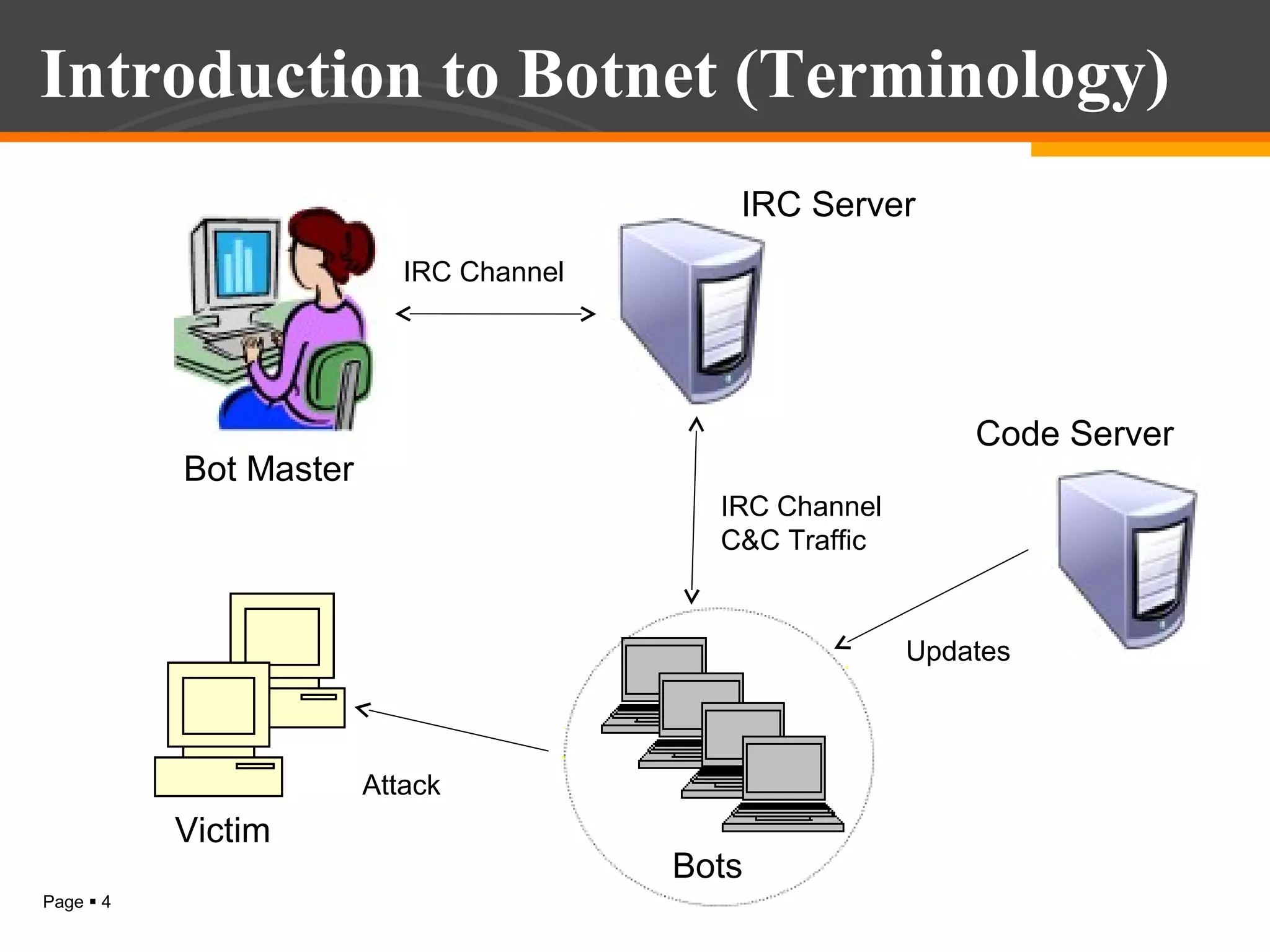
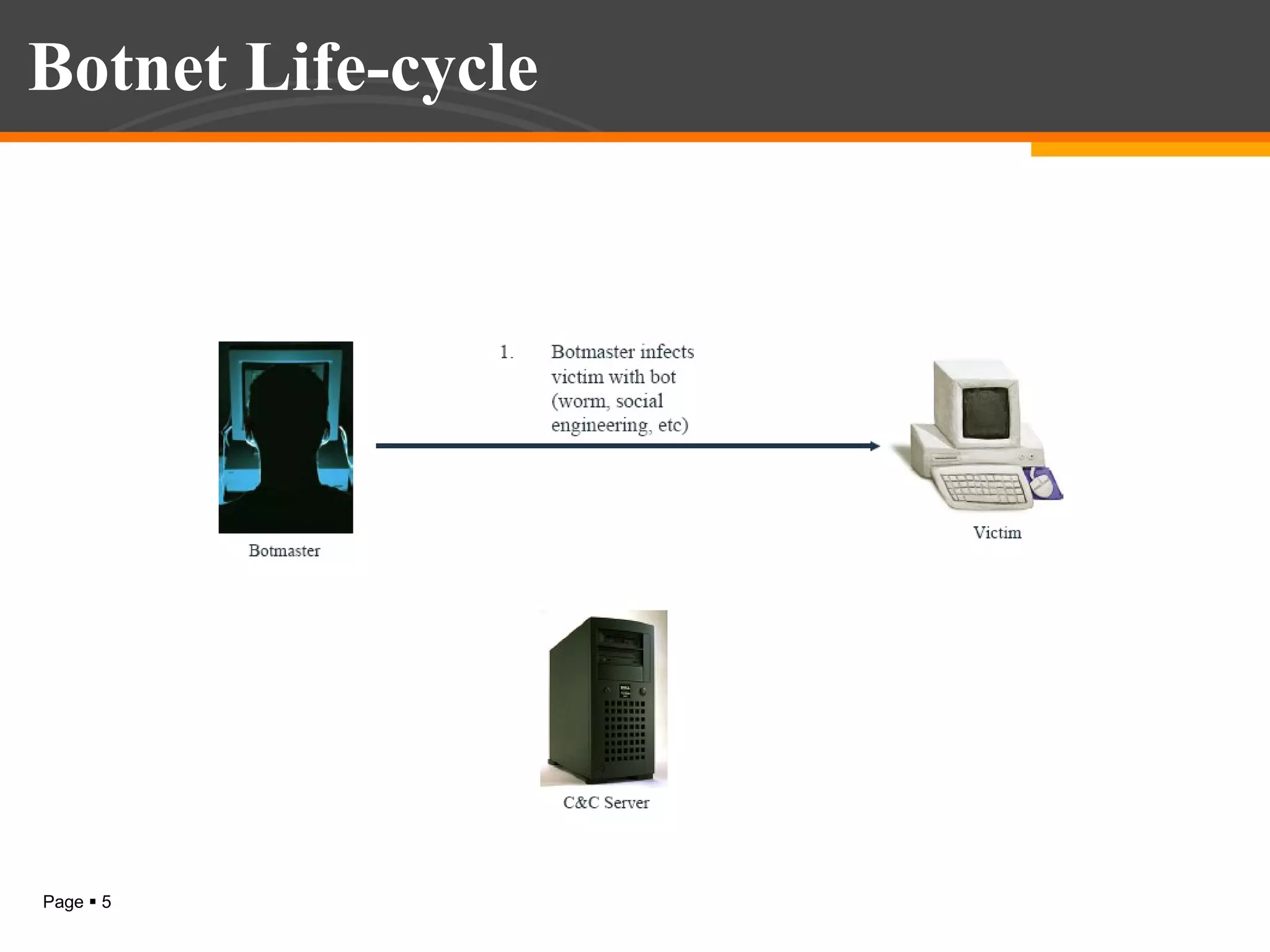
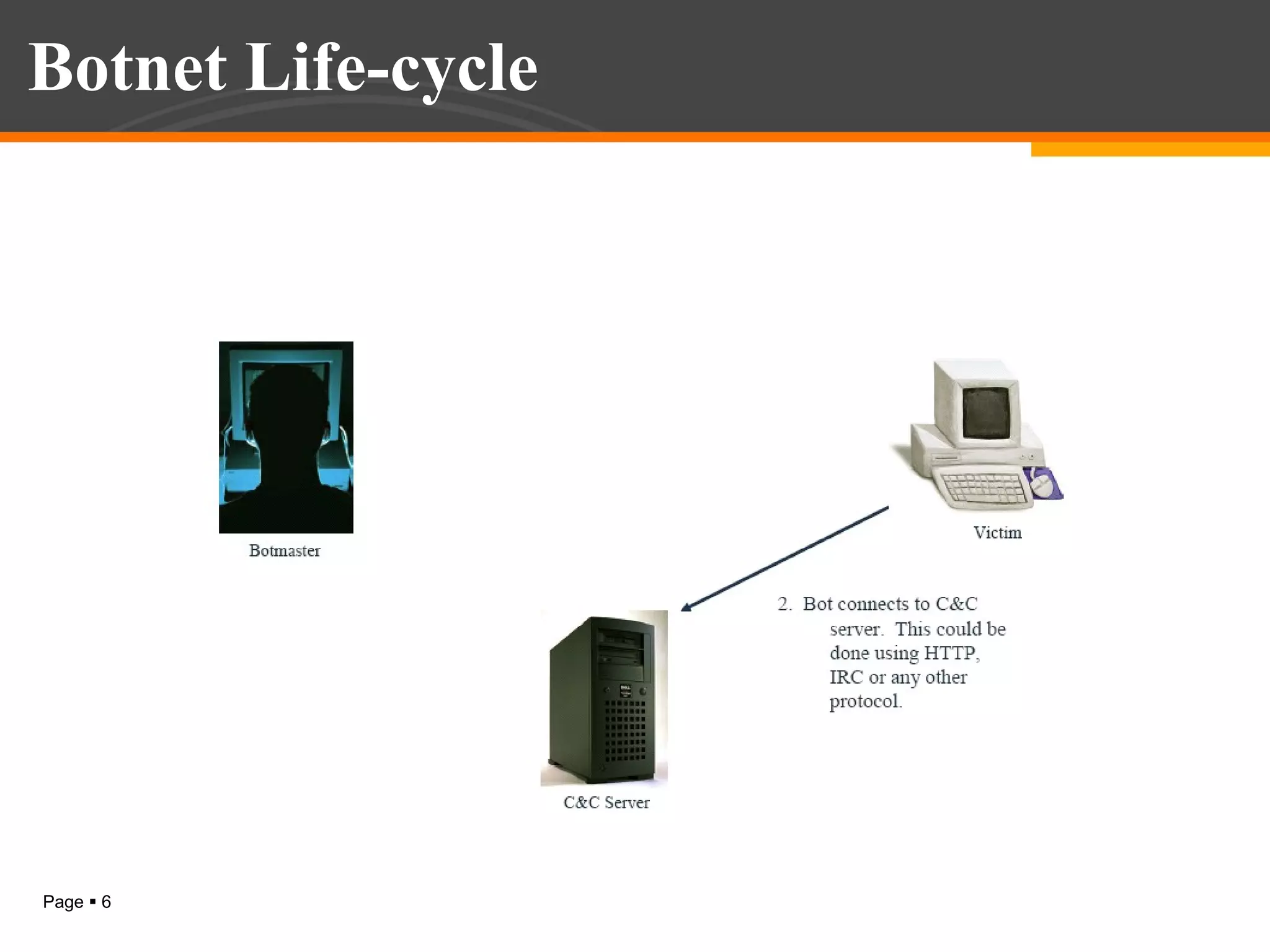
