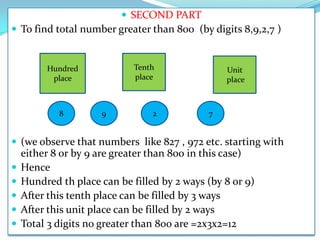
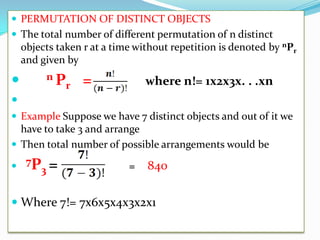
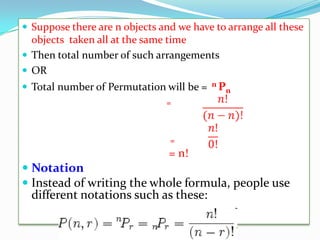
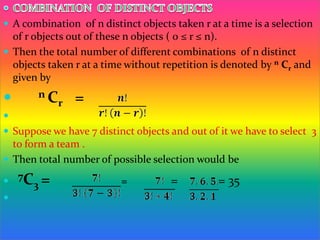
The document discusses multiplication and addition principles for counting the total number of ways an operation can be performed. It then provides an example of counting the number of 3-digit numbers that can be formed using the digits 8, 9, 2, 7 without repetition, and the numbers of those greater than 800. Permutations and combinations are also defined, with the difference being whether order matters. Various examples are given of using permutations and combinations to count arrangements and selections.