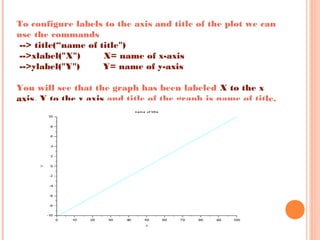
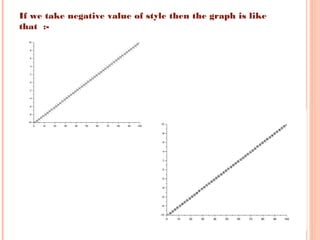
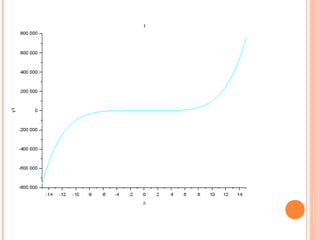
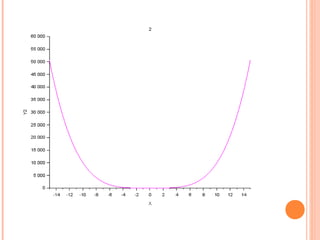
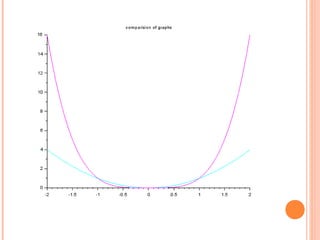
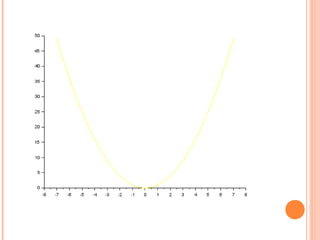
Scilab is a free and open source software for numerical computation providing a powerful computing environment for engineering and scientific applications. It includes hundreds of mathematical functions and a high-level programming language for advanced data structures and 2D and 3D graphical functions. Scilab was created in 1990 by researchers from INRIA and ENPC to provide an alternative to proprietary software like MATLAB. While MATLAB has more optimization and integration with other programs, Scilab is sufficient for educational and casual purposes and is available free of cost. This document discusses how to use Scilab for plotting graphs, setting labels and titles, comparing different graphs, and shifting graphs.