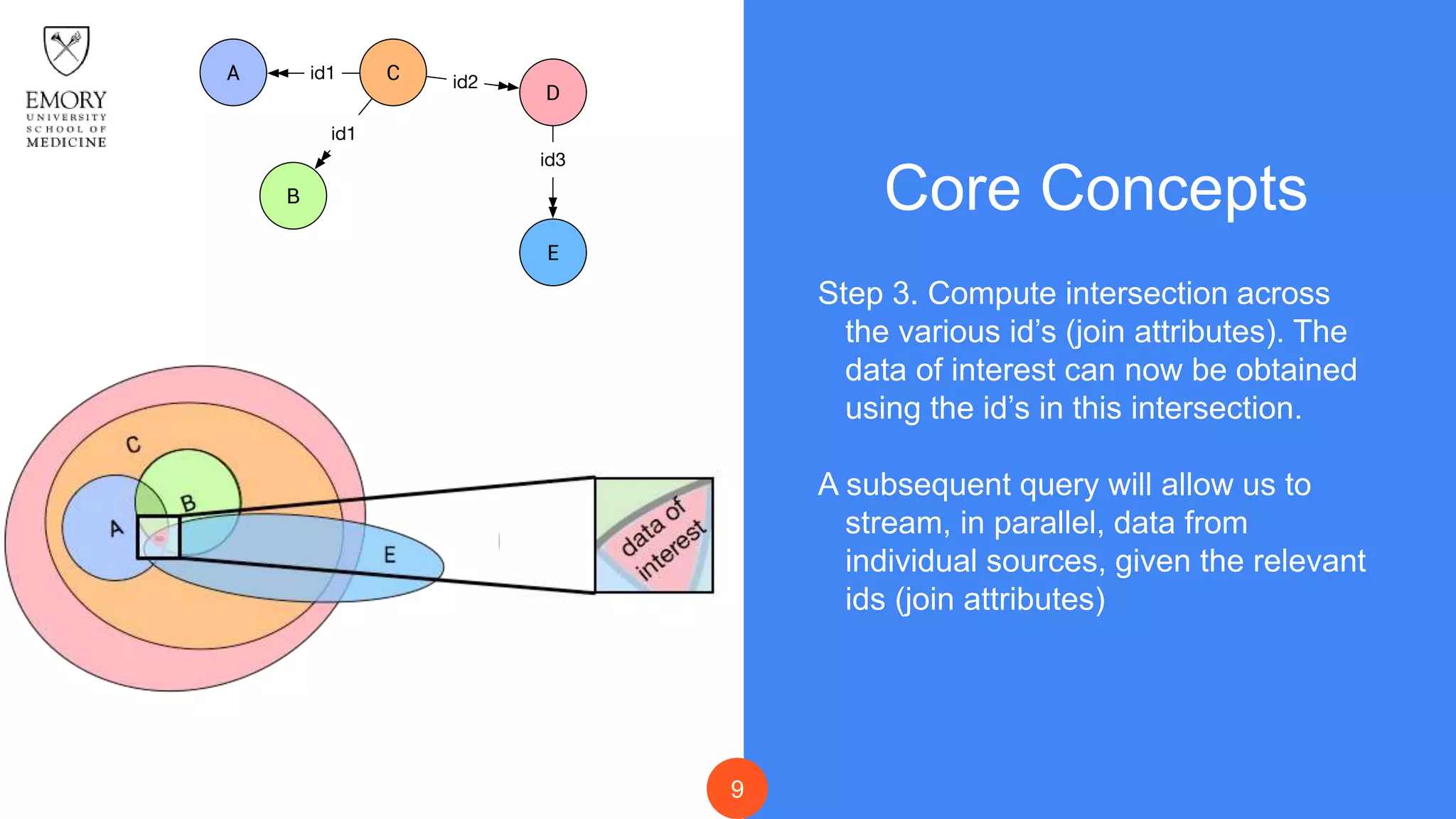
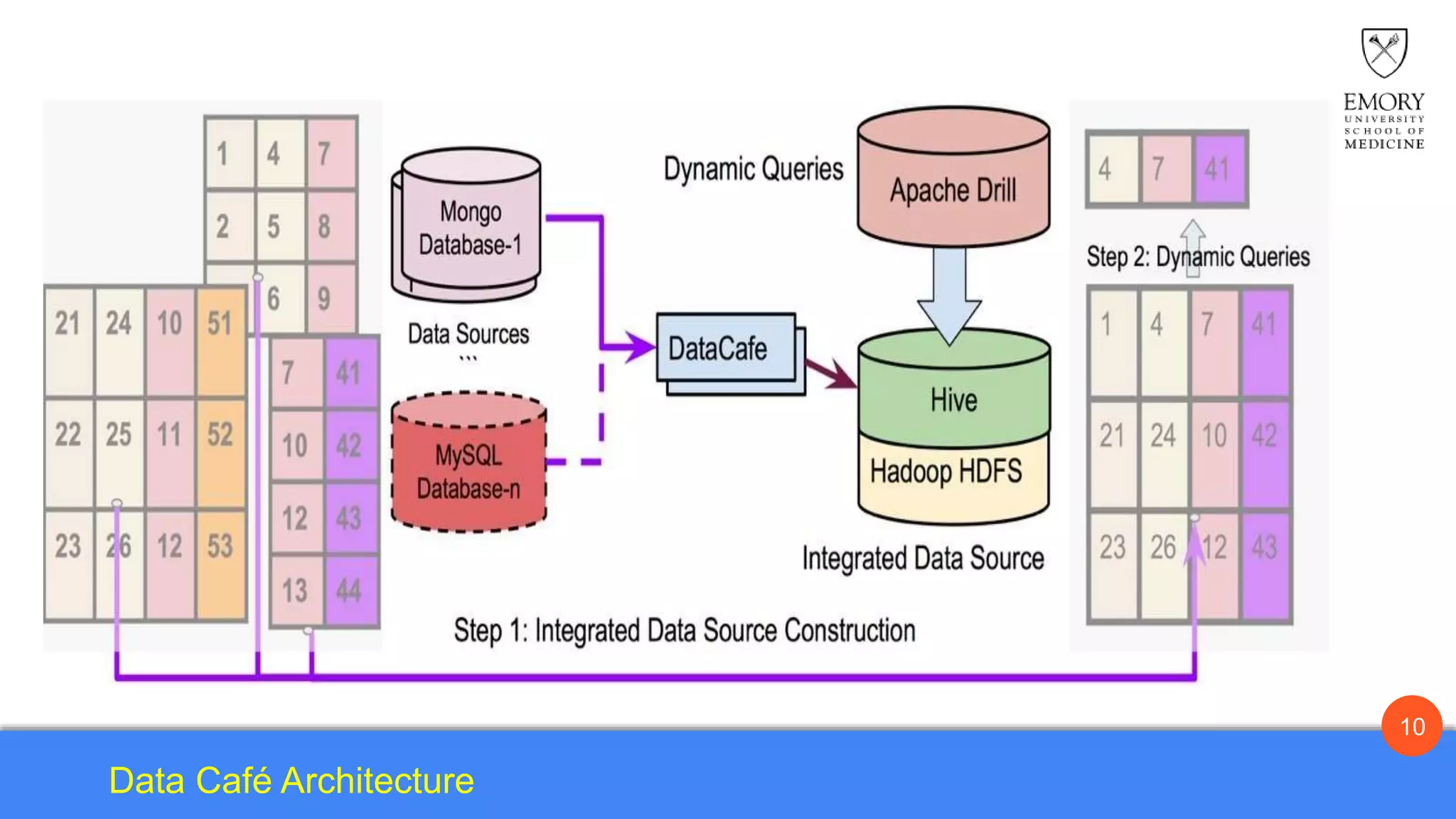
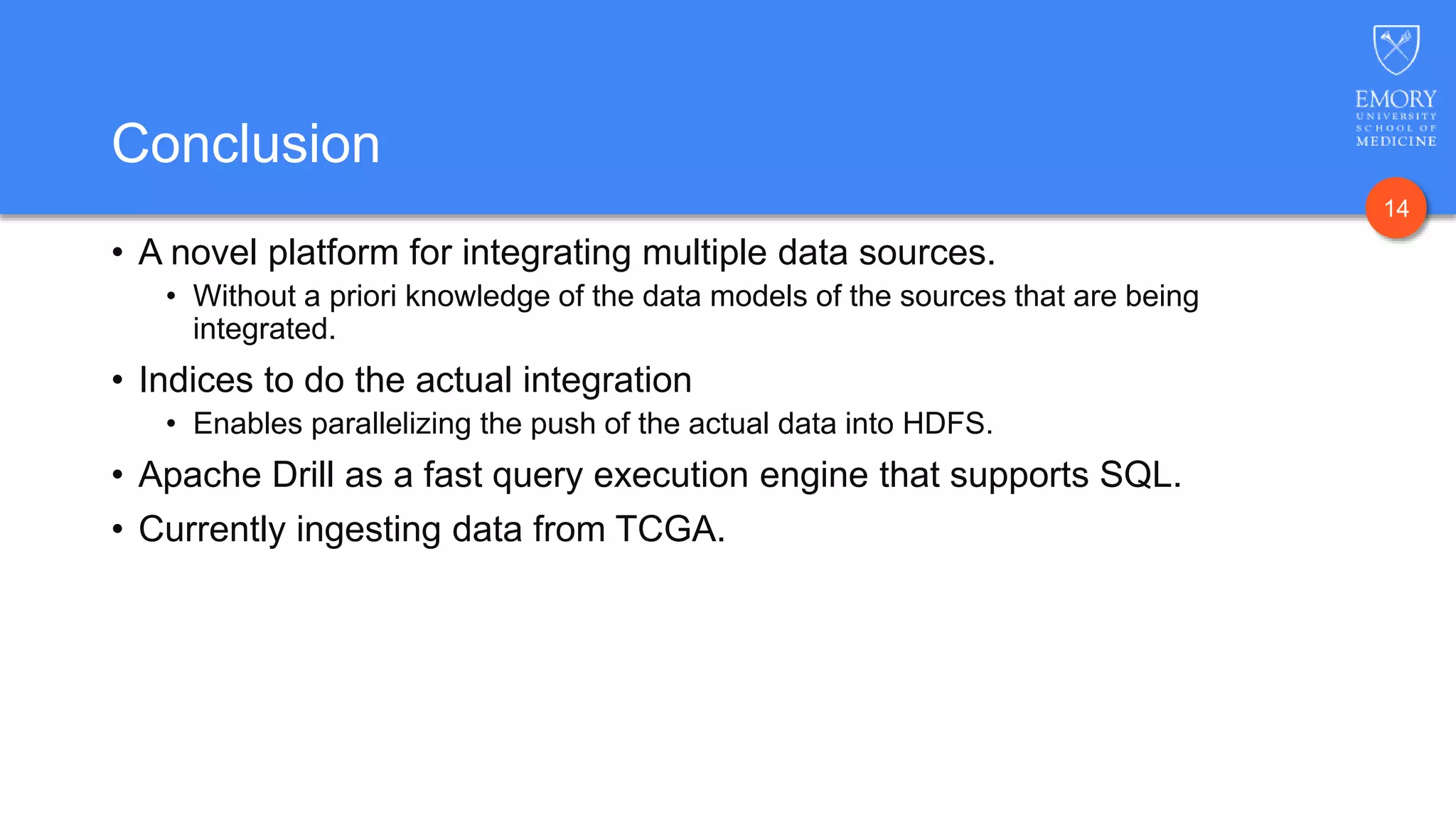
The document presents Data Café, a platform designed for creating biomedical data lakes, facilitating the integration of diverse datasets without prior knowledge of their schemas. It emphasizes the use of Apache Drill for agile query execution and highlights the platform's capability to support complex queries across multiple sources. Ongoing developments aim to enhance integration with larger data stores and imaging tools for improved precision medicine applications.








![Acknowledgements
Google Summer of Code 2015
NCIP/Leidos 14X138, caMicroscope
— A Digital Pathology Integrative
Query System; Ashish Sharma PI
Emory/WUSTL/Stony Brook
NCI U01 [1U01CA187013-01],
Resources for development and
validation of Radiomic Analyses &
Adaptive Therapy, Fred Prior, Ashish
Sharma (UAMS, Emory)
The results published here are in part
based upon data generated by the
TCGA Research Network:
http://cancergenome.nih.gov/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datacafe-presentation-v4-160326153037/75/Data-Cafe-A-Platform-For-Creating-Biomedical-Data-Lakes-16-2048.jpg)
