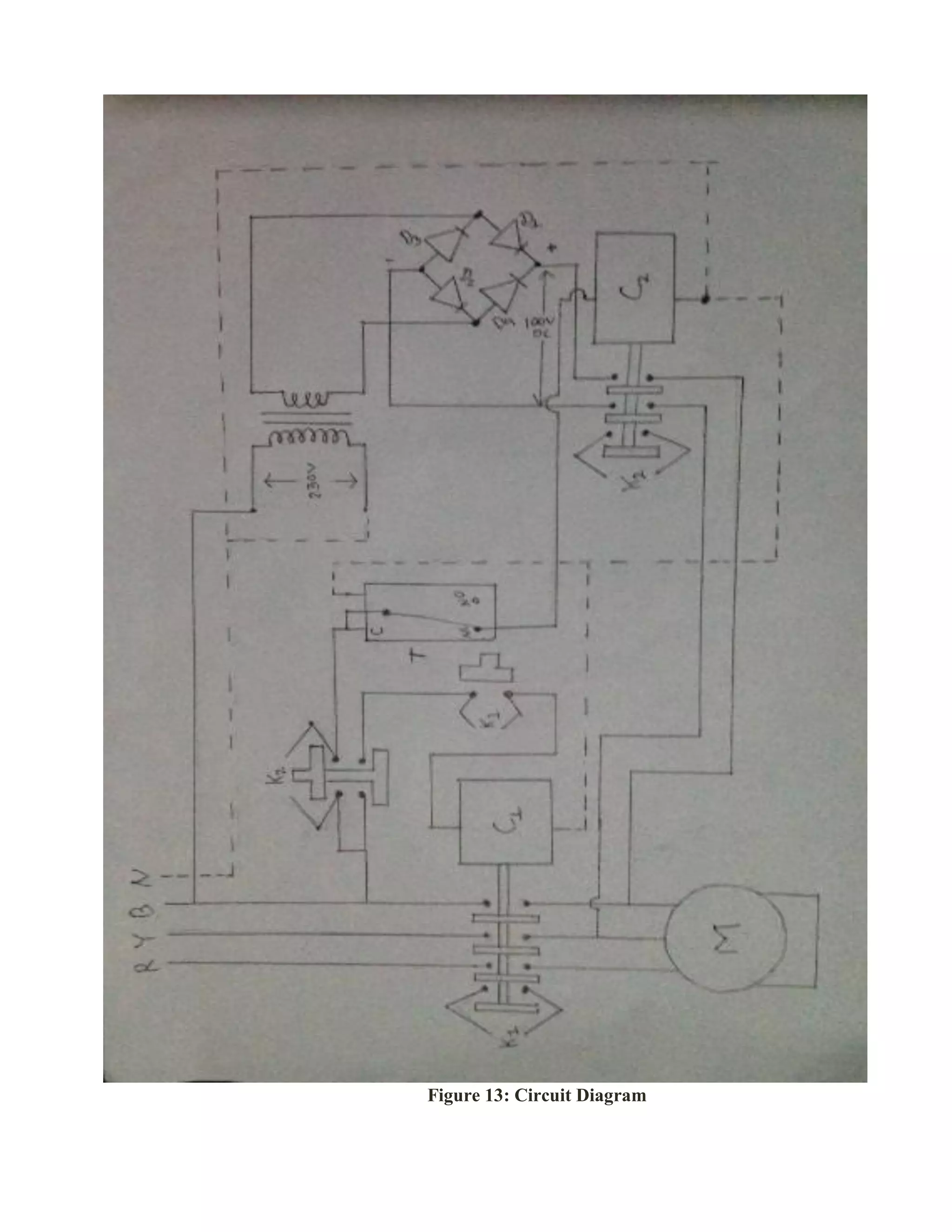
This document presents a project report on DC injection braking of an induction motor. The project aims to brake a 3-phase induction motor by disconnecting the 3-phase supply and connecting a DC supply to one of the motor windings. Various components are used including two contactors, three transformers in series to obtain 110V, a timer switch, two NO NC switches, a rectifier circuit, and the induction motor. When the motor is running, one contactor is energized to supply power, and when de-energized, the other contactor is energized to inject DC into the winding, causing braking. The DC supply is obtained by stepping down the voltage with transformers and rectifying it. The timer