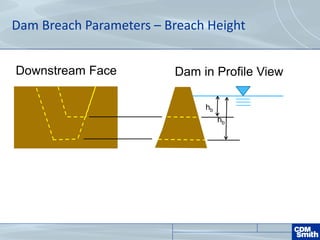
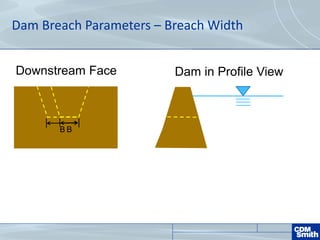
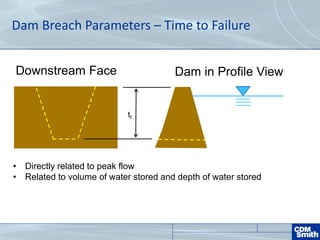
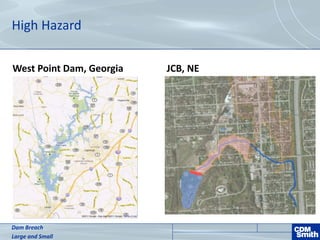
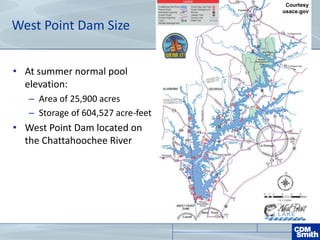
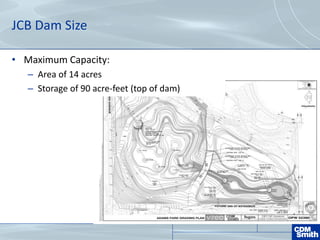
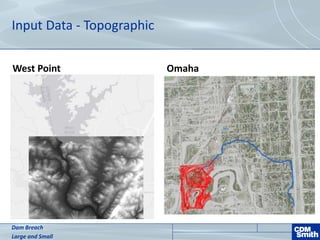
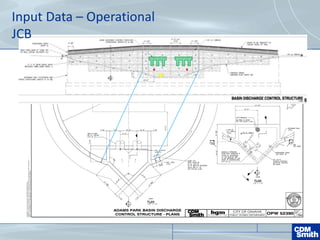
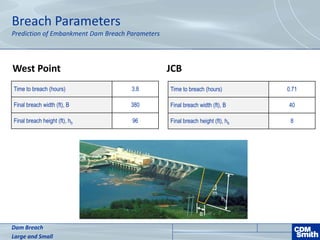
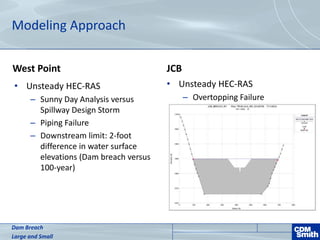
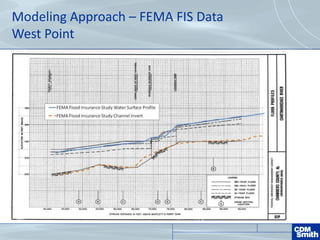
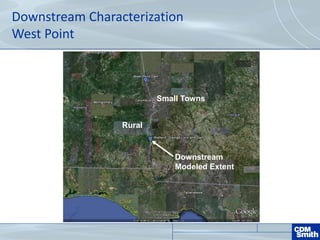
The document analyzes the technical aspects of dam breaches for both large and small dams, detailing key breach parameters such as height, width, and time to failure. It compares two specific dams, West Point Dam in Georgia and John Creighton Boulevard Dam in Nebraska, highlighting their respective flood control purposes and breach modeling approaches. The analysis emphasizes the importance of understanding dam breach hazards and developing effective emergency action plans to manage community flood risks.