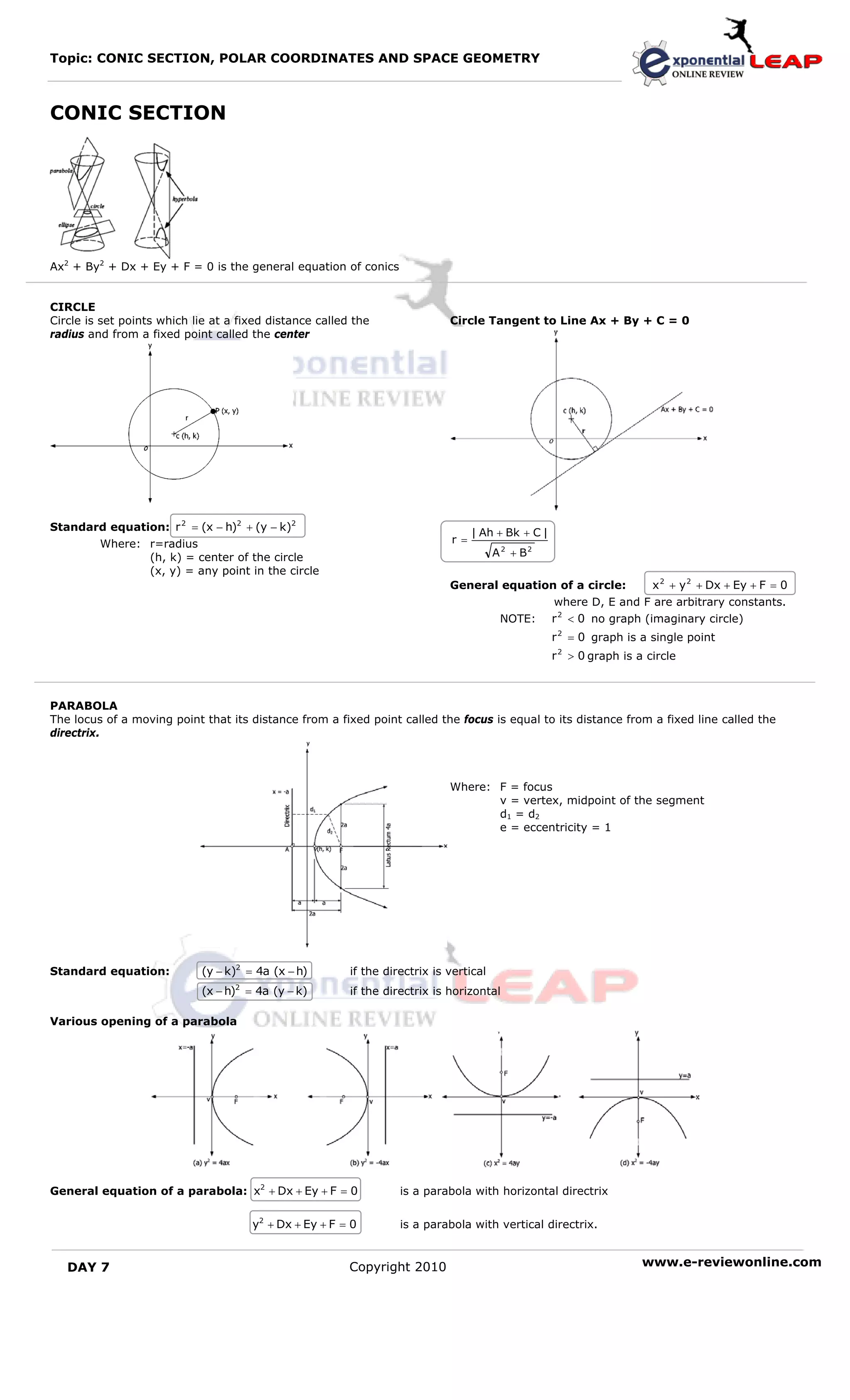
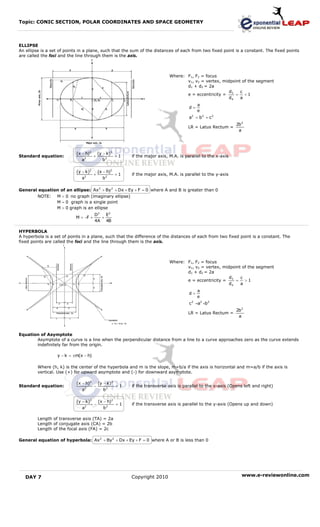
1. The document discusses conic sections such as circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas defined by standard and general equations.
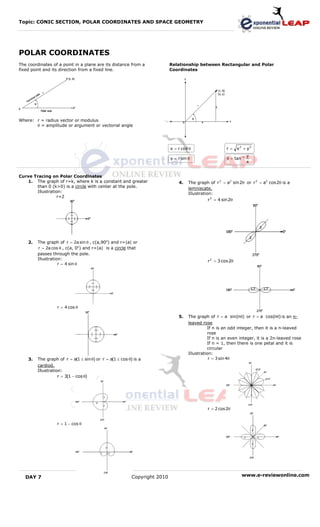
2. It also covers polar coordinates and how to trace curves using polar equations like r=k, r=a±b sinθ, and r=a(1±sinθ).
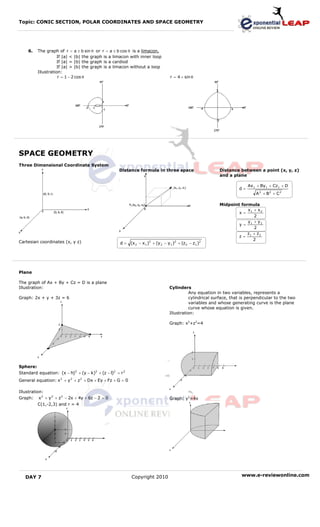
3. Additionally, the document introduces concepts of space geometry like the three dimensional coordinate system, planes, cylinders, spheres, and quadratic surfaces including ellipsoids, hyperboloids, paraboloids.