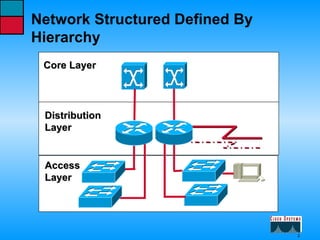
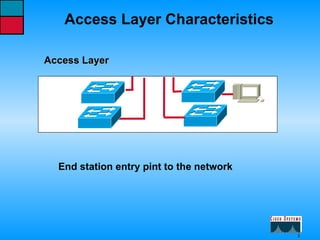
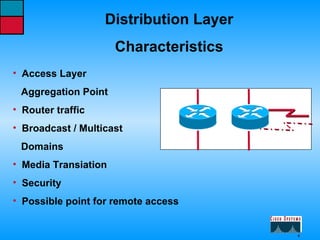
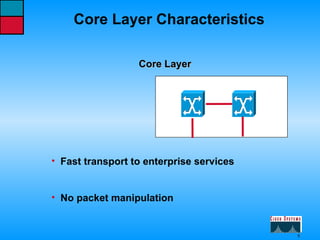
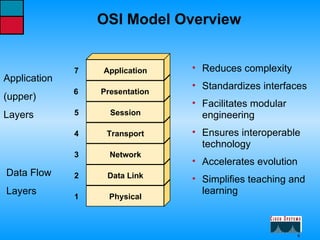
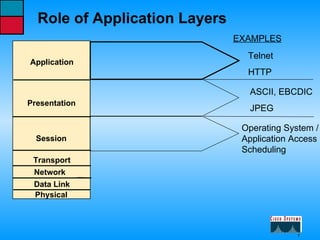
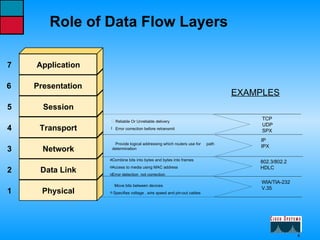
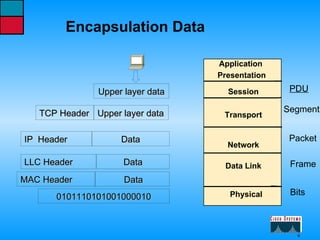
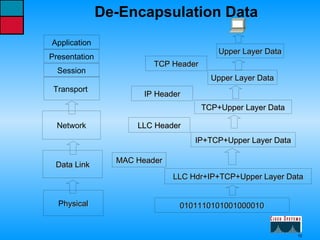
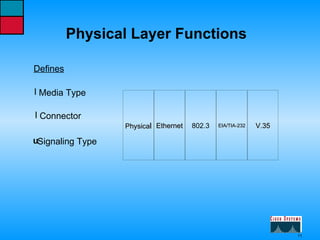
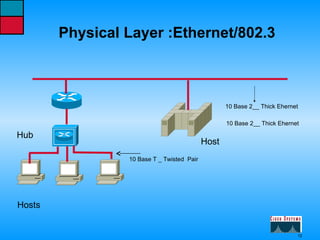
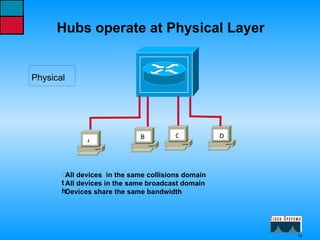
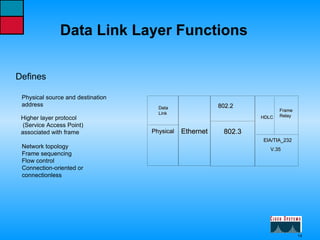
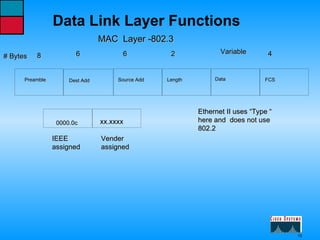
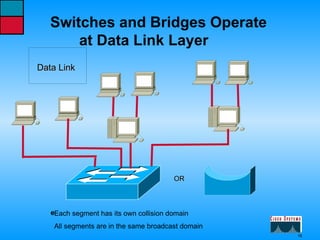
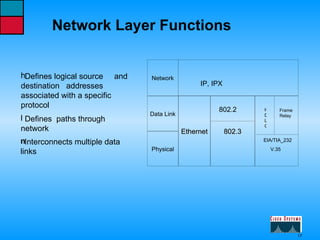
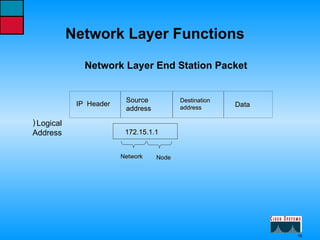
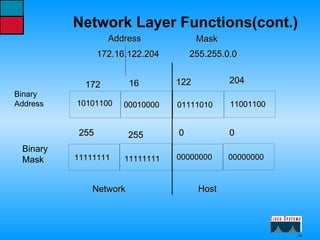
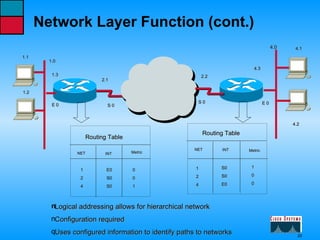
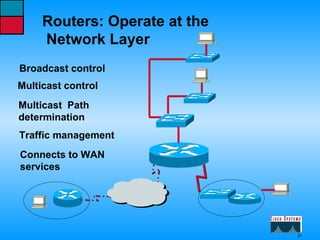
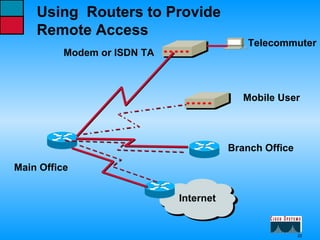
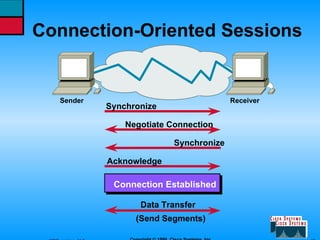
This document describes the roles and functions of different layers in the OSI model. It explains that the access layer is the entry point for end stations to the network. The distribution layer aggregates traffic from the access layer. The core layer provides fast transport across the enterprise with no packet manipulation. It also summarizes that hubs operate at the physical layer, switches and bridges at the data link layer, and routers at the network layer.