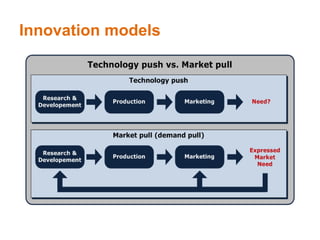
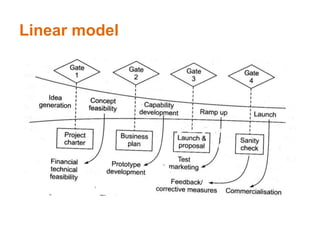
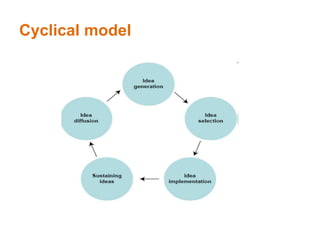
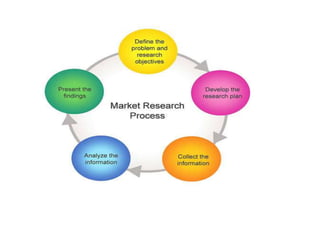
This document provides an overview of business principles including marketing, sales, financial management, and innovation. It discusses key topics such as defining business markets, organizational goals and factors that influence innovation, different business structures, marketing mix and techniques, importance of financial planning and budgets, and principles of market research. The objectives are to help understand customer interactions, external influences on business, legal obligations, and what drives new product development and marketing strategies. Various models of innovation and factors affecting organizational goals are presented.