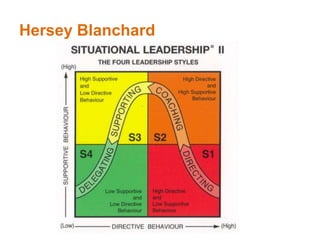
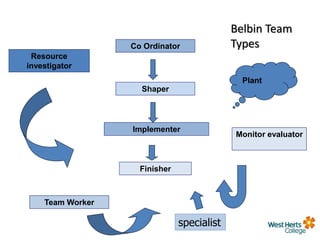
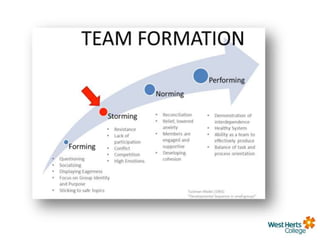
This document provides an overview of leadership and management concepts for a Level 5 Award in Leadership and Management Skills program. It discusses definitions of leadership and management, different leadership styles including trait, behavioral, contingency and transformational theories. It also covers team roles, stages of team development, and characteristics of effective teams. Activities are included to help participants assess their own leadership style and the prevailing styles in their organization, as well as team roles and problem solving. The next session will focus on motivation, emotional intelligence and employee engagement.