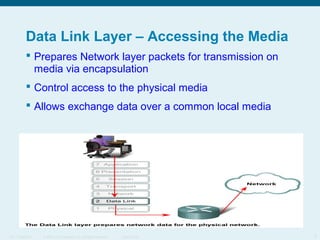
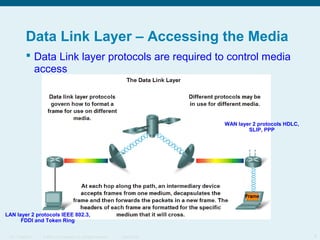
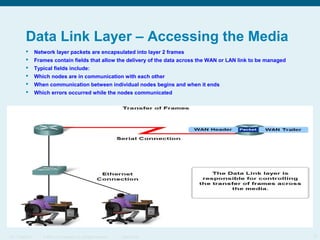
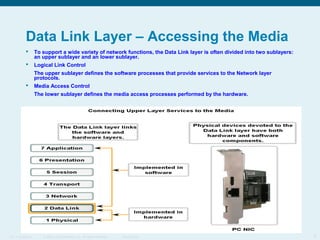
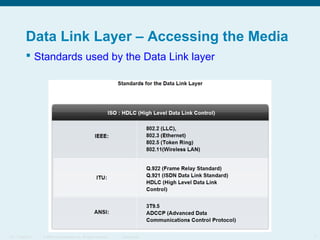
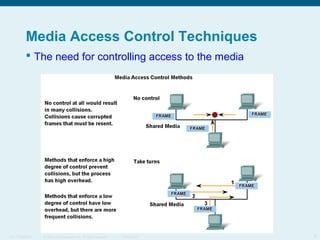
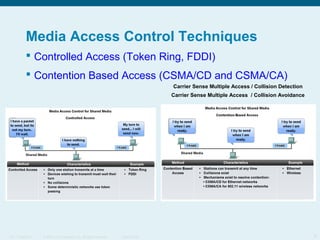
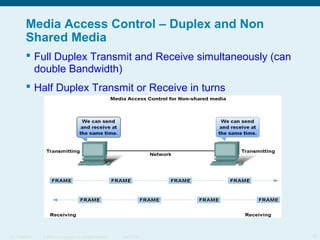
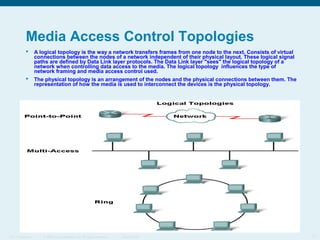
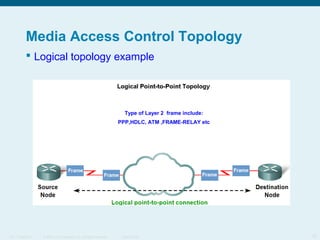
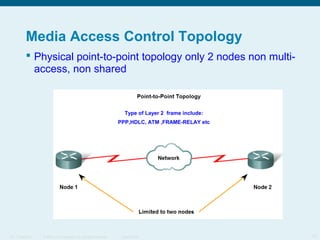
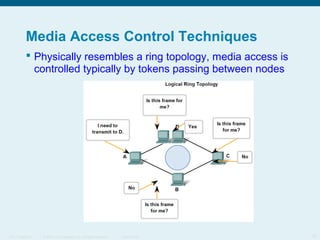
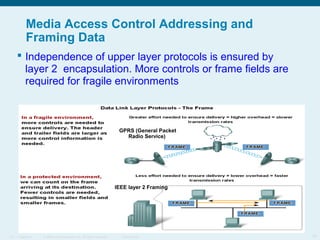
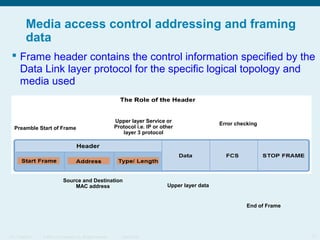
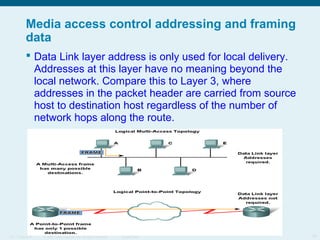
This document discusses the data link layer, which prepares network layer packets for transmission by encapsulating them into frames. It identifies common data link layer protocols for both LANs and WANs. The data link layer controls media access through logical link control and media access control sublayers. Media access control methods include controlled access like token ring and contention-based access like CSMA/CD. Frame structure is also discussed, with frames containing source/destination addresses, error checking fields, and encapsulated network layer data. Different frame types are used depending on the logical and physical network topology.