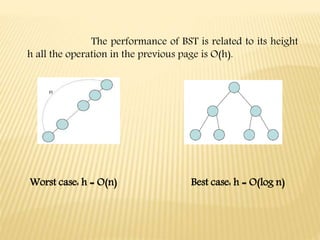
This document discusses Red-Black Trees, which are balanced binary search trees where each node is colored red or black. There are properties that ensure the tree remains balanced during insertions and deletions. Insertion may require rotations to fix violations of properties from adding a new node. Deletion of a node may also require rotations to maintain balance. Red-Black Trees support common binary search tree operations like search, insert, and delete in O(log n) time due to the balancing properties.