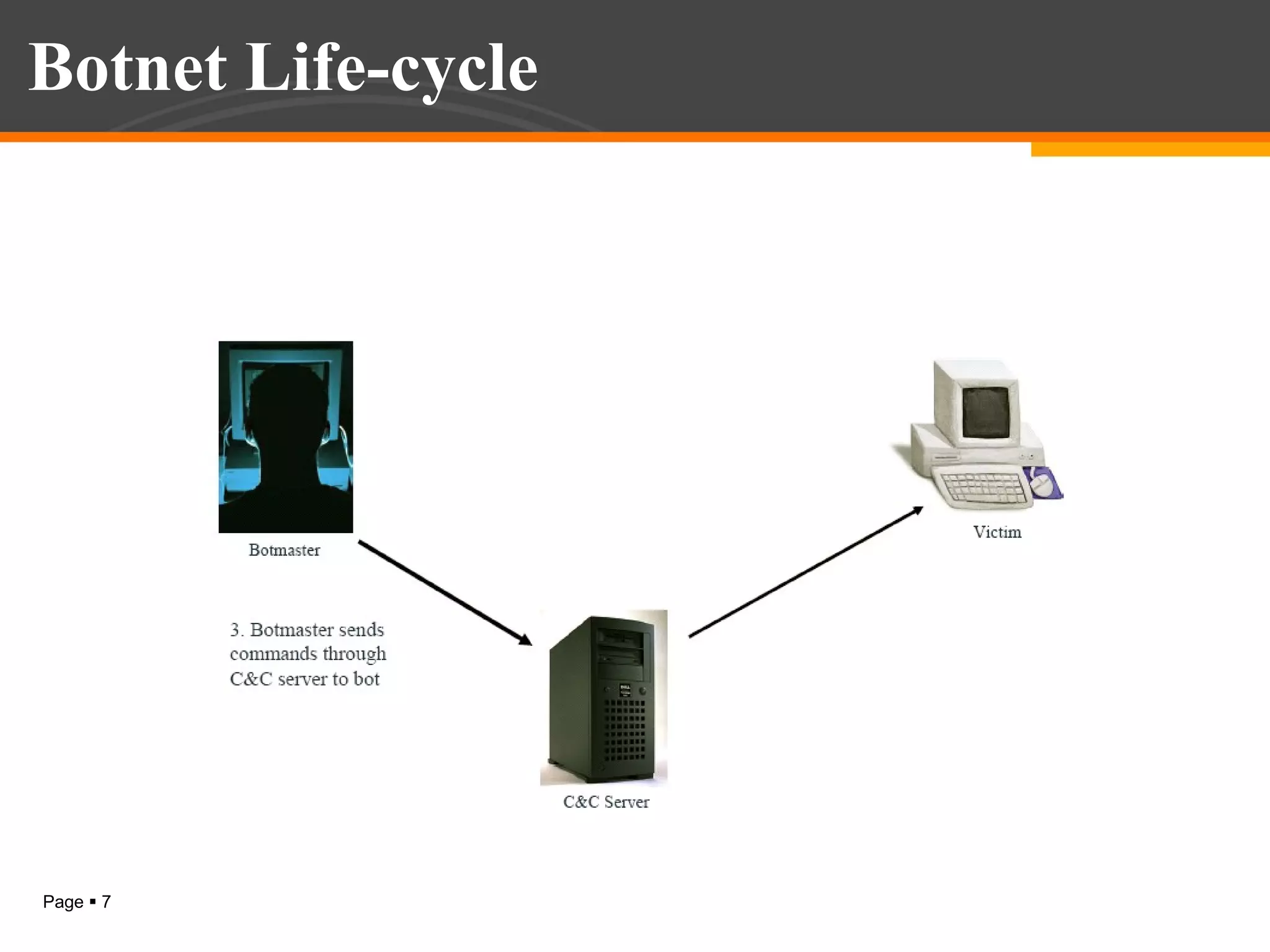
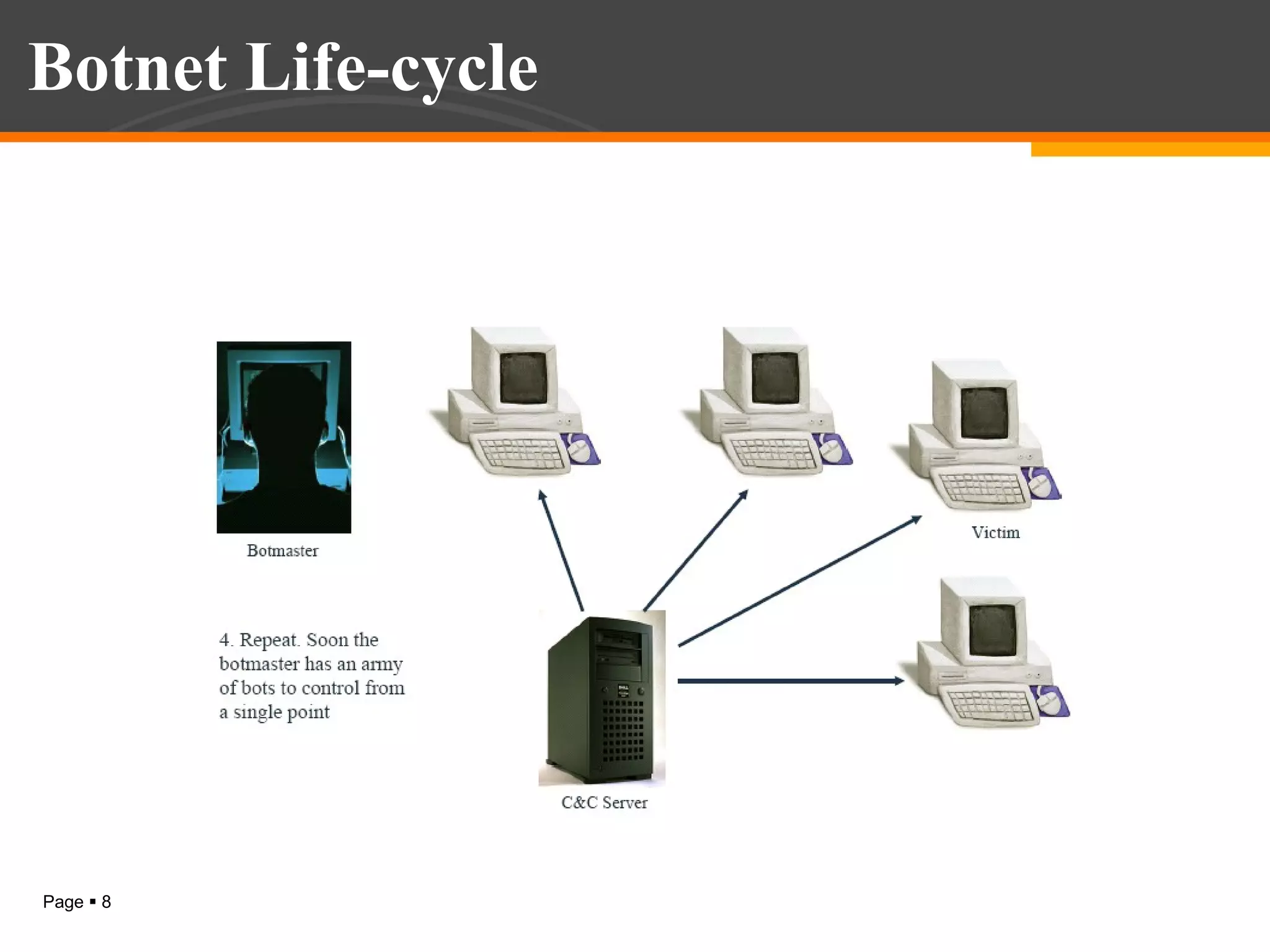
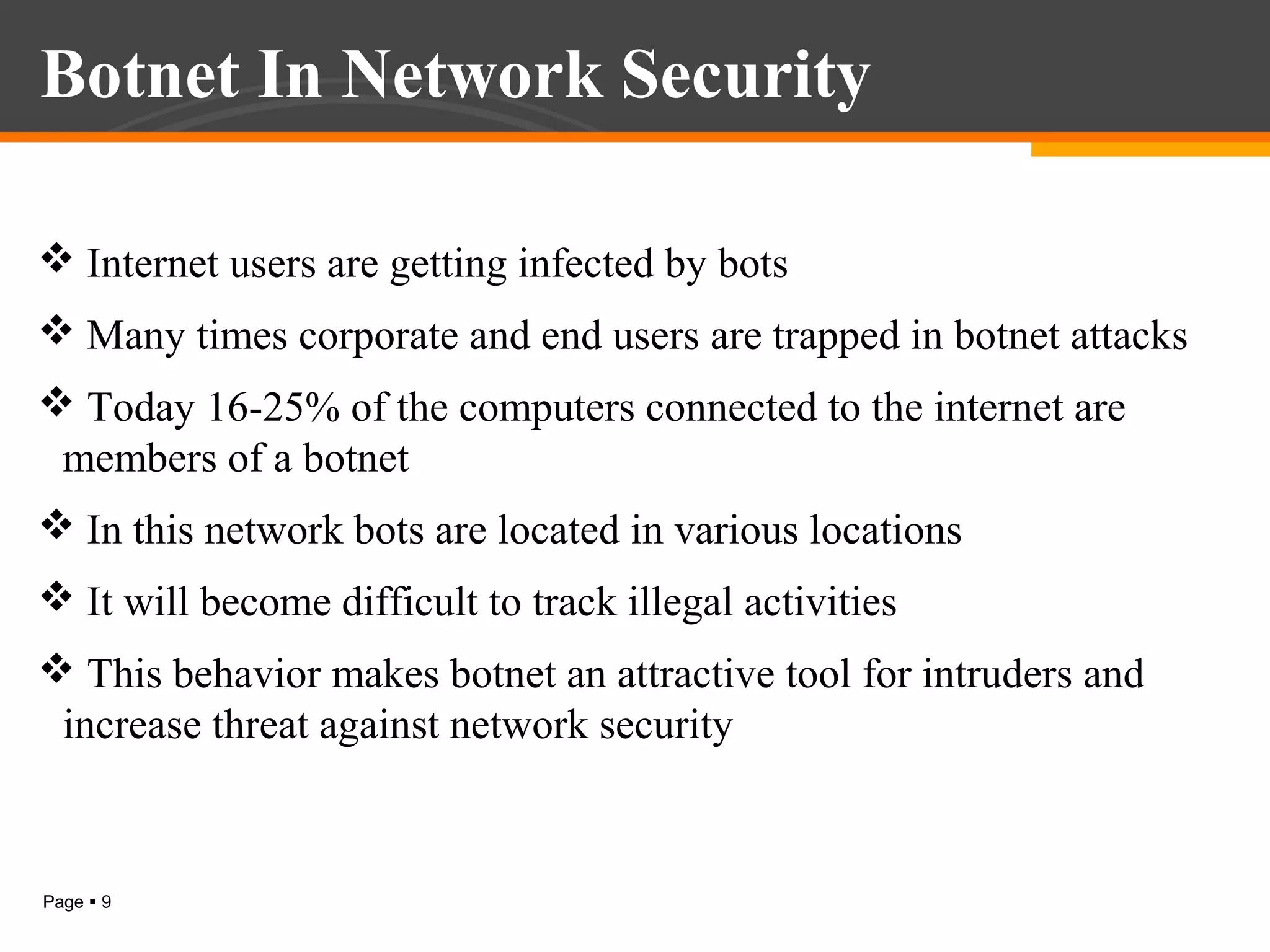
