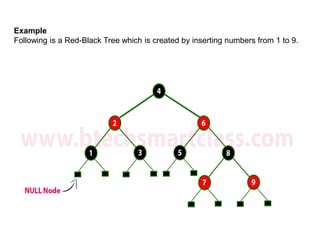
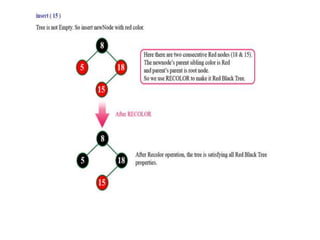
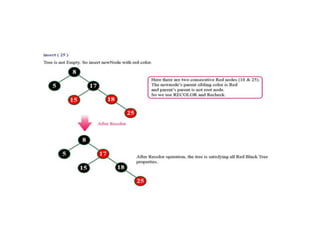
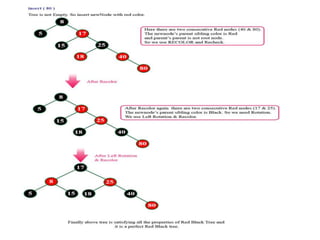
The document discusses red-black trees, which are a type of self-balancing binary search tree. Red-black trees ensure that no simple path from root to leaf is more than twice as long as any other path, keeping the tree balanced. Each node contains a color attribute (red or black) in addition to the standard key, left, right, and parent pointers. The document then describes the properties and algorithms for inserting and deleting nodes from red-black trees while maintaining the balancing properties.




![Left rotation:
y=right[x]; right[x] left[y];
If(left[y]!=nil) p[left[y]]=x;
p[y]=p[x];
if(p[x]==nil) {root=y;}
else
if (left[p[x]]==x) left[p[x]]=y;
else right[p[x]]=y;
left[y]=x; p[x]=y;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2red-blacktrees-240226014847-d51d32e9/85/Unit-2-ADvanced-Data-Sturctures-and-Algorithms-Red-black_trees-ppt-7-320.jpg)
![Left rotation:
y=right[x]; right[x] left[y];
If(left[y]!=nil) p[left[y]]=x;
p[y]=p[x];
if(p[x]==nil) {root=y;}
else
if (left[p[x]]==x) left[p[x]]=y;
else right[p[x]]=y;
left[y]=x; p[x]=y;
Right rotation:
x=left[y]; left[y]=right[x];
If(right[x]!=nil) p[right[x]]=y;
p[x]=p[y];
if(p[y]==nil) root=x;
If(left[p[y]]=y) left[p[y]]=x;
else right[p[y]]=x;
right[x]=y; p[y]=x;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2red-blacktrees-240226014847-d51d32e9/85/Unit-2-ADvanced-Data-Sturctures-and-Algorithms-Red-black_trees-ppt-9-320.jpg)
![Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Left rotation:
y=right[x]; right[x] left[y]; If(left[y]!=nil) p[left[y]]=x; p[y]=p[x];
if(p[x]==nil) {root=y;} else if (left[p[x]]==x) left[p[x]]=y; else right[p[x]]=y;
left[y]=x; p[x]=y;
Right rotation:
x=left[y]; left[y]=right[x];
If(right[x]!=nil) p[right[x]]=y;
p[x]=p[y]; if(p[y]==nil) root=x;
If(left[p[y]]=y) left[p[y]]=x;
else right[p[y]]=x;
right[x]=y; p[y]=x;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2red-blacktrees-240226014847-d51d32e9/85/Unit-2-ADvanced-Data-Sturctures-and-Algorithms-Red-black_trees-ppt-11-320.jpg)


![Case 1,2,3: p[z] is the left child of p[p[z]].
Correspondingly, there are 3 other cases,
In which p[z] is the right child of p[p[z]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2red-blacktrees-240226014847-d51d32e9/85/Unit-2-ADvanced-Data-Sturctures-and-Algorithms-Red-black_trees-ppt-14-320.jpg)







