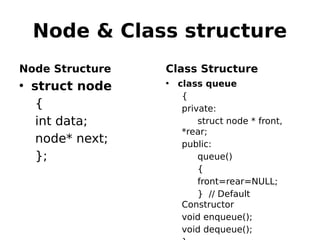
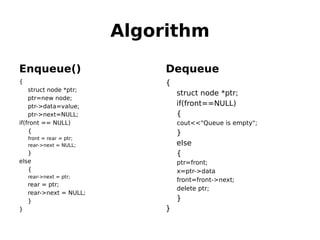
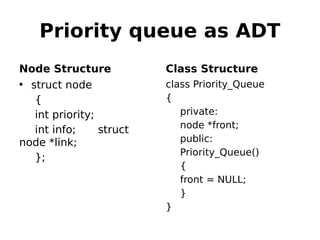
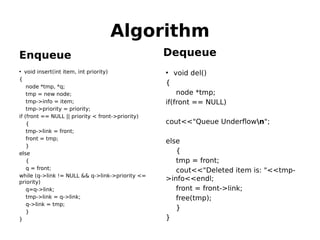
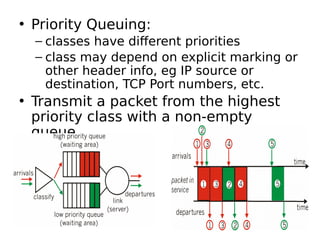
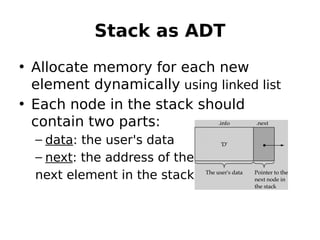
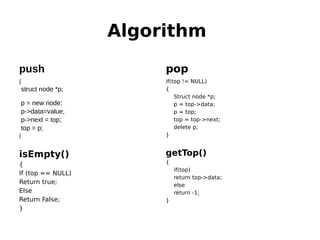
This document outlines two assignments for a course on data structures and files. The first assignment involves implementing a stack using a linked list and using it for infix, postfix, and prefix notation conversions and evaluations. The second assignment involves implementing a priority queue using a linked list to service patients in a hospital based on priority of illness. Key algorithms for stack, queue, and priority queue operations are described.










![Algorithm: Infix to Postfix
Conversion
• Algorithm(infixtopostfix)
• Create stack
• Set postfix to null string
• i=0
• for all tokens ‘ch’ in the infix expression
• token=ch[i]
• if(token=‘(’)
– Push(stack, token)
• elseif(token=‘)’)
– Pop(stack, token)
– while(token!=‘(’)
- append token to postfix expression
- pop(stack, token)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsflkdp-180222053638/85/Data-Structures-and-Files-13-320.jpg)