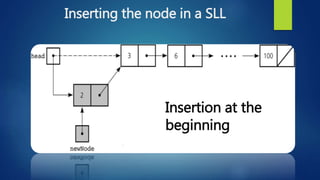
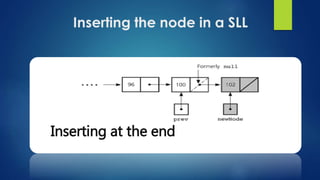
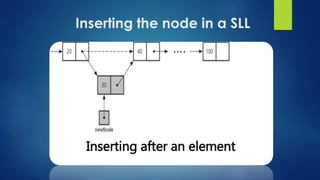
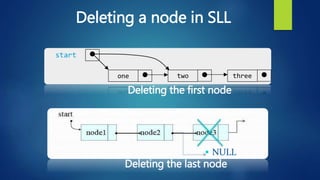
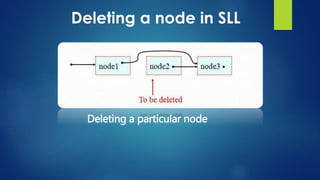
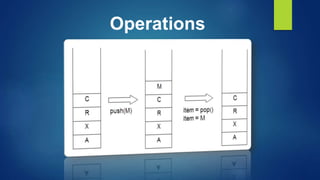
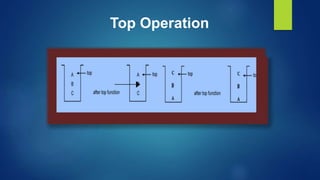
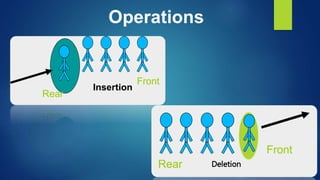
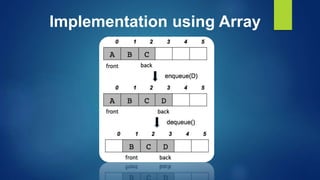
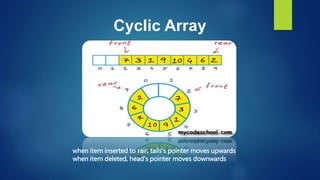
This document provides an overview of different data structures including linked lists, stacks, queues, and priority queues. It describes linked lists as a linear data structure composed of nodes with data and address fields. It discusses different types of linked lists such as singly linked lists, circular singly linked lists, and doubly linked lists. It also describes how to perform operations like insertion and deletion on singly linked lists. The document further explains stacks, queues, and priority queues, describing their representations and basic operations.