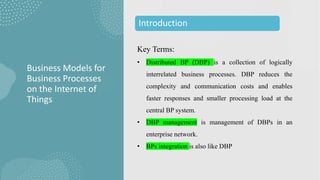
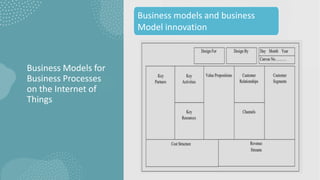
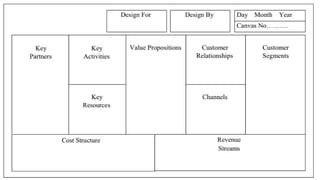
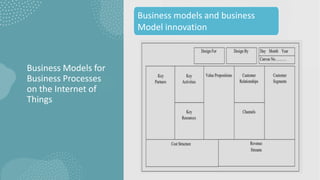
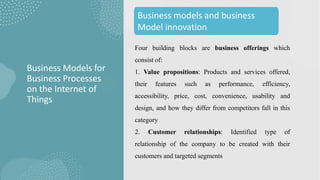
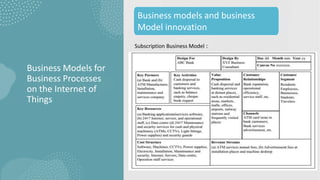
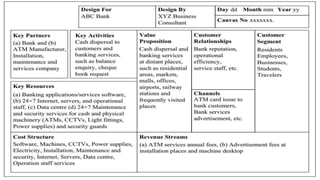
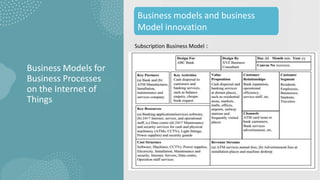
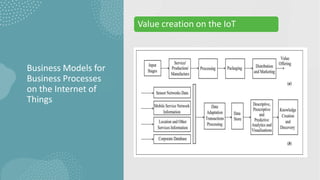
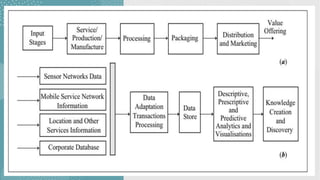
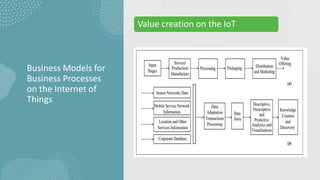
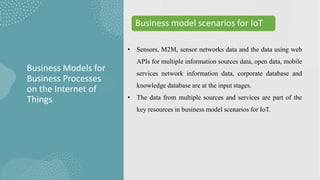
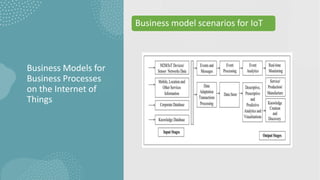
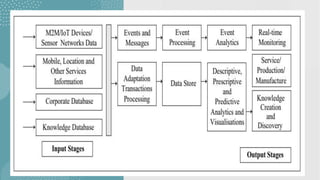
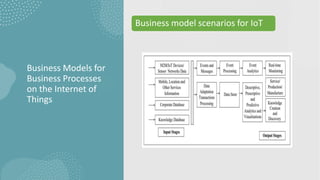
The document discusses business models for business processes on the Internet of Things. It covers key topics like IoT applications, business models, value creation using IoT, and business model scenarios for IoT. Business models need innovation to adapt to new customer access and interactions enabled by technologies like cloud computing and mobile communications. Value is created on IoT through addressing emergent needs, information convergence, and recurrent revenue from networked products. Example business model scenarios for IoT leverage data from multiple sources like sensors, M2M, and open data.