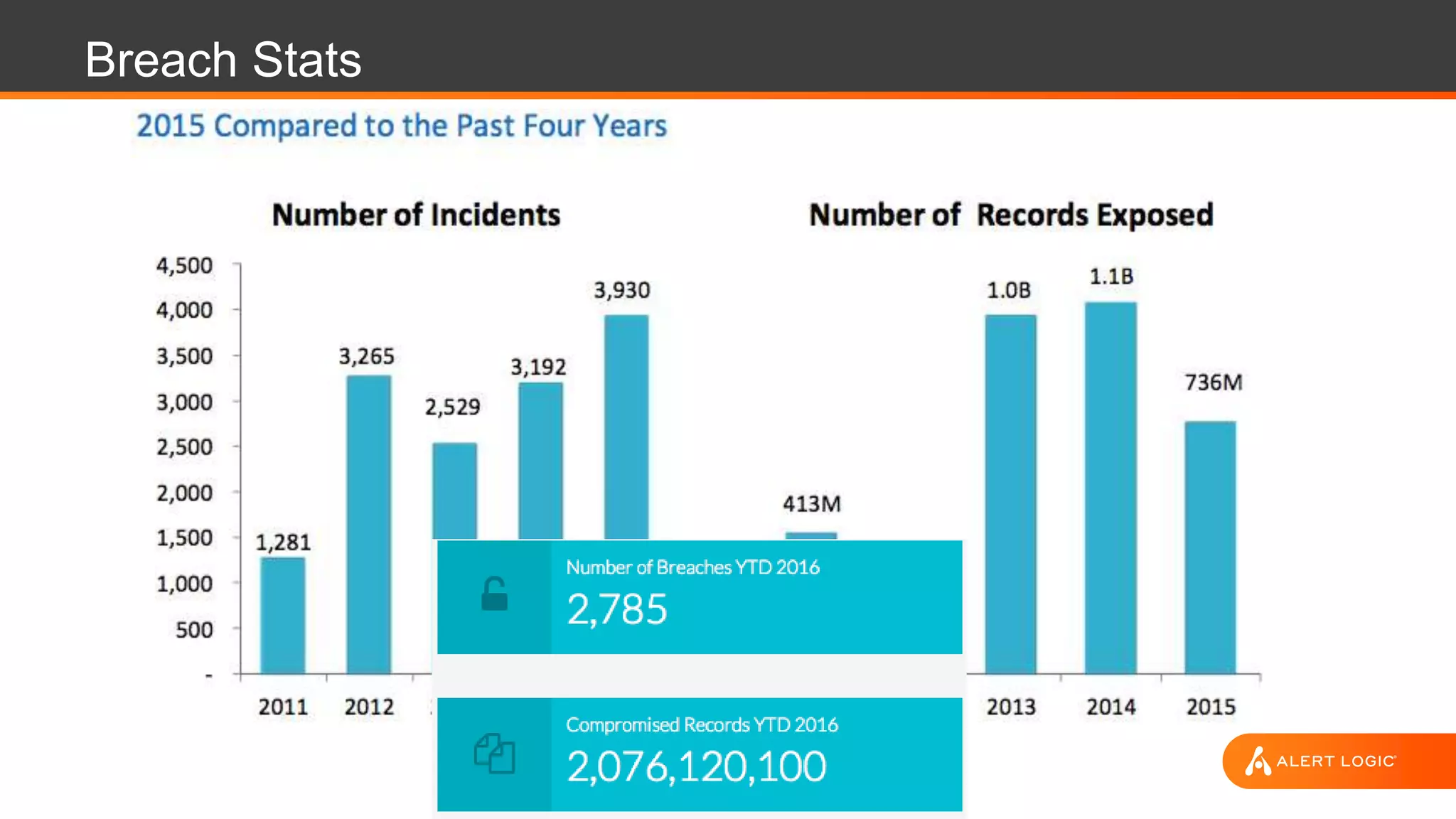
