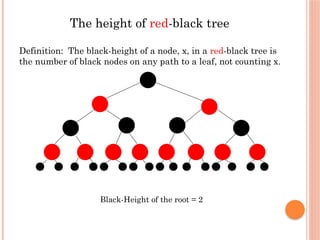
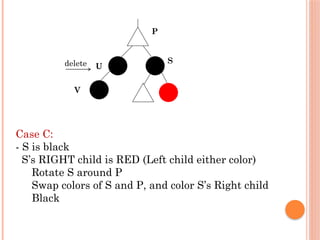
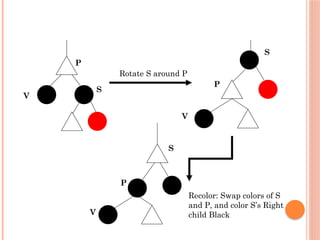
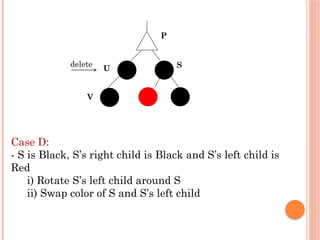
The document provides an analysis of red-black trees, which are a type of binary search tree characterized by specific properties about node coloring (red and black) and the arrangement of nodes. It discusses the process of deleting nodes in a red-black tree and highlights various cases that arise during deletion, emphasizing the complexity involved compared to insertion. The overall performance metrics indicate that both the height and operations for deletion remain logarithmic in relation to the number of nodes in the tree.