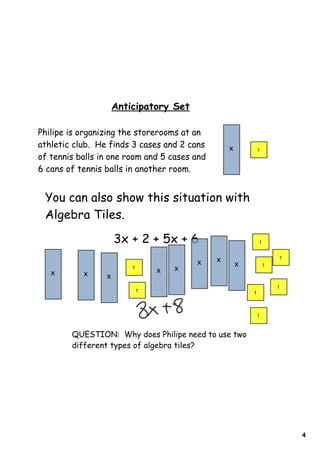
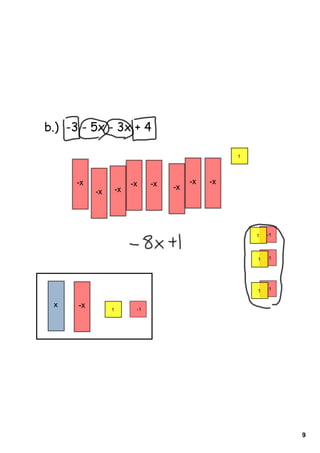
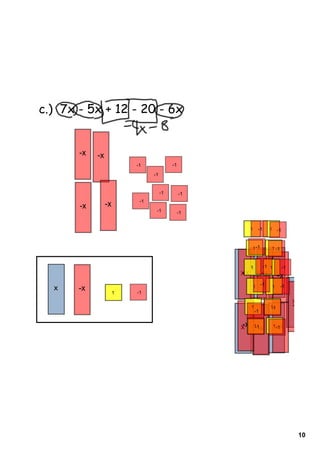
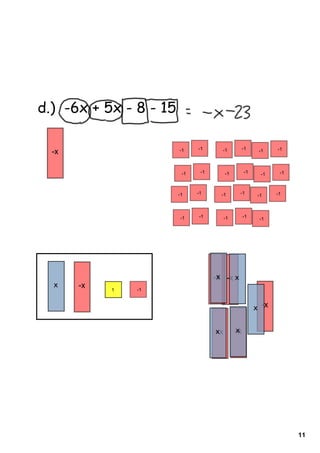
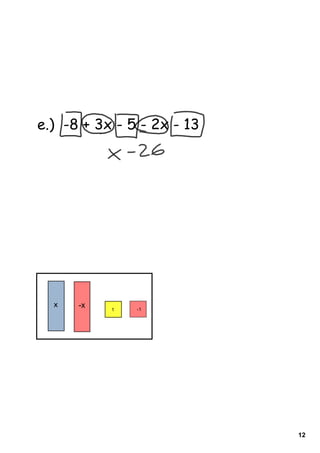
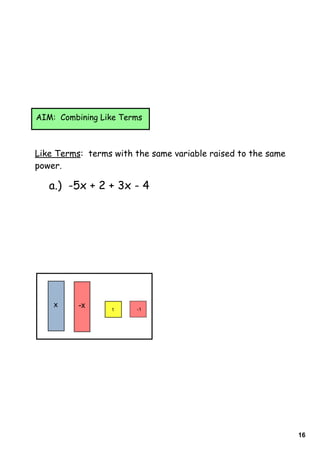
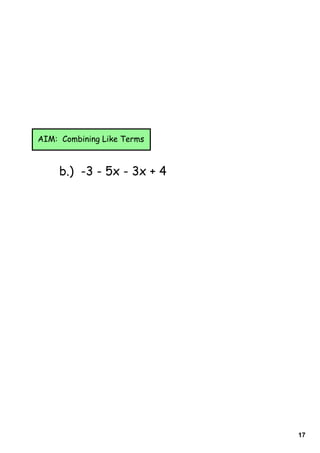
1) The document provides instructions and examples for combining like terms in algebraic expressions. It contains examples of combining terms with the same variable raised to the same power.
2) The document explains that like terms must have the same variable raised to the same power in order to be combined using addition or subtraction. Coefficients are the numbers multiplied by variables.
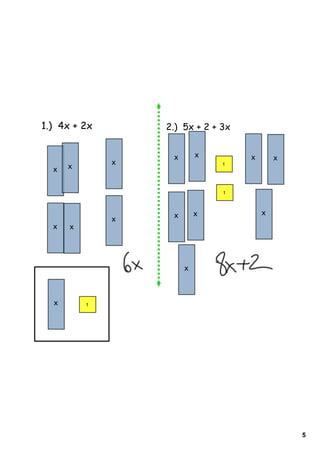
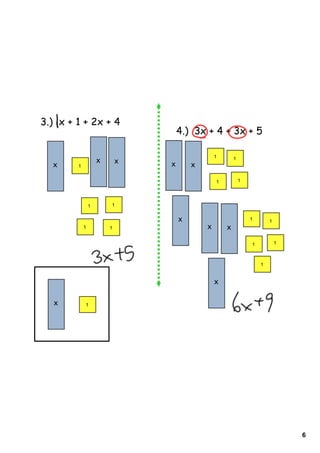
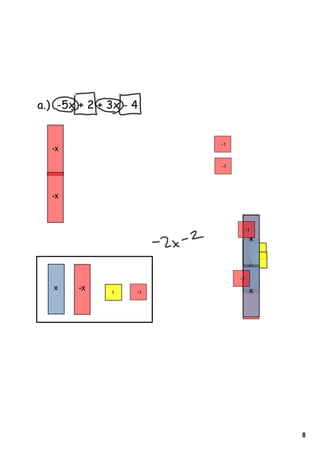
3) Several worked examples are provided of combining like terms in algebraic expressions by collecting terms with the same variables and exponents.