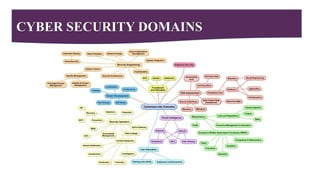
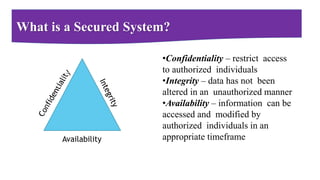
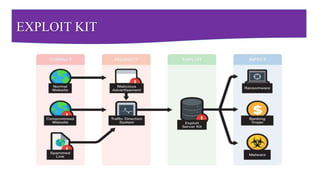
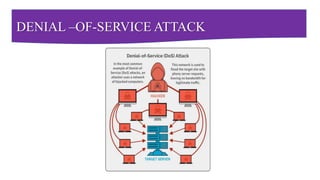
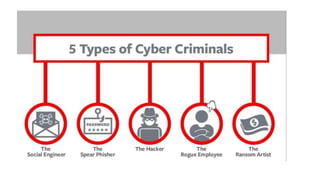
This document provides a comprehensive overview of cybersecurity, emphasizing its importance and various types, including network, cloud, endpoint, mobile, IoT, and application security. It details threats such as identity theft, phishing, and ransomware, along with the evolving challenges posed by cybercriminals, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. The document concludes by highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect individual and organizational data, while outlining the roles of different types of hackers.