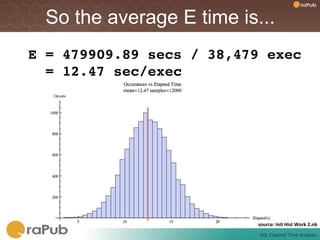
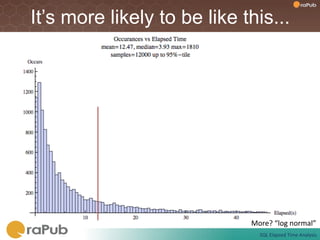
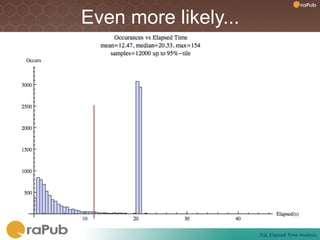
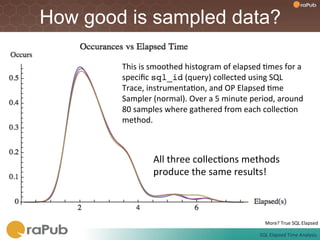
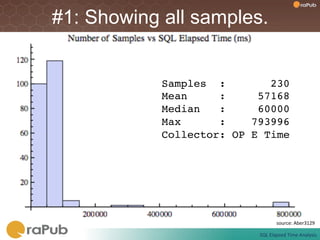
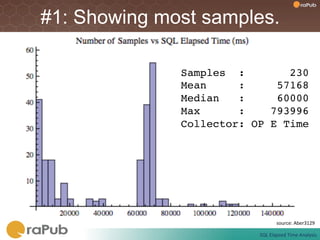
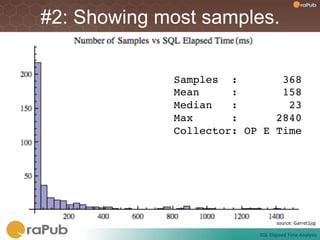
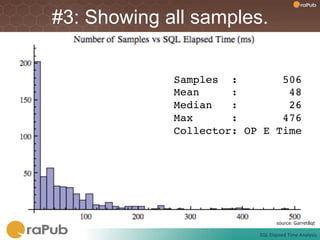
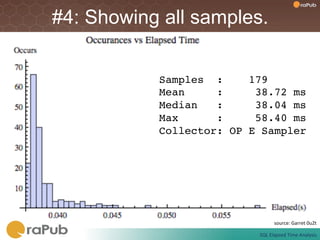
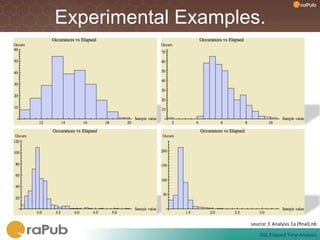
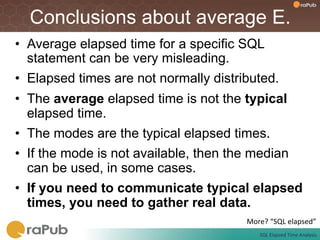
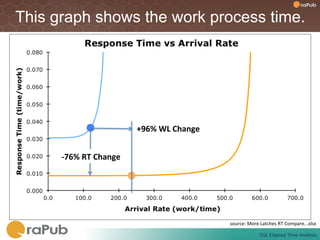
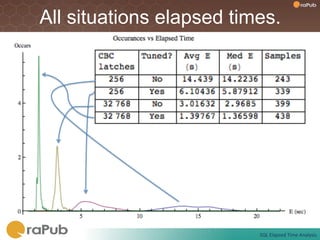
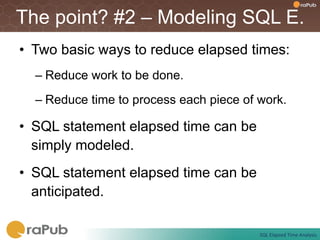
Craig Shallahamer presents on analyzing SQL elapsed times. He discusses that average elapsed time can be misleading as times are not normally distributed. The typical times are better represented by the mode or median. Gathering real data samples is important to understand elapsed times. Elapsed time can be modeled as work per execution multiplied by time per unit of work. Tuning reduces work and therefore elapsed times.