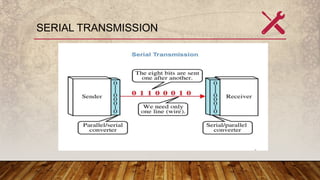
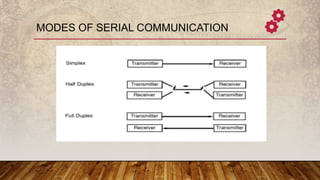
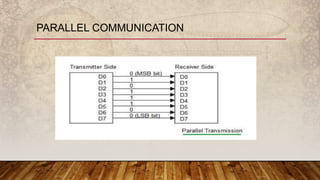
The document discusses serial and parallel communication, outlining their advantages and disadvantages, along with synchronous and asynchronous data transmission methods. Serial communication transmits data one bit at a time using a shift register and requires less wiring, while parallel communication transmits multiple bits simultaneously but is more complex and costly. Synchronous transmission operates with a common clock for improved speed, whereas asynchronous transmission does not require synchronization but involves additional start and stop bits.