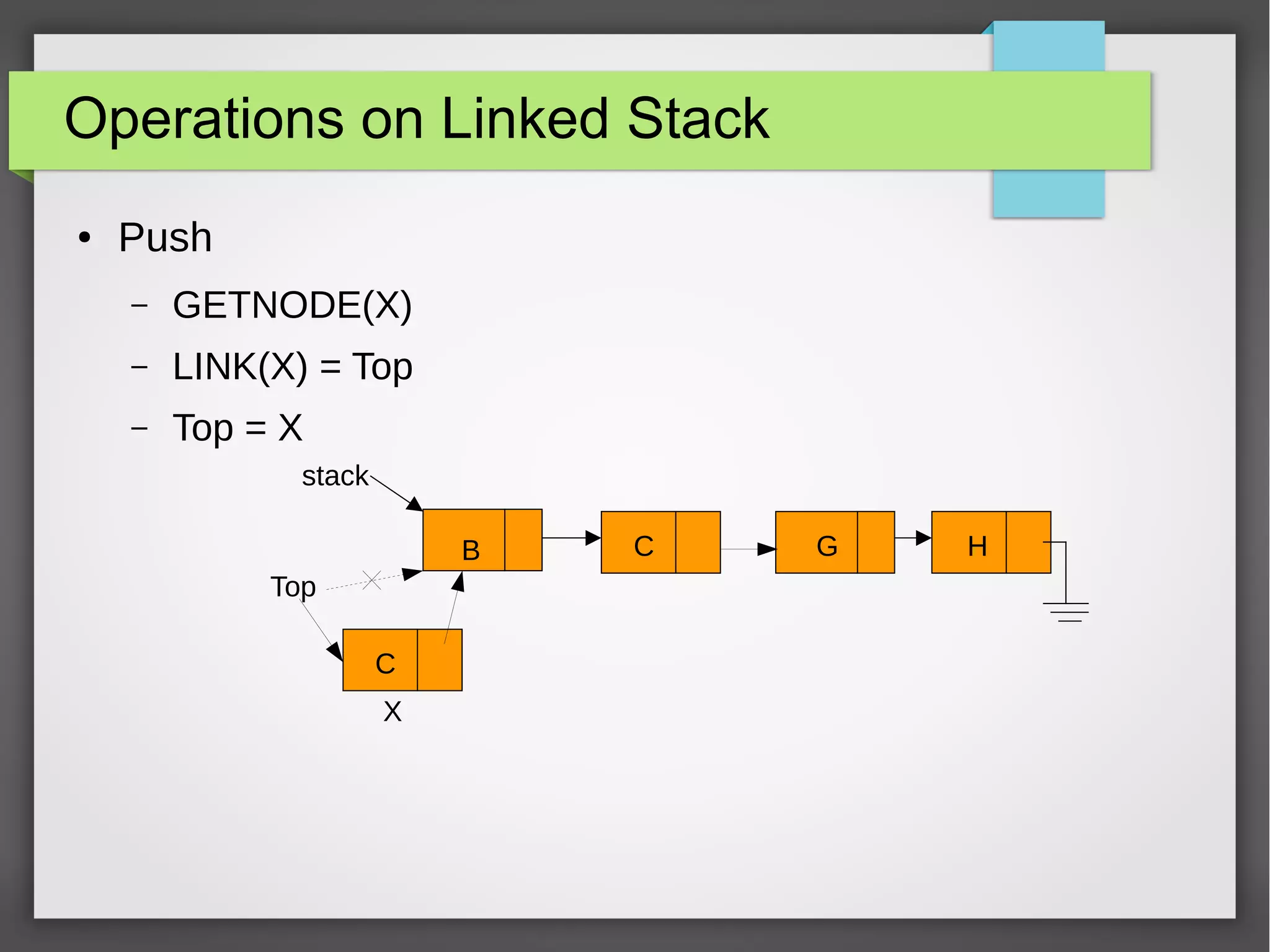
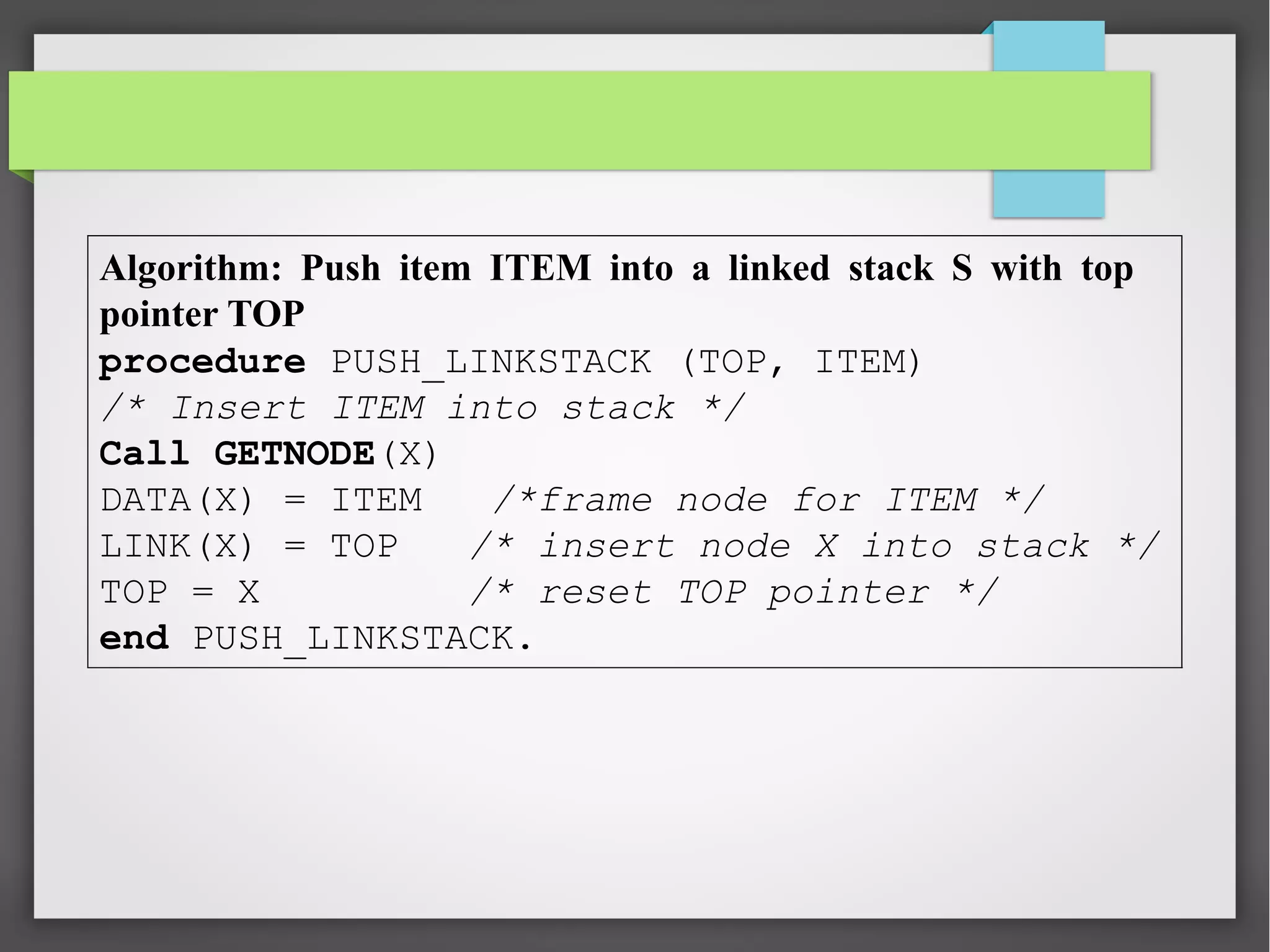
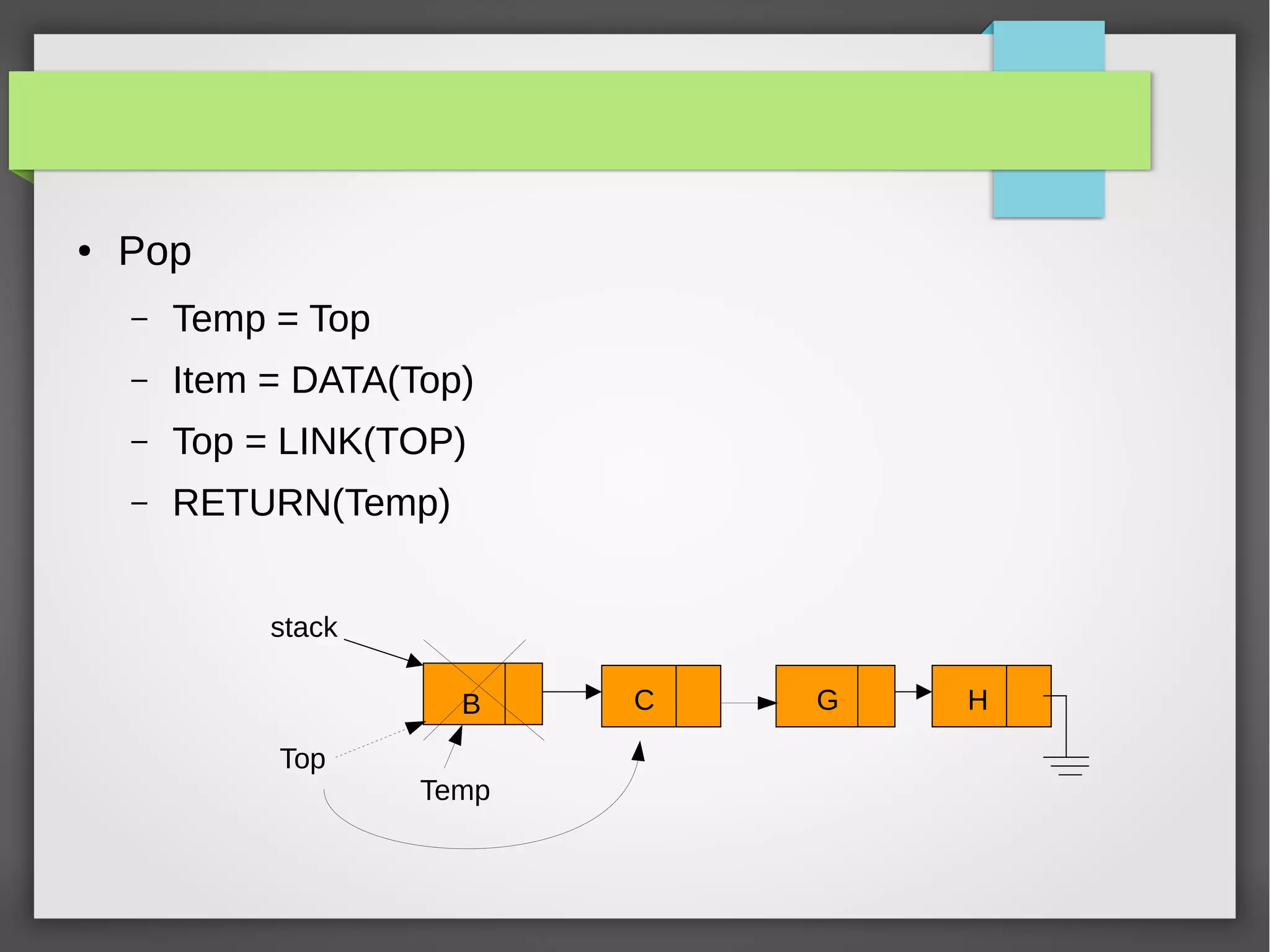
