Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
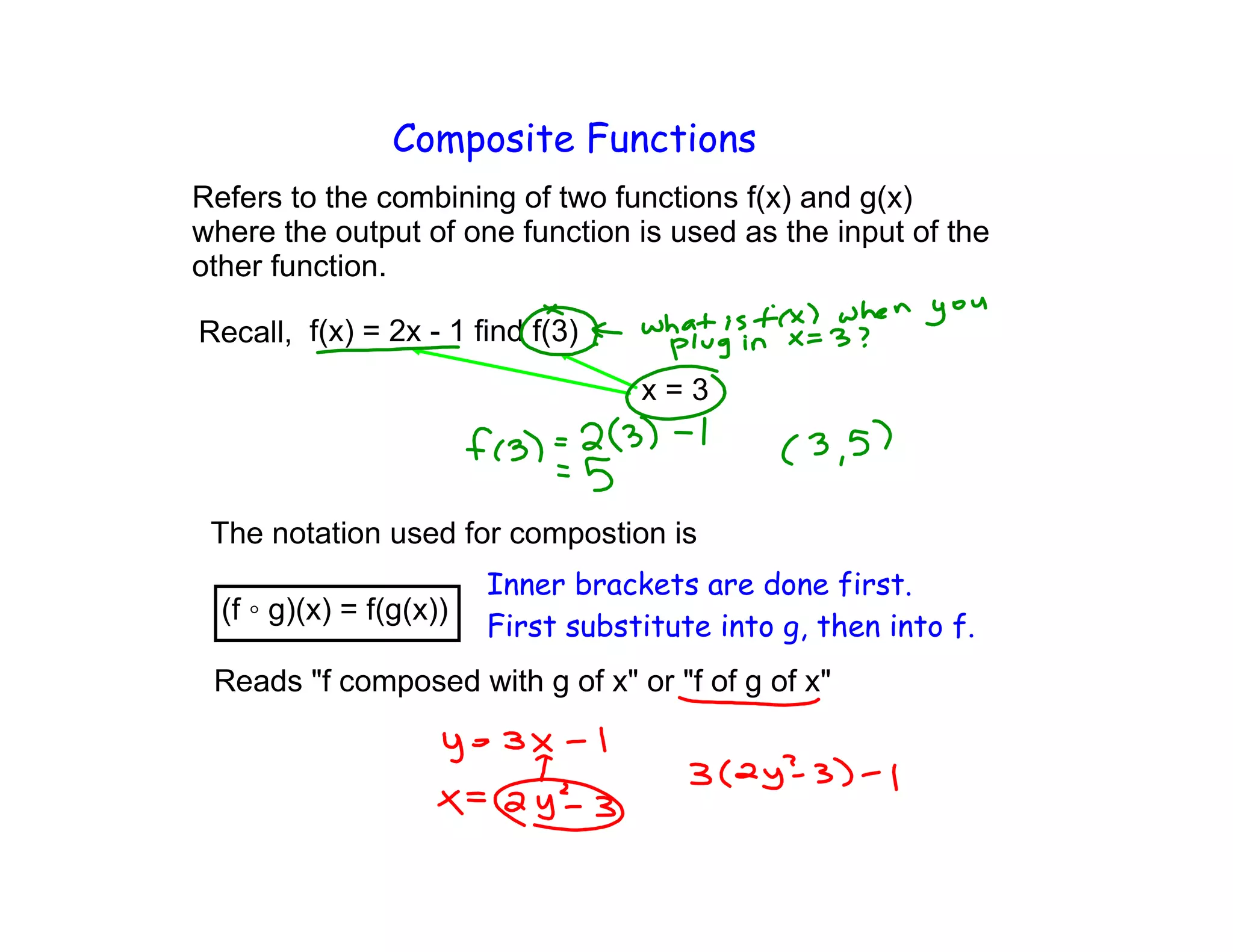
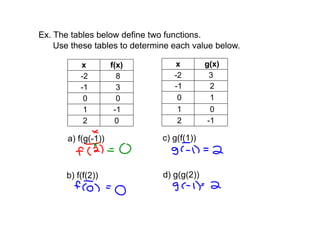
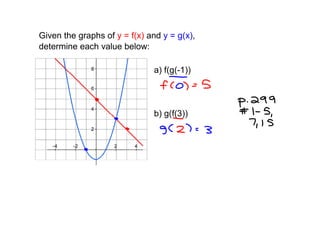
Composite functions refer to combining two functions, where the output of the inner function is used as the input of the outer function. This is denoted as f(g(x)), where g(x) is evaluated first, and then substituted into f(x). Examples using tables and graphs are provided to demonstrate evaluating composite functions.


