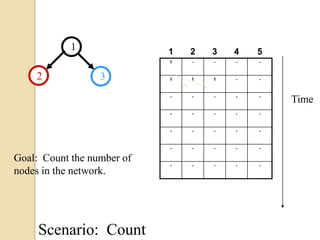
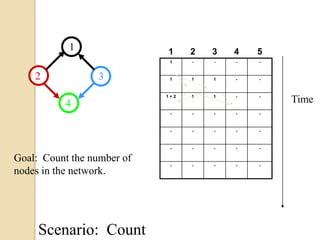
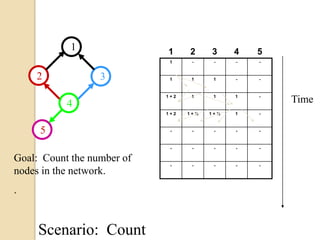
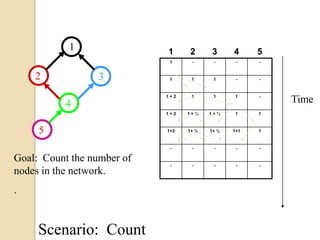
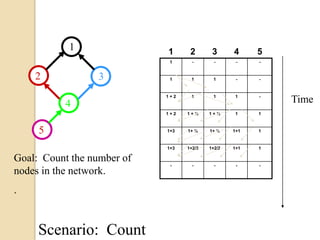
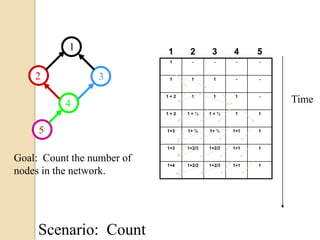
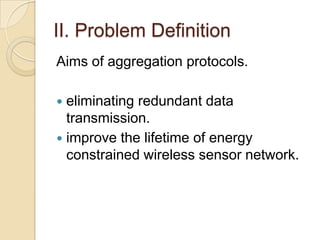
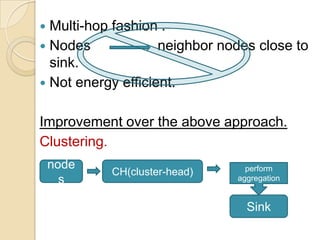
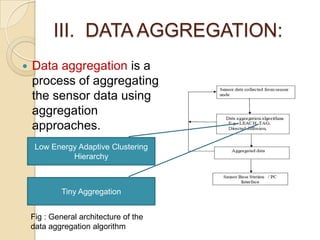
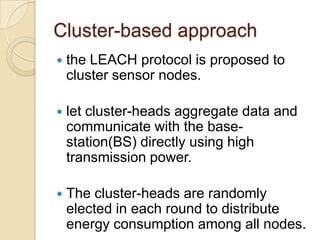
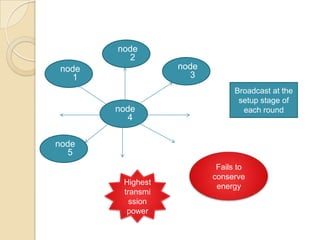
This document discusses data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. It describes how sensor nodes are clustered and cluster heads perform data aggregation to compress and combine data before transmitting it to conserve energy. Various data aggregation techniques are explained, including centralized, in-network, tree-based and cluster-based approaches. The cluster-based LEACH protocol is discussed in detail, as well as issues with clustering. Query processing and different query models are also summarized. Simulation tools for analyzing sensor network algorithms are listed.












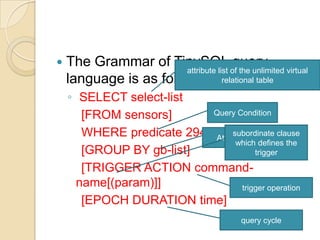
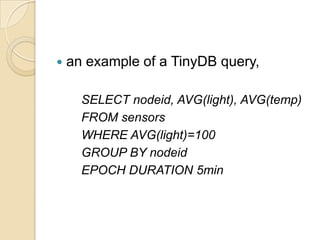
![The Grammar of TinySQL query language is as follows: SELECT select-list [FROM sensors] WHERE predicate 294 [GROUP BY gb-list] [TRIGGER ACTION command-name[(param)]] [EPOCH DURATION time] attribute list of the unlimited virtual relational tableQuery Conditionsubordinate clause which defines the triggerAttribute listtrigger operationquery cycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation2-110907112312-phpapp02/85/Presentation-on-sensor-network-34-320.jpg)