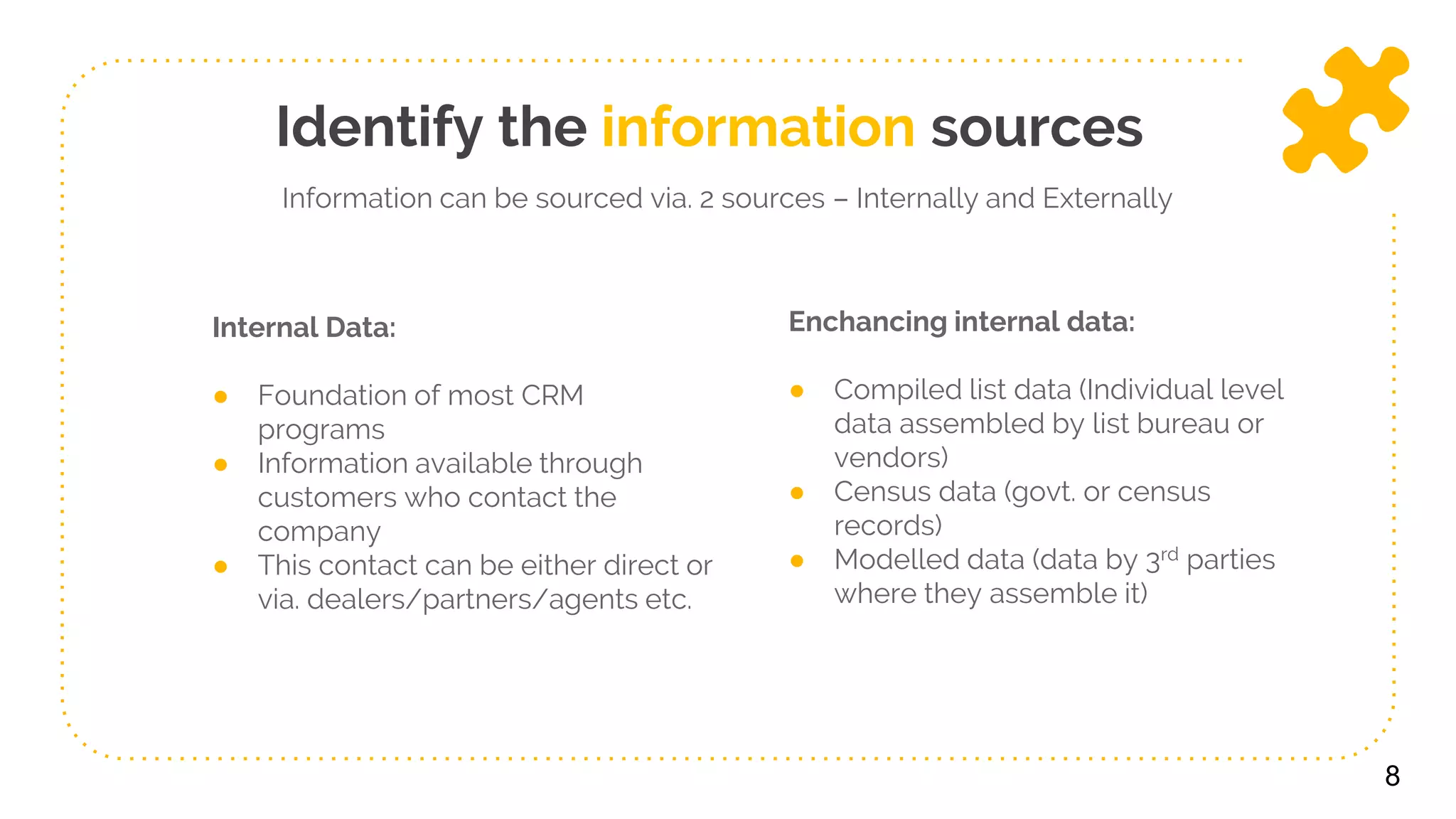
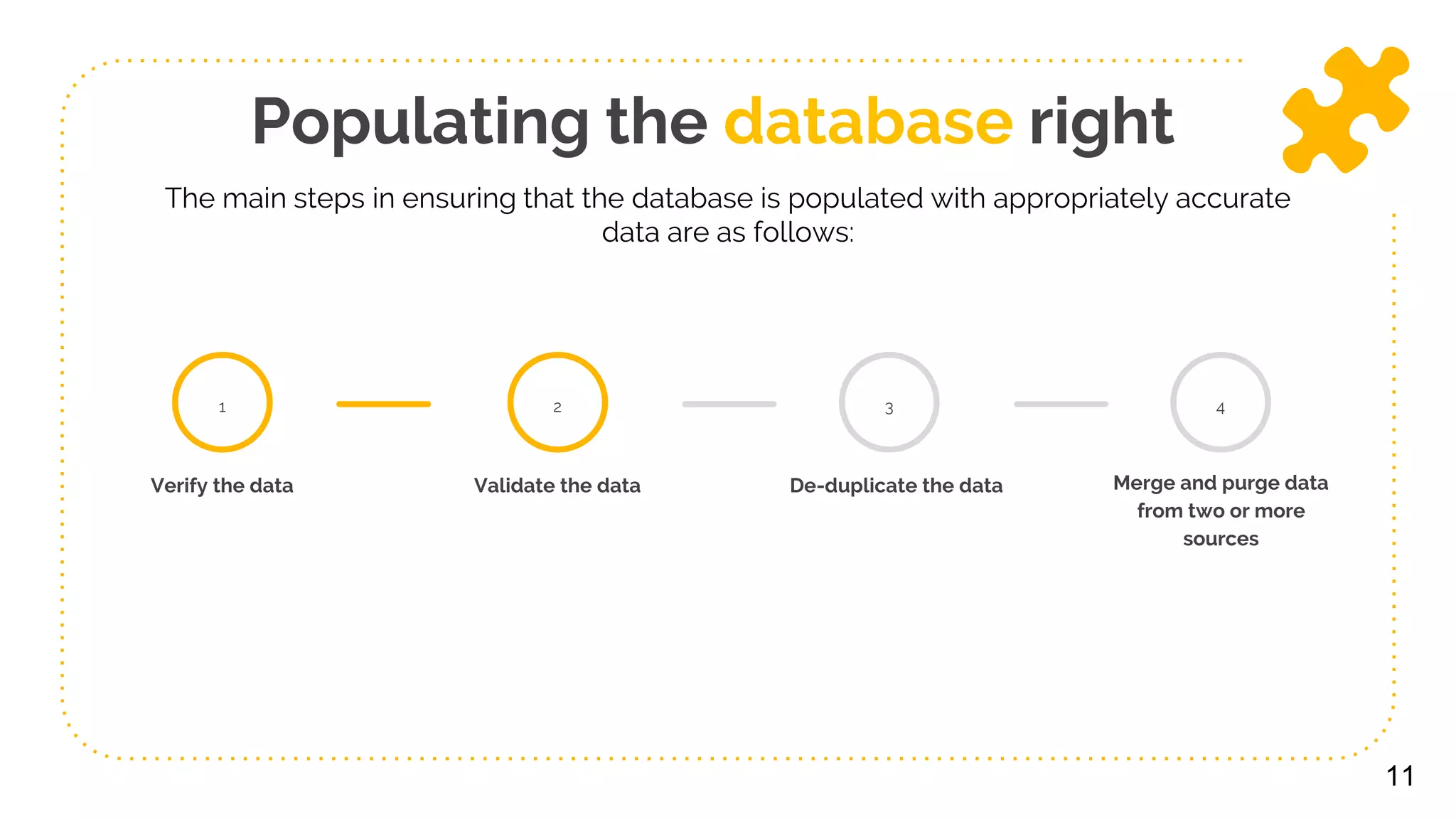
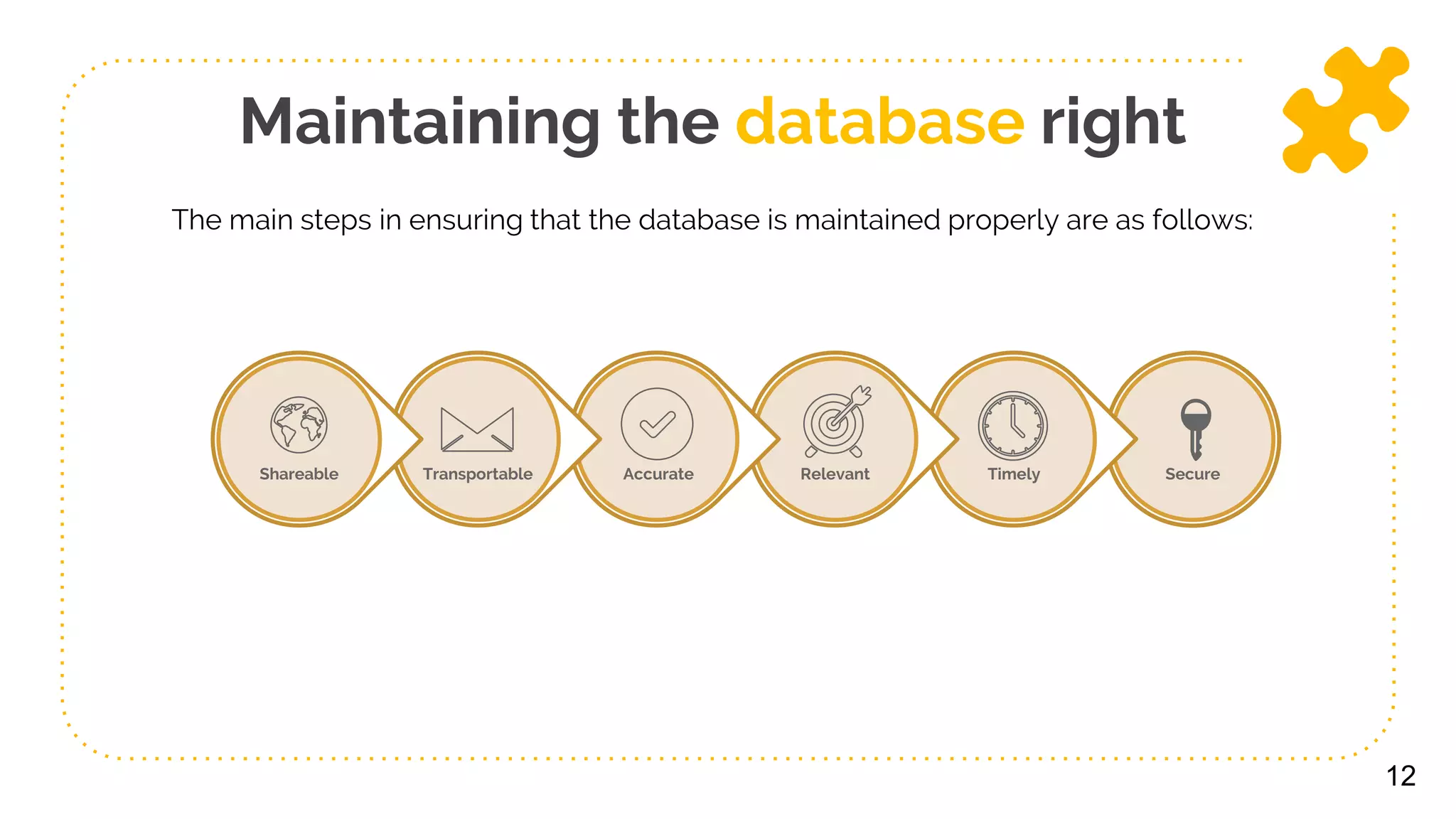
The document presents a comprehensive overview of data collection, storage, and access, distinguishing between data and information. It outlines key functions of databases, the importance of internal and external data sources, and strategies for effectively populating and maintaining databases. Additionally, it addresses the implications of big data and emphasizes the significance of accessibility and analysis for informed decision-making.