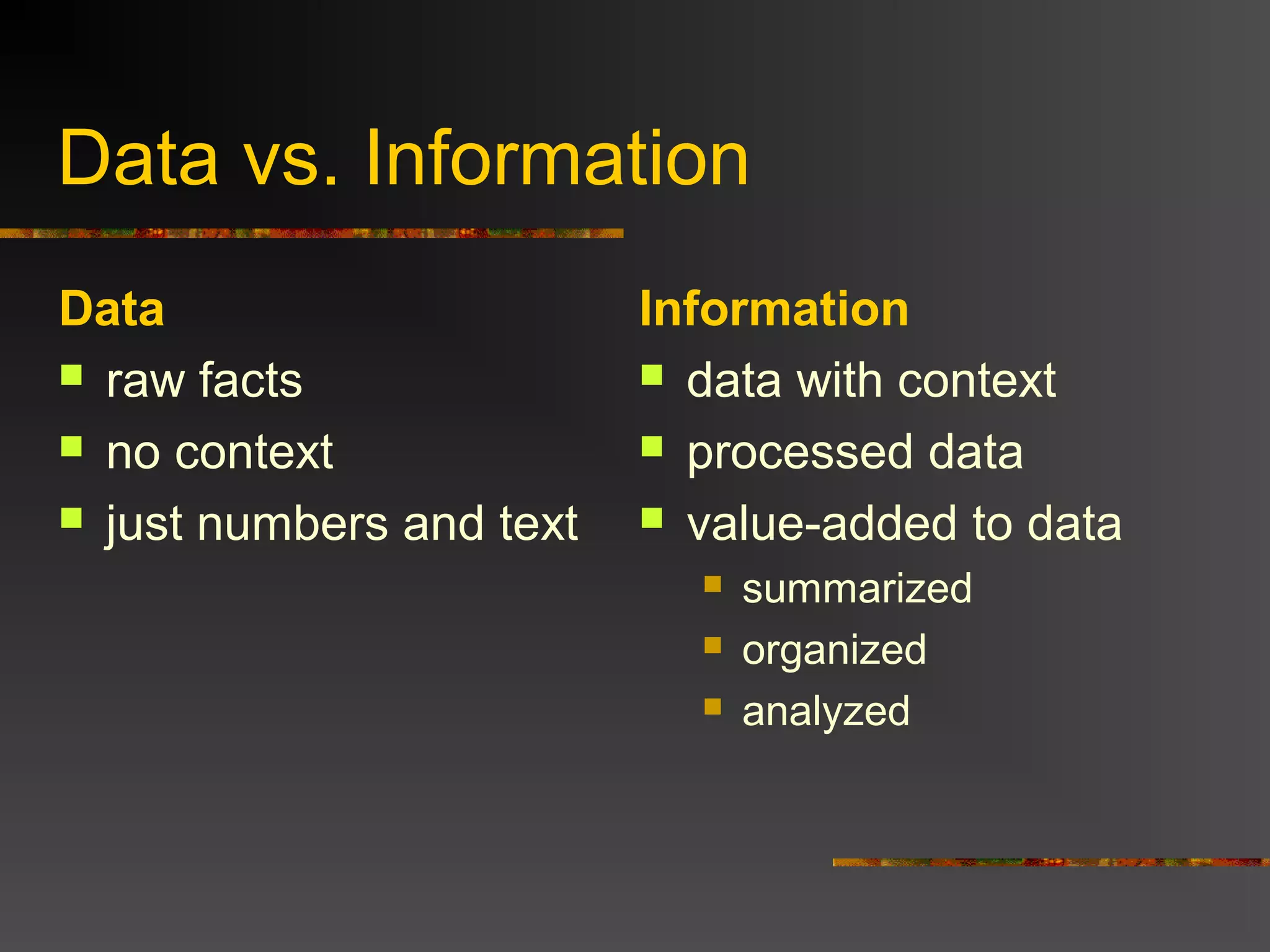
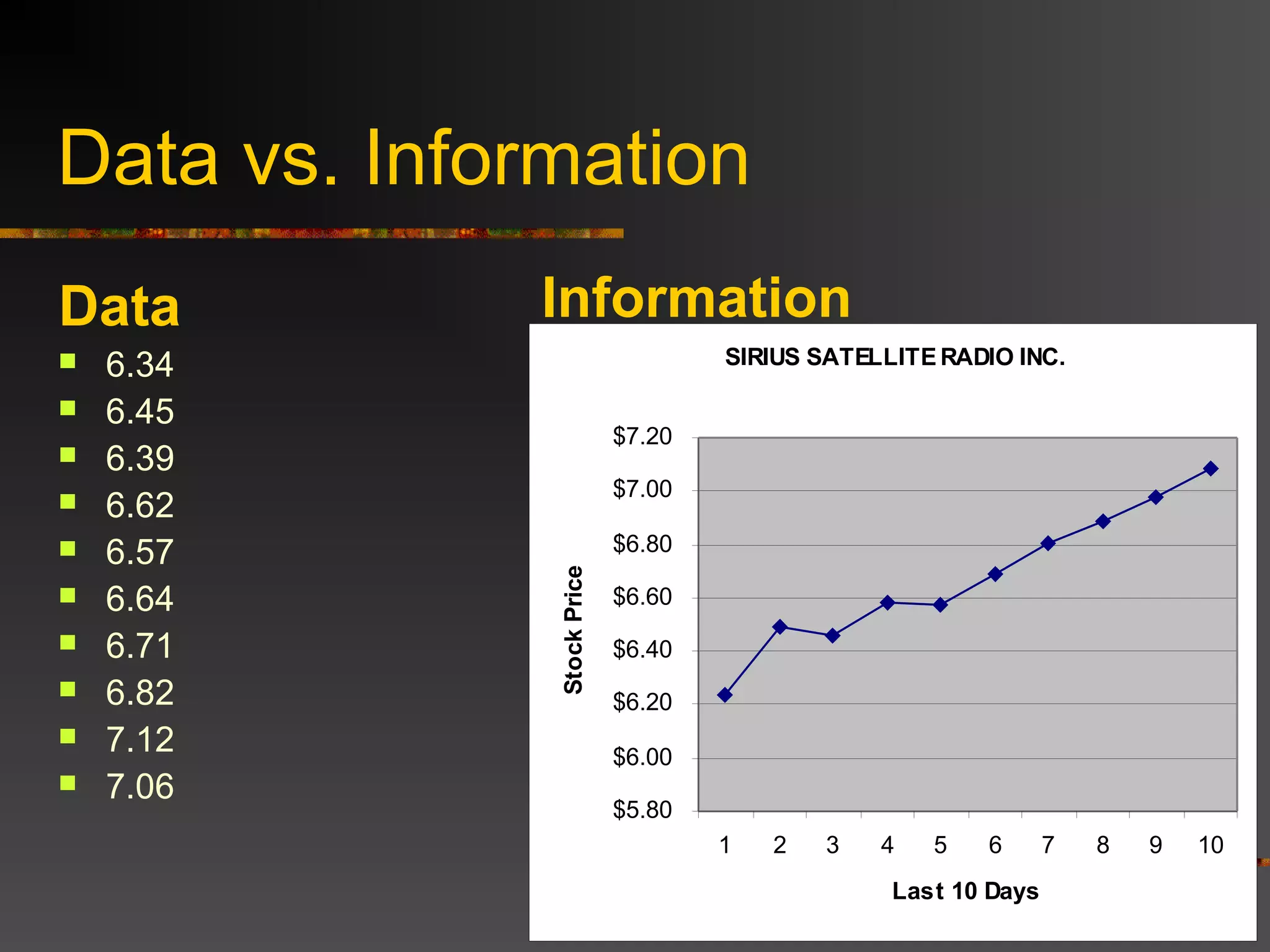
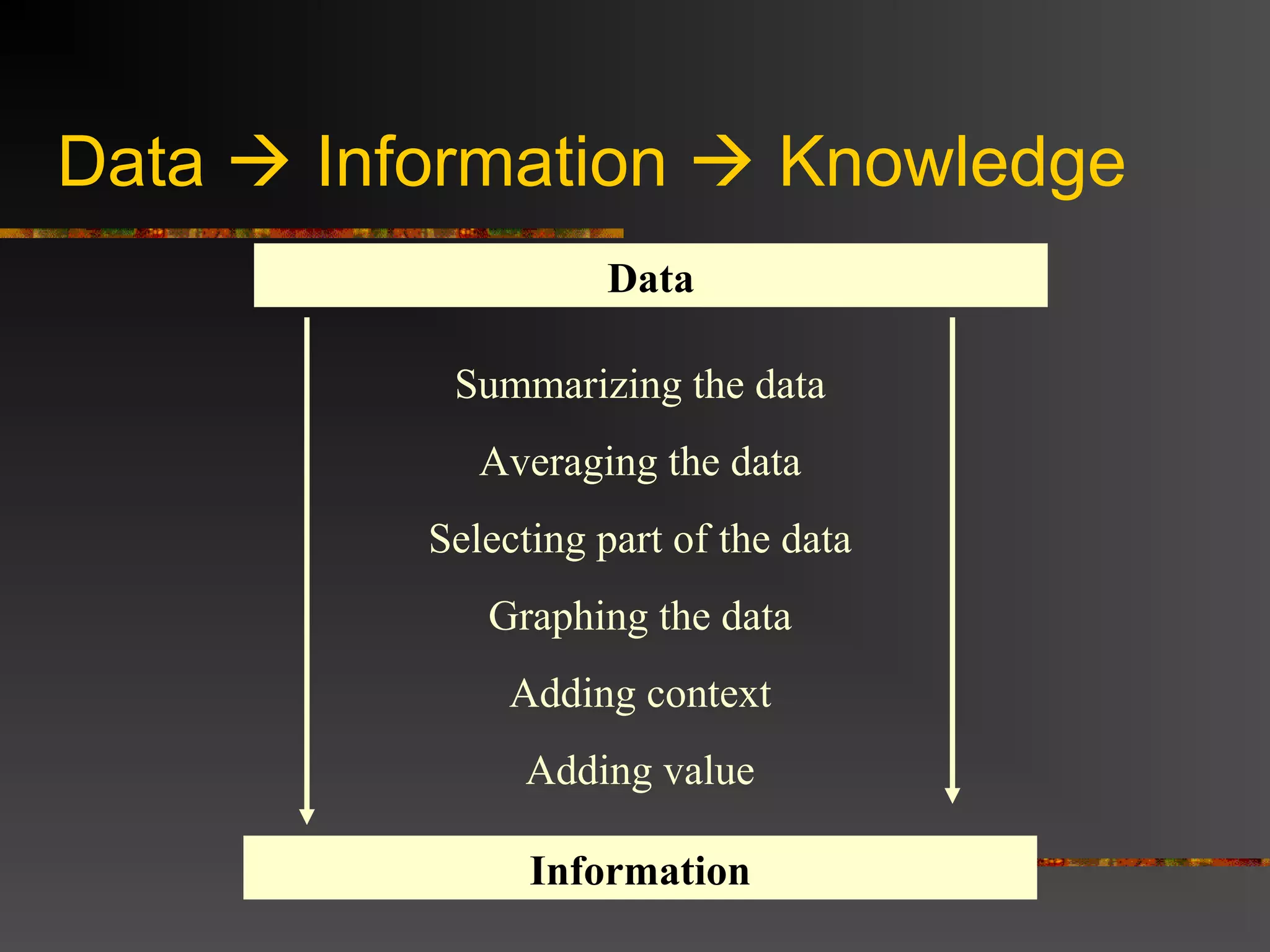
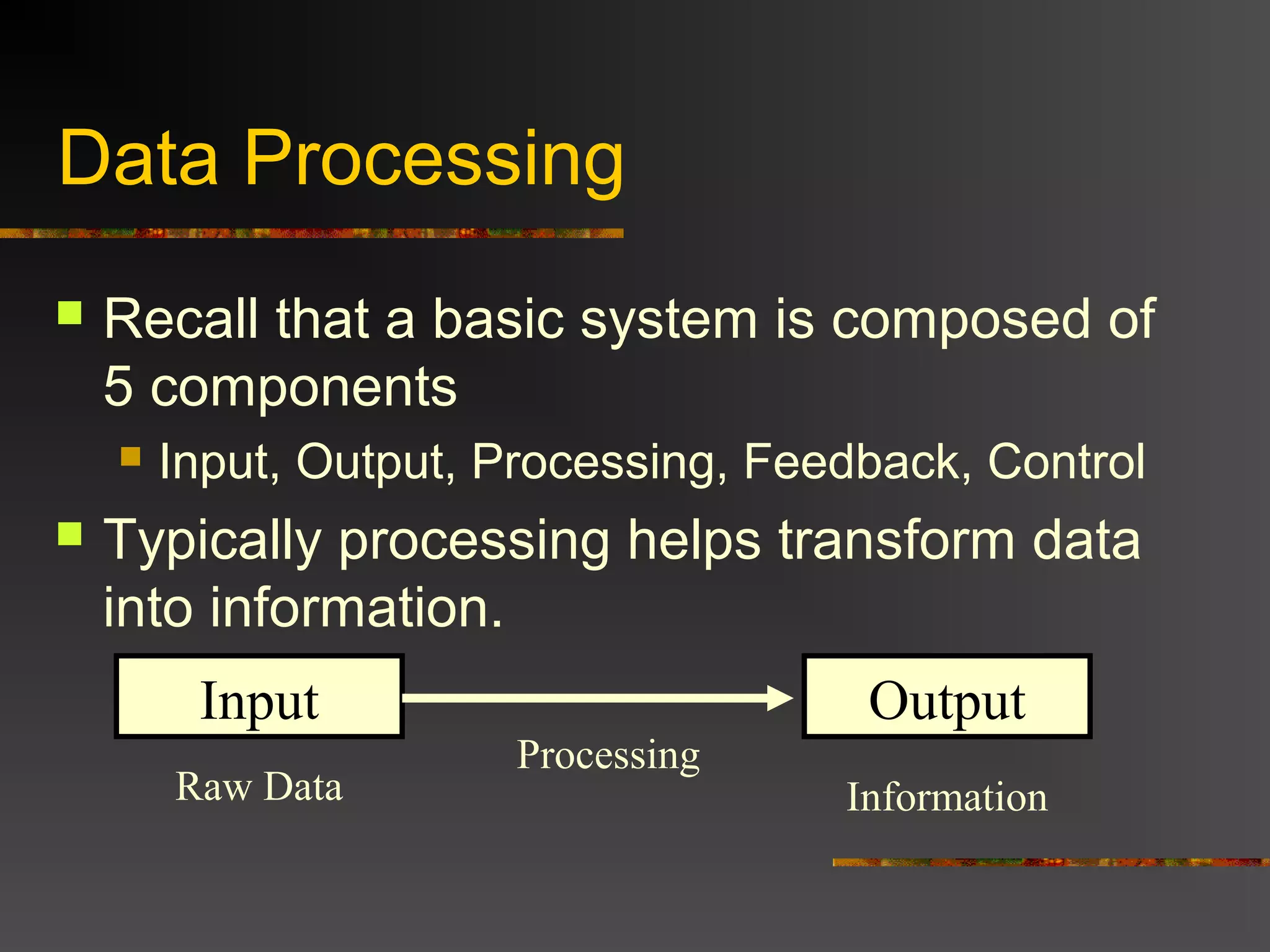
The document discusses the difference between data and information. Data refers to raw facts without context, while information is processed data that has been organized, analyzed, and given context and meaning. The document provides examples to illustrate the difference, such as a number representing different things depending on the context or information added to raw stock prices and dates to give them meaning and value. Overall, the key difference is that information is data that has been processed and transformed to have value and context.