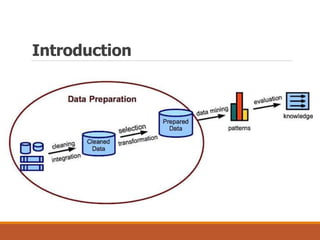
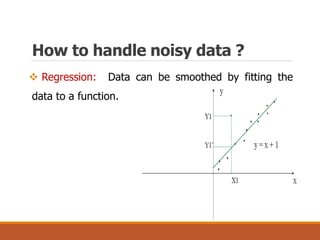
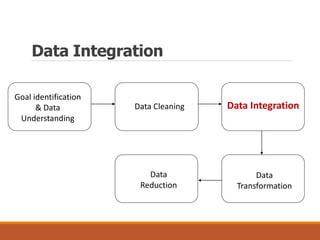
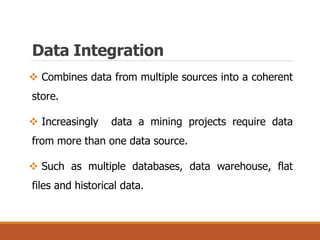
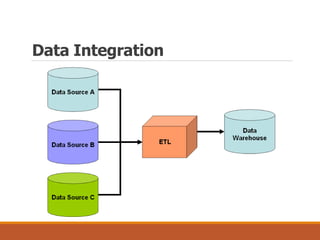
The document discusses data preparation and processing, emphasizing the importance of handling noisy and inconsistent data. It outlines methods for data cleaning, integration, transformation, and reduction, as well as strategies for dealing with noise and inconsistencies in data. Key techniques mentioned include binning, clustering, combined inspections, and data warehousing for coherent data storage and analysis.