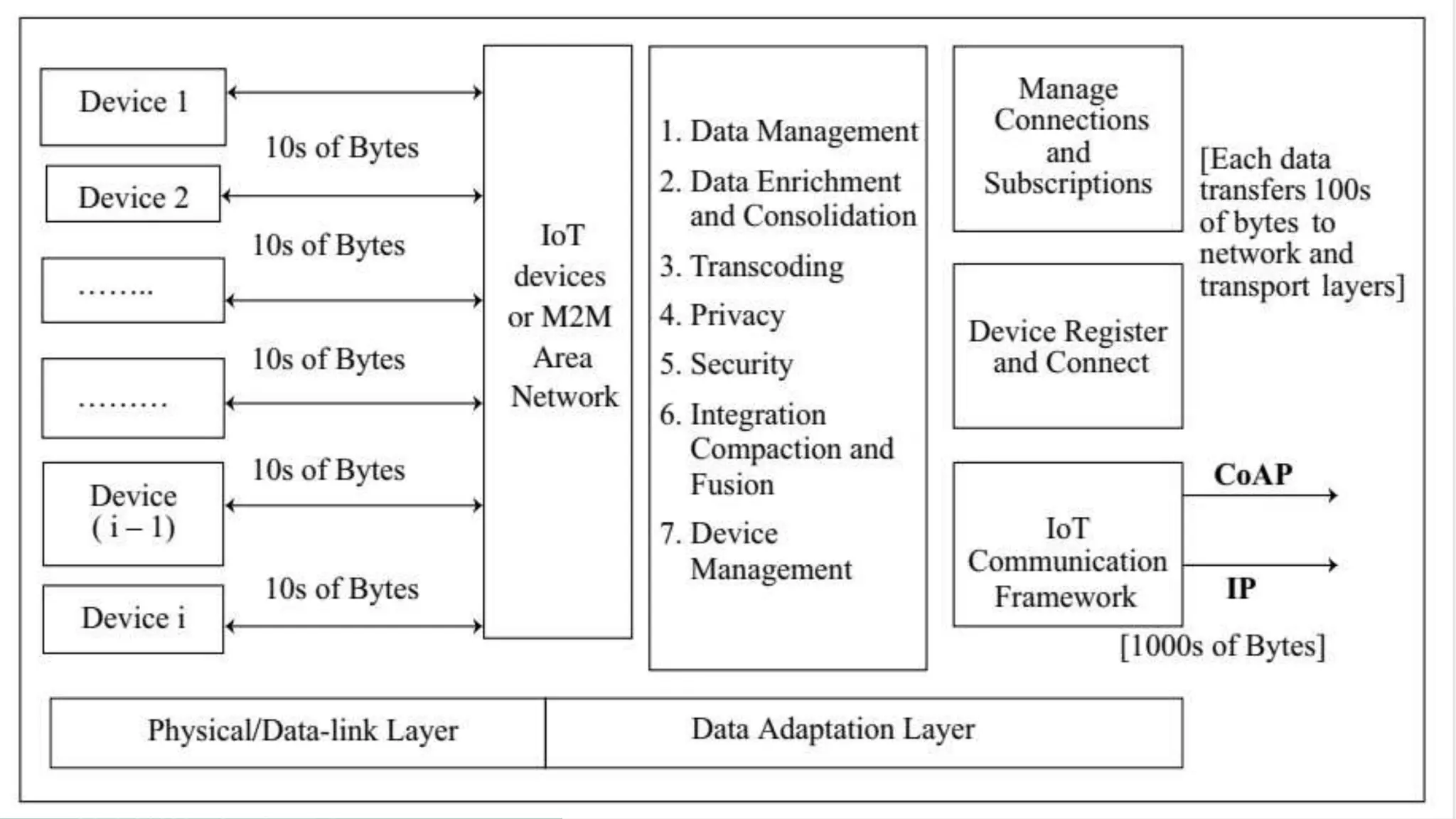
The document discusses the functions of a gateway in an IoT/M2M system. The gateway performs data enrichment, consolidation, and device management. It has several key functions including transcoding data formats, ensuring privacy and security, gathering and enriching data from devices, aggregating and compacting data, and managing device identities, configurations, and faults.