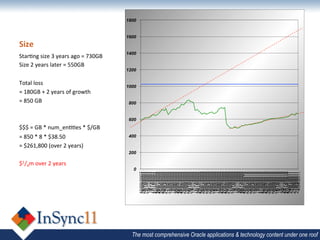
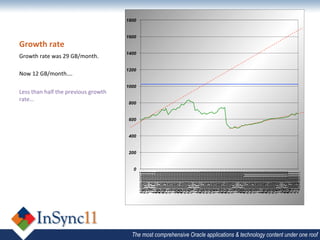
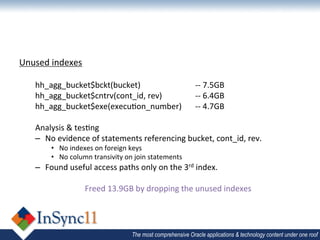
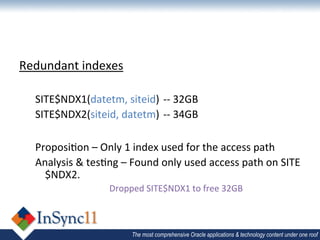
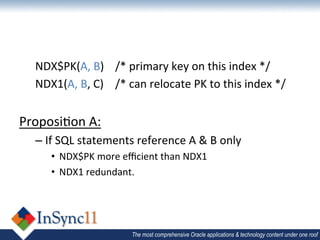
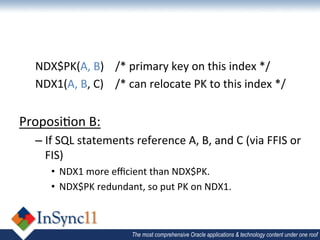
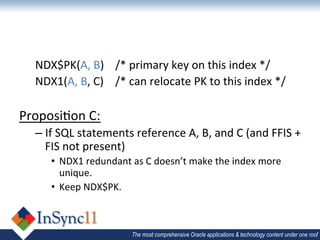
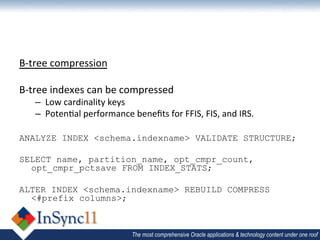
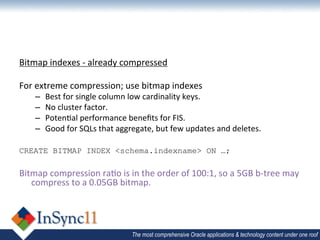
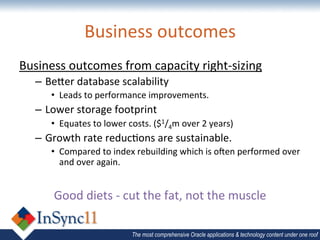
The document discusses database optimization techniques including right-sizing the database capacity, identifying unused tables and indexes to drop, archiving expired data to reduce table sizes, improving insert performance with direct-path inserts, rebuilding tables to increase block density, enabling table compression, and identifying unnecessary indexes. Specific examples are provided where these techniques reduced database sizes from 850GB to 550GB, dropped an unused 84GB table, reduced a table from 62GB to 5GB by deleting expired data, and rebuilt a table from 42GB to 2GB to improve block density.