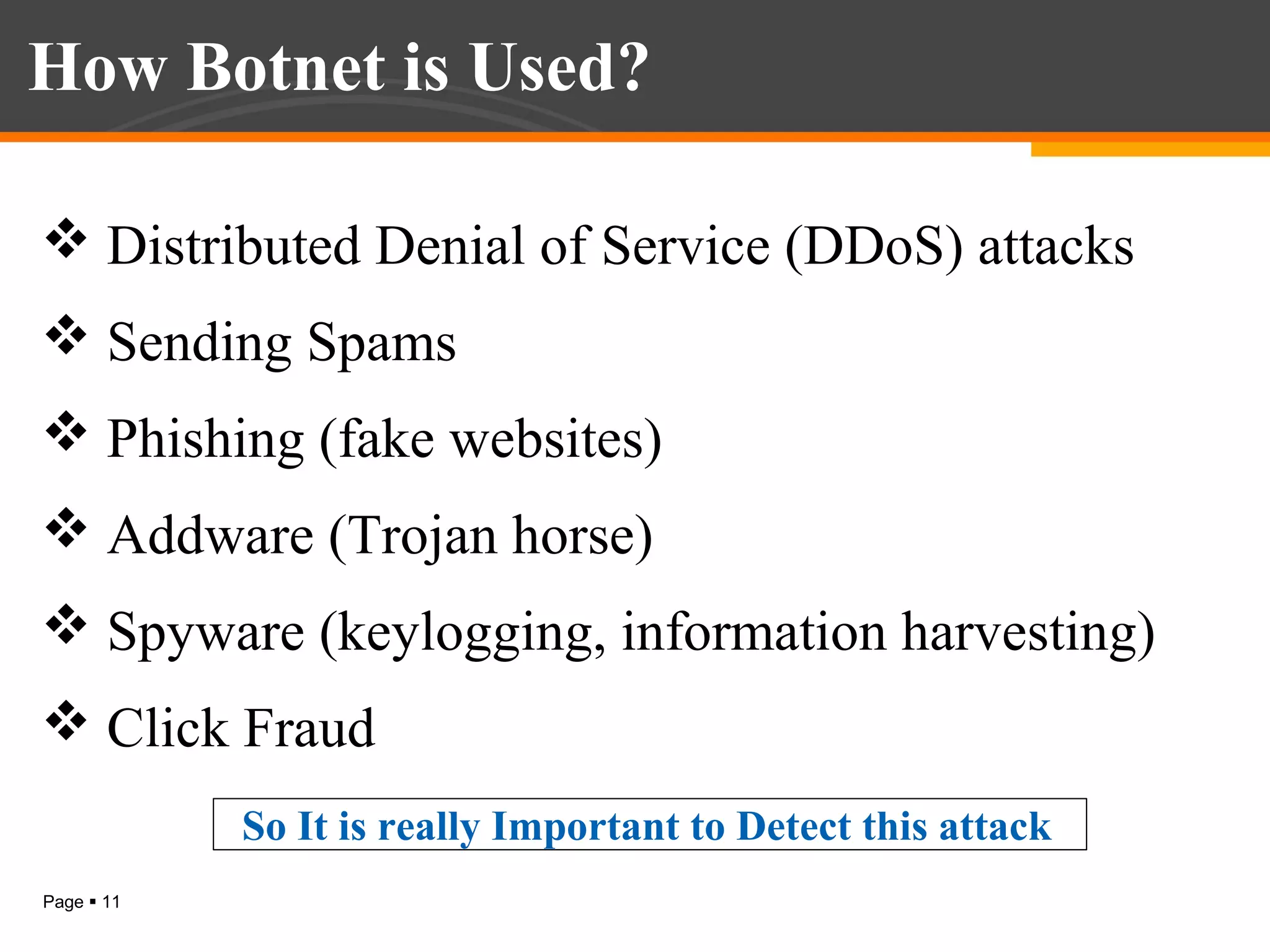
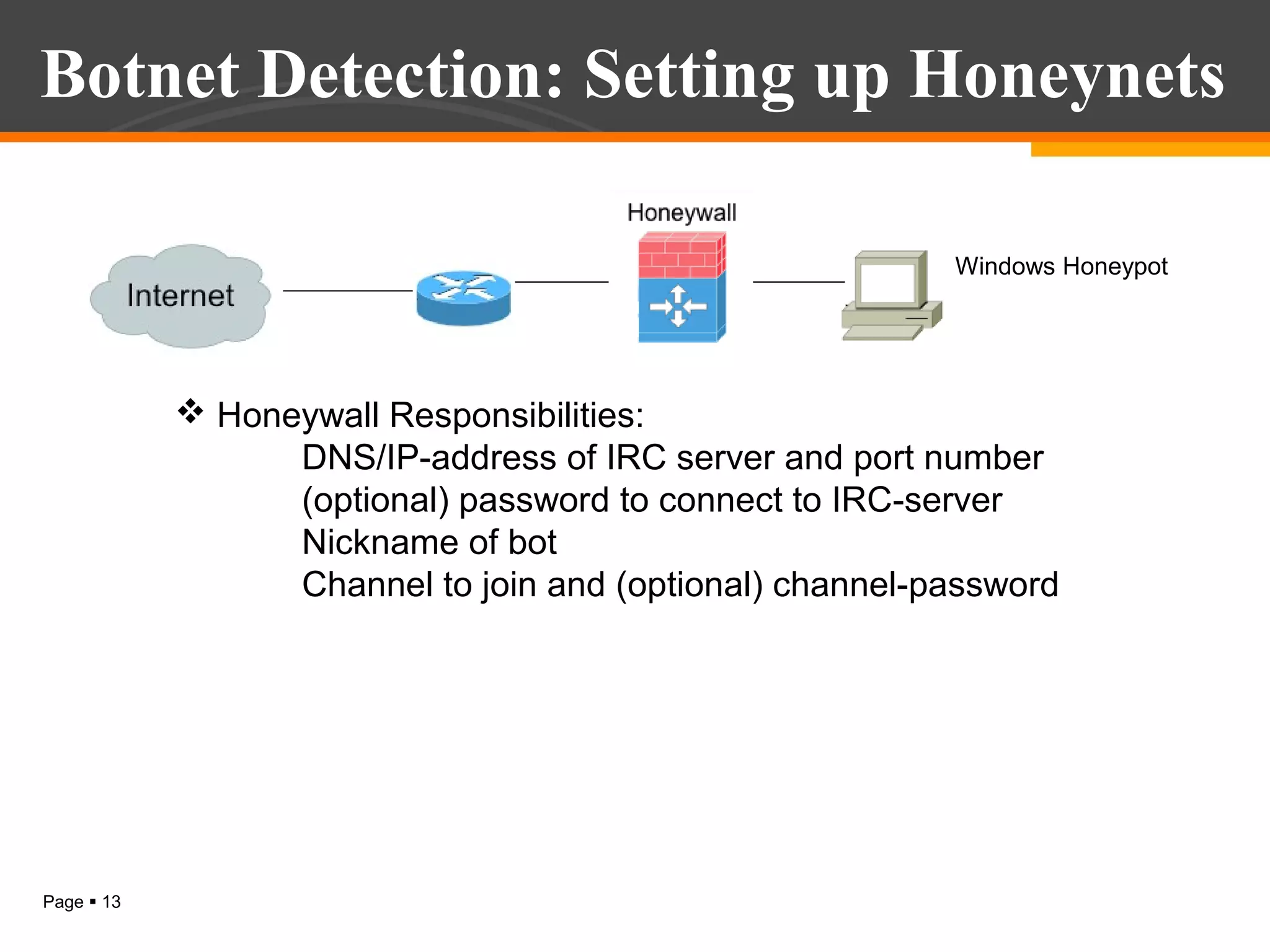
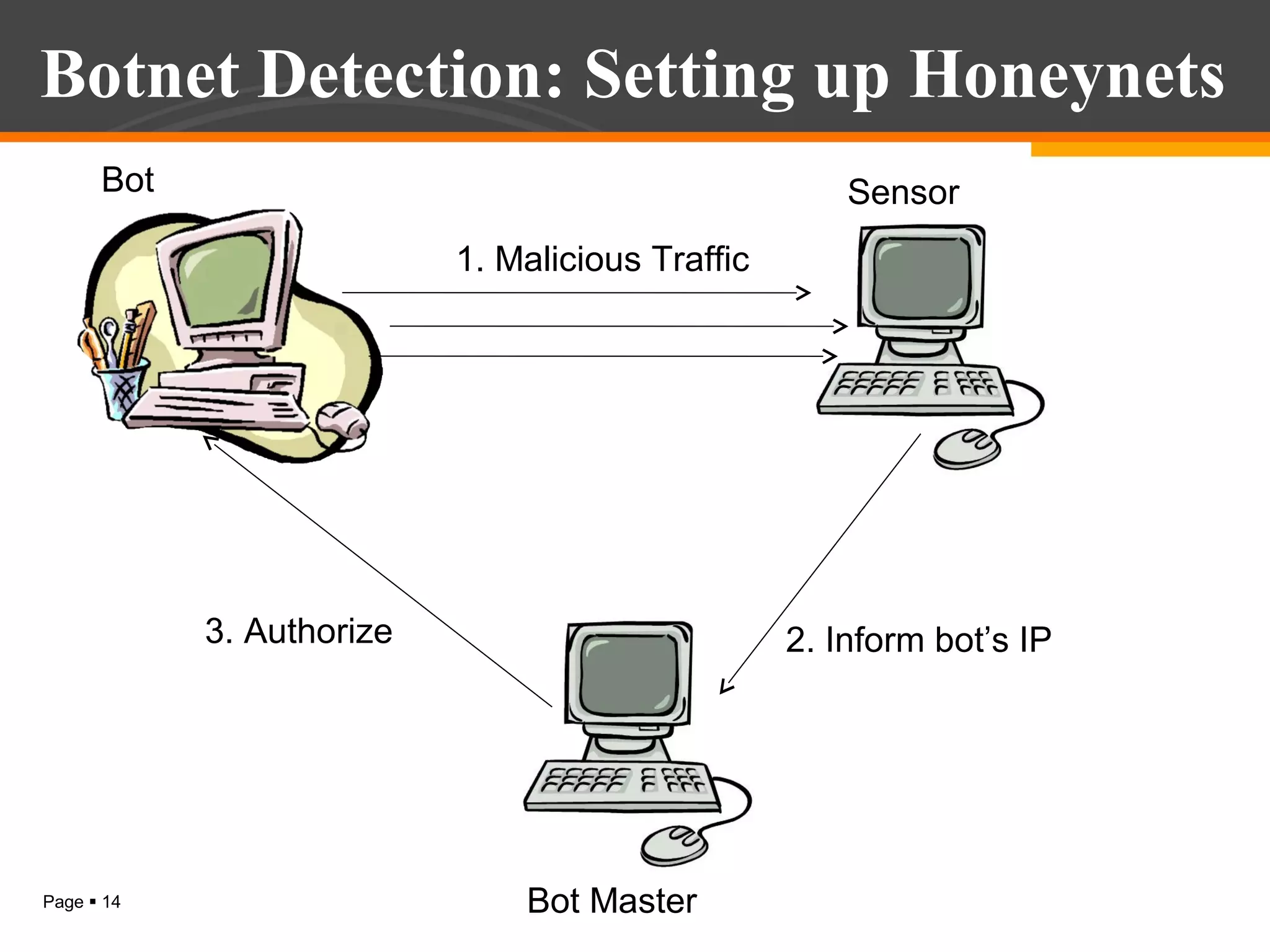
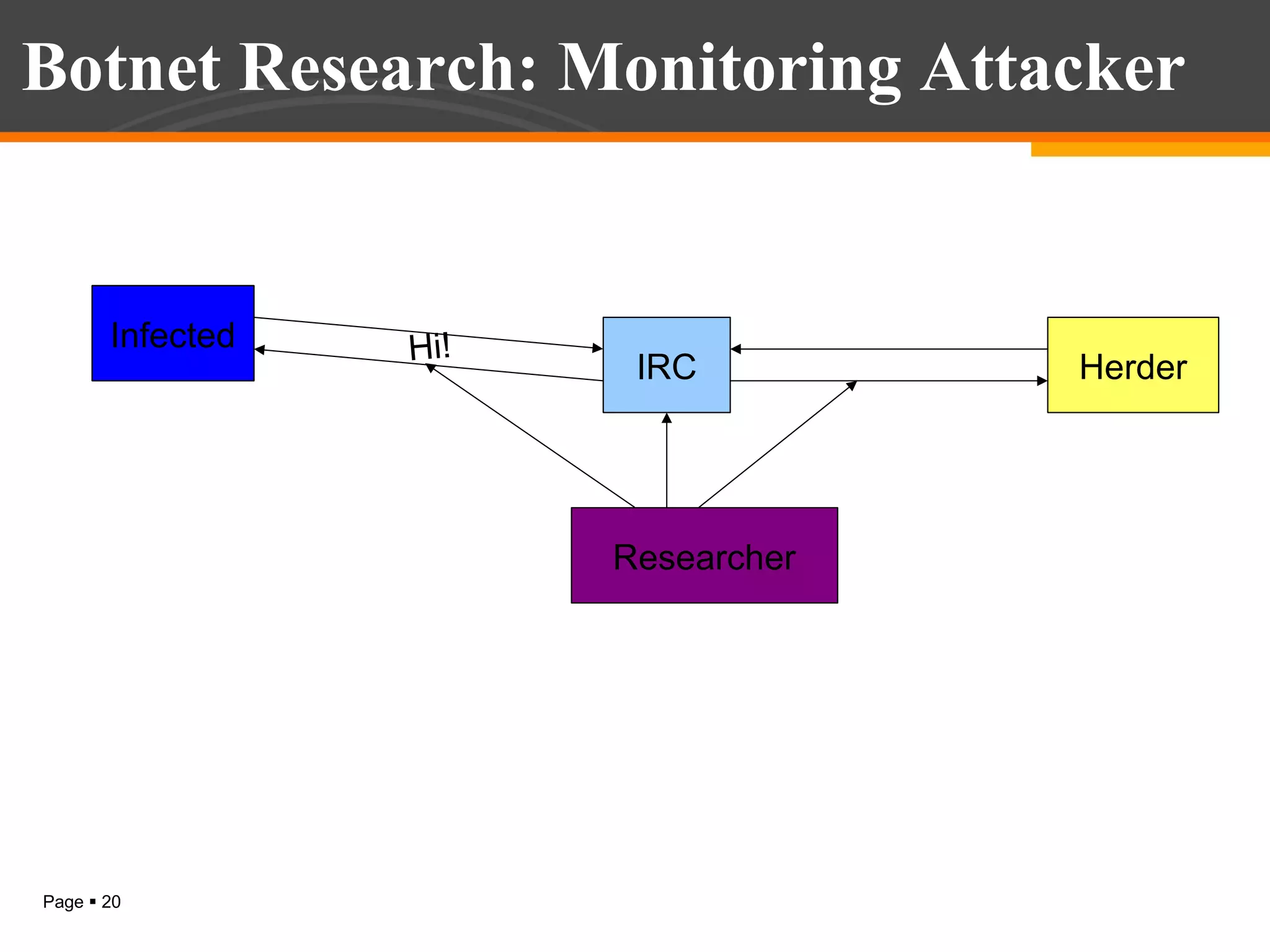
The document discusses botnet detection techniques. It provides an introduction to botnets, describing their terminology and lifecycle. It then covers how botnets pose a threat to network security and how they are used for distributed denial of service attacks, spamming, phishing and more. The document outlines two main approaches to botnet detection: setting up honeynets to monitor infected machines and passive traffic monitoring using signature-based, anomaly-based and DNS-based techniques. It also discusses preventing botnet infections and concludes that botnets are a significant cybersecurity threat and detecting them is important.