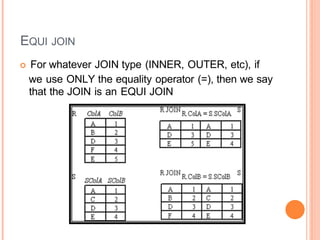
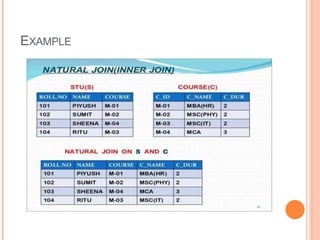
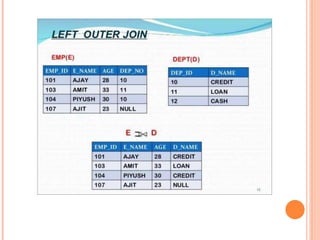
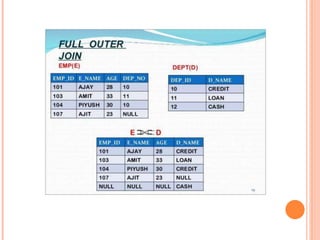
This document summarizes relational algebra and different types of joins. It introduces relational algebra and defines fundamental operations like selection, projection, union, set difference, and cartesian product. It then focuses on the join operation, explaining that a join combines tuples from two relations. The document defines equi joins, theta joins, natural joins, and outer joins. It provides examples of each join type and concludes with a thank you.