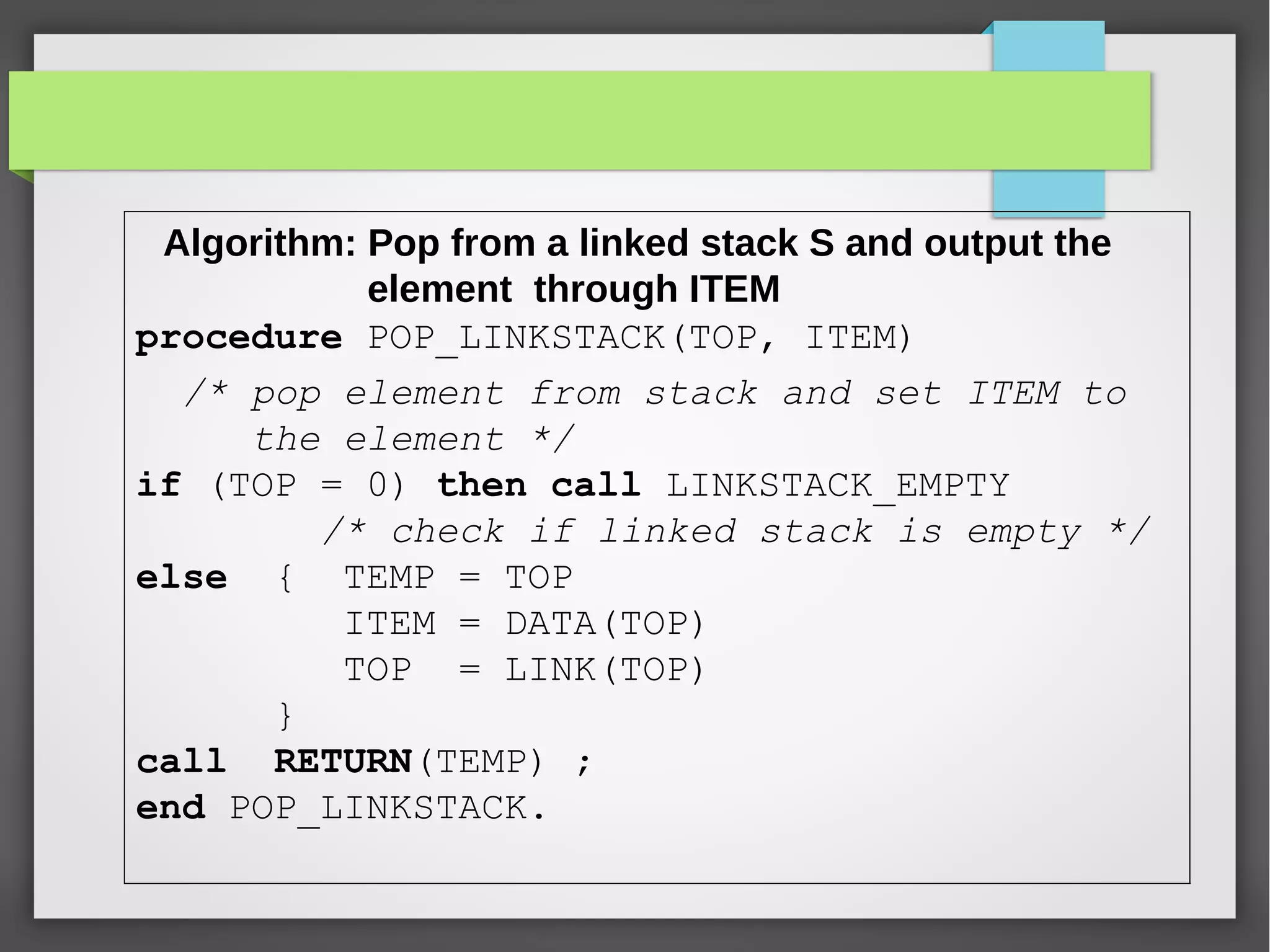
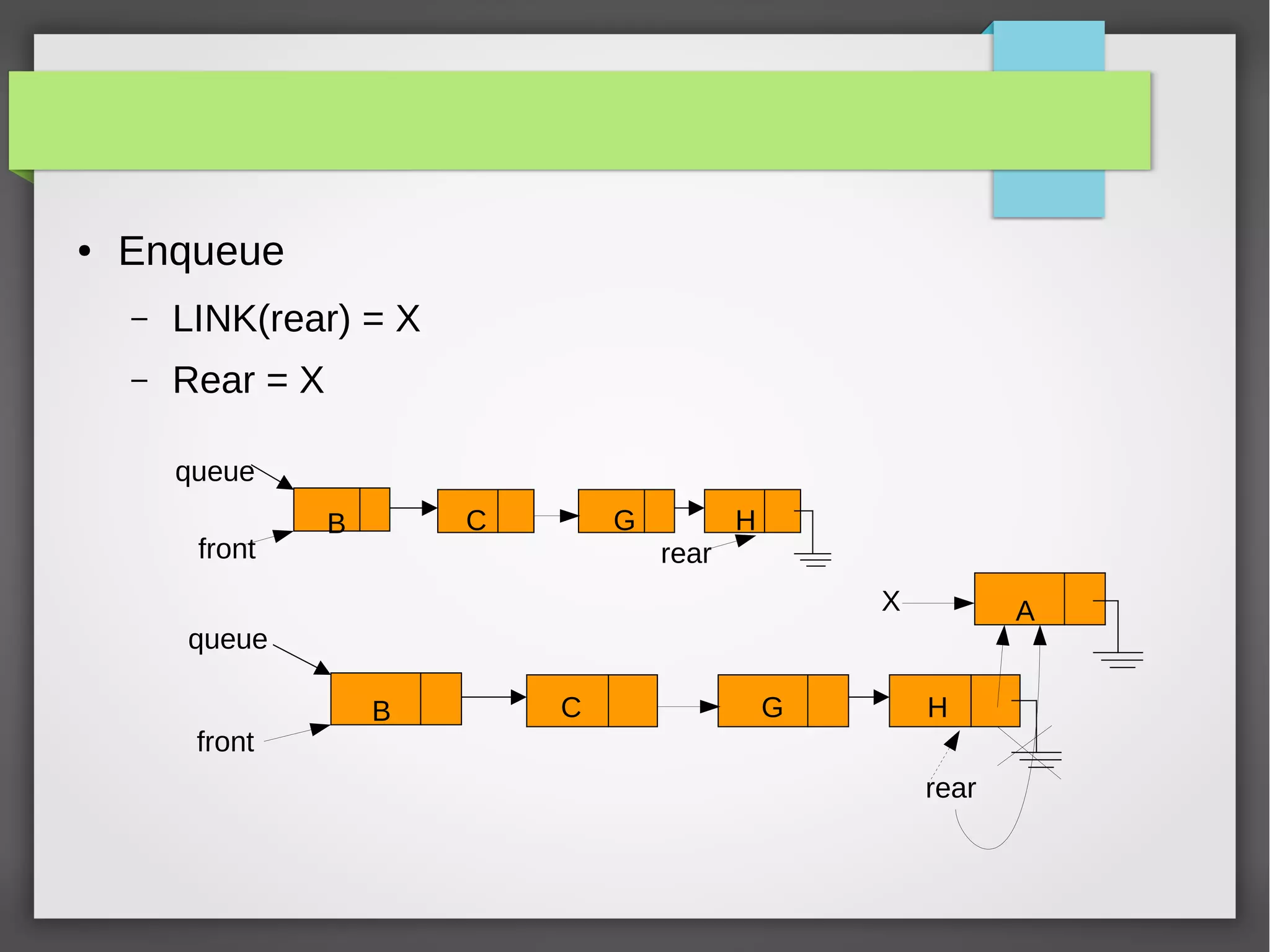
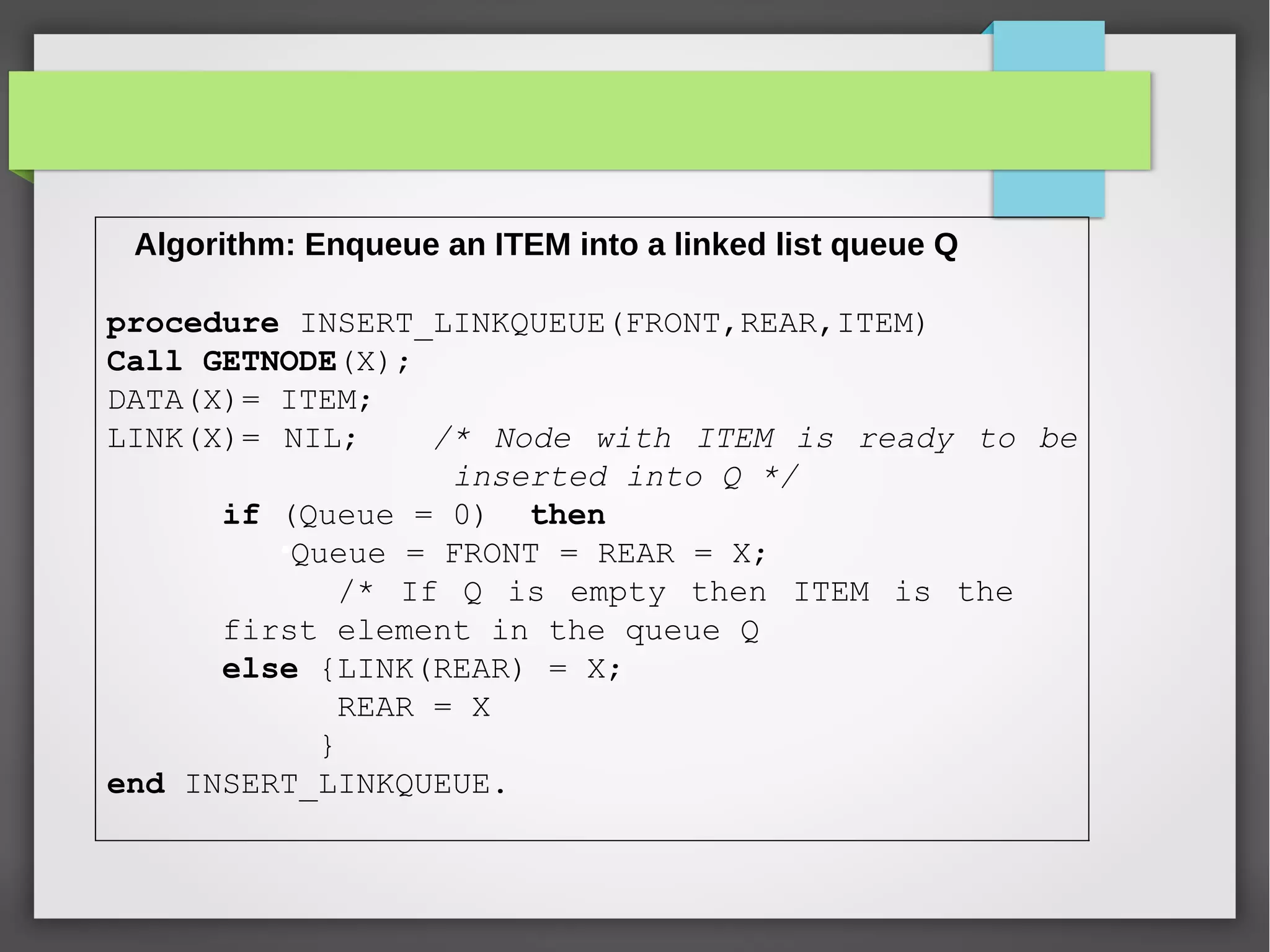
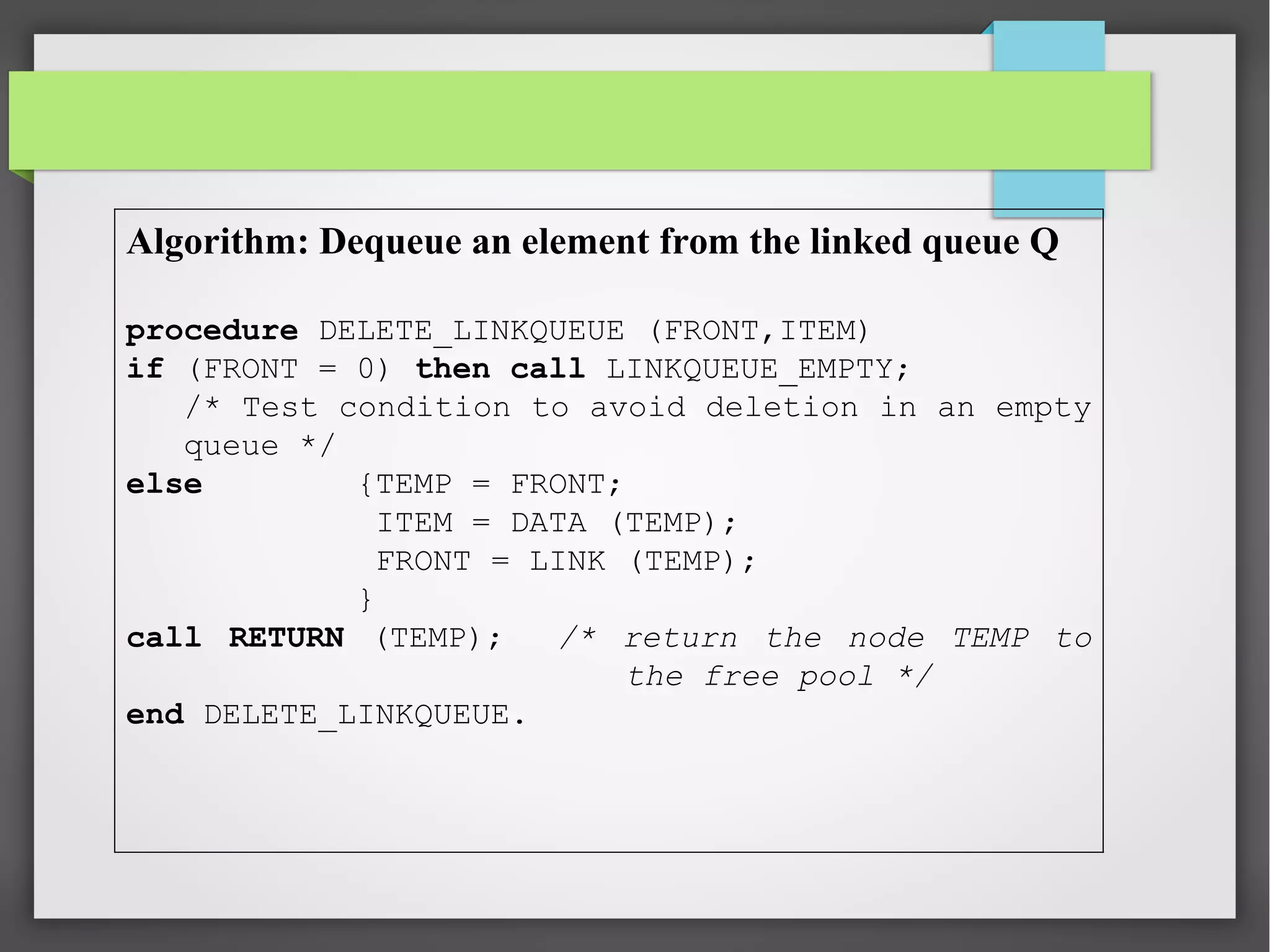
