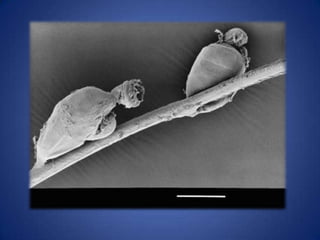
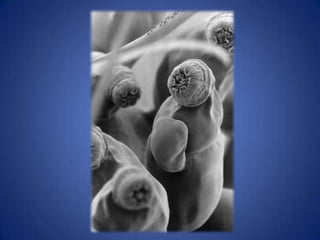
- Phylum Cycliophora are microscopic marine invertebrates that were discovered in 1995 living commensally on lobster mouthparts. Only a few possible species are known.
- They have a multicellular, bilateral, acoelomate body that is hundreds of micrometers in length with an epidermis, cuticle, individual muscles, and unknown nervous system.
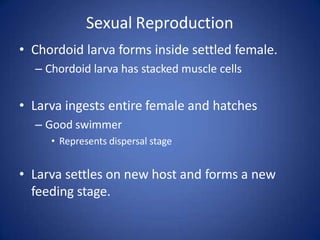
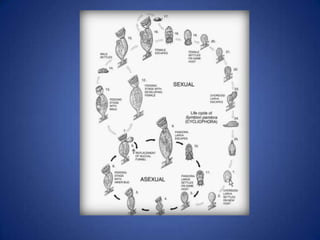
- They reproduce both asexually through budding and sexually, with multiple motile larval stages that allow settlement on new hosts.