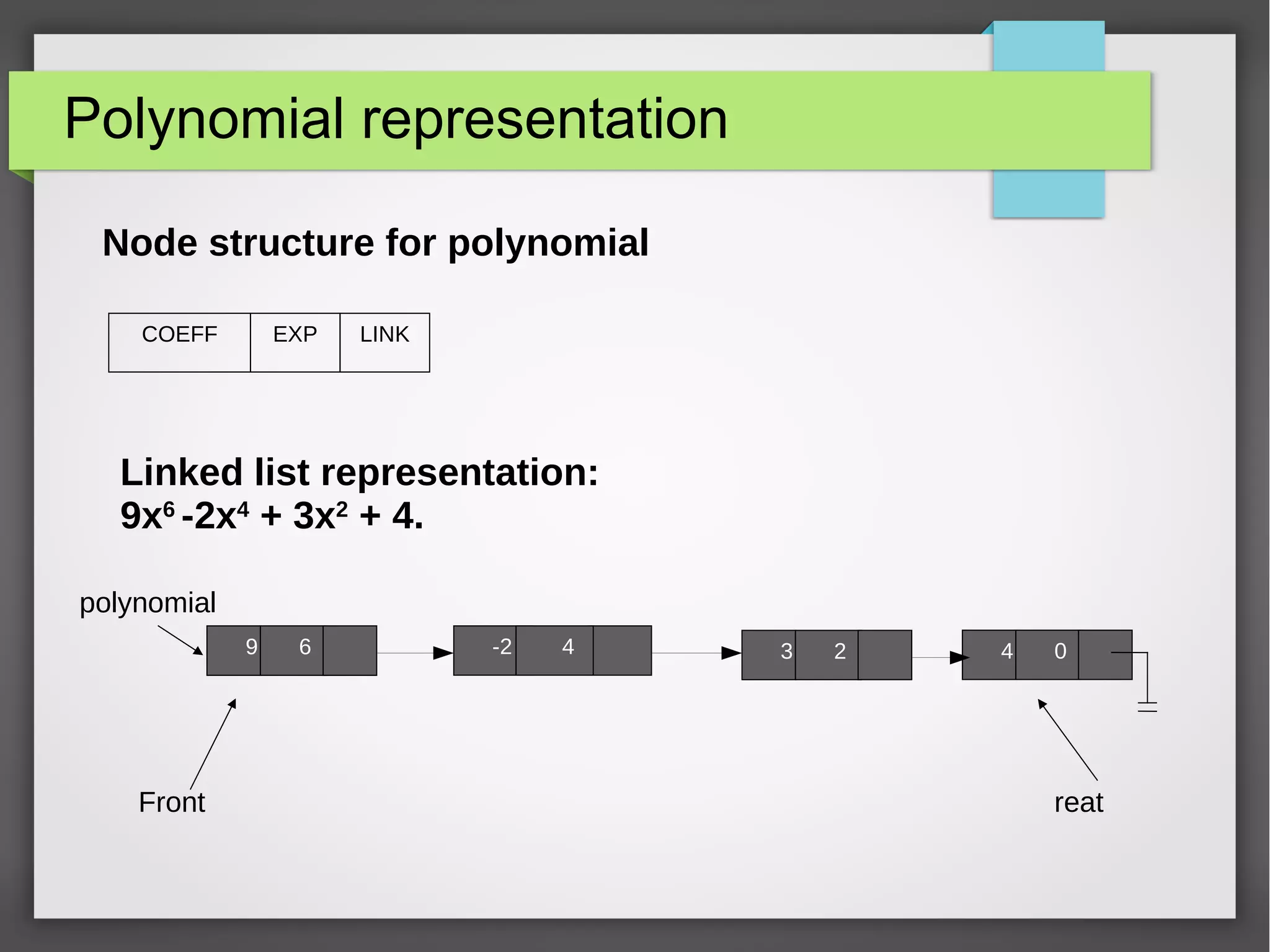
The document discusses linked stacks and linked queues. It provides an introduction to linked stacks and linked queues and how they are commonly implemented using singly linked lists. It then describes the key operations for each - push, pop, enqueue, and dequeue. Algorithms for each operation are presented using pseudocode. Examples of applications that can make use of linked stacks and queues are given, such as balancing symbols in an expression and representing polynomials.



![Implementing Stack and Queue Using Linked List
6
1
2
3
4
5
A
B
E
D
G
F
Top = 6
1 2 3 4 5 6
B C
Front=1 Rear = 3
Stack[1:6] Queue[1:6]
B C G H
stack
Top
B C G H
queue
front rear](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linked-stack-and-linked-queue-210505044721/75/Linked-stack-and-linked-queue-4-2048.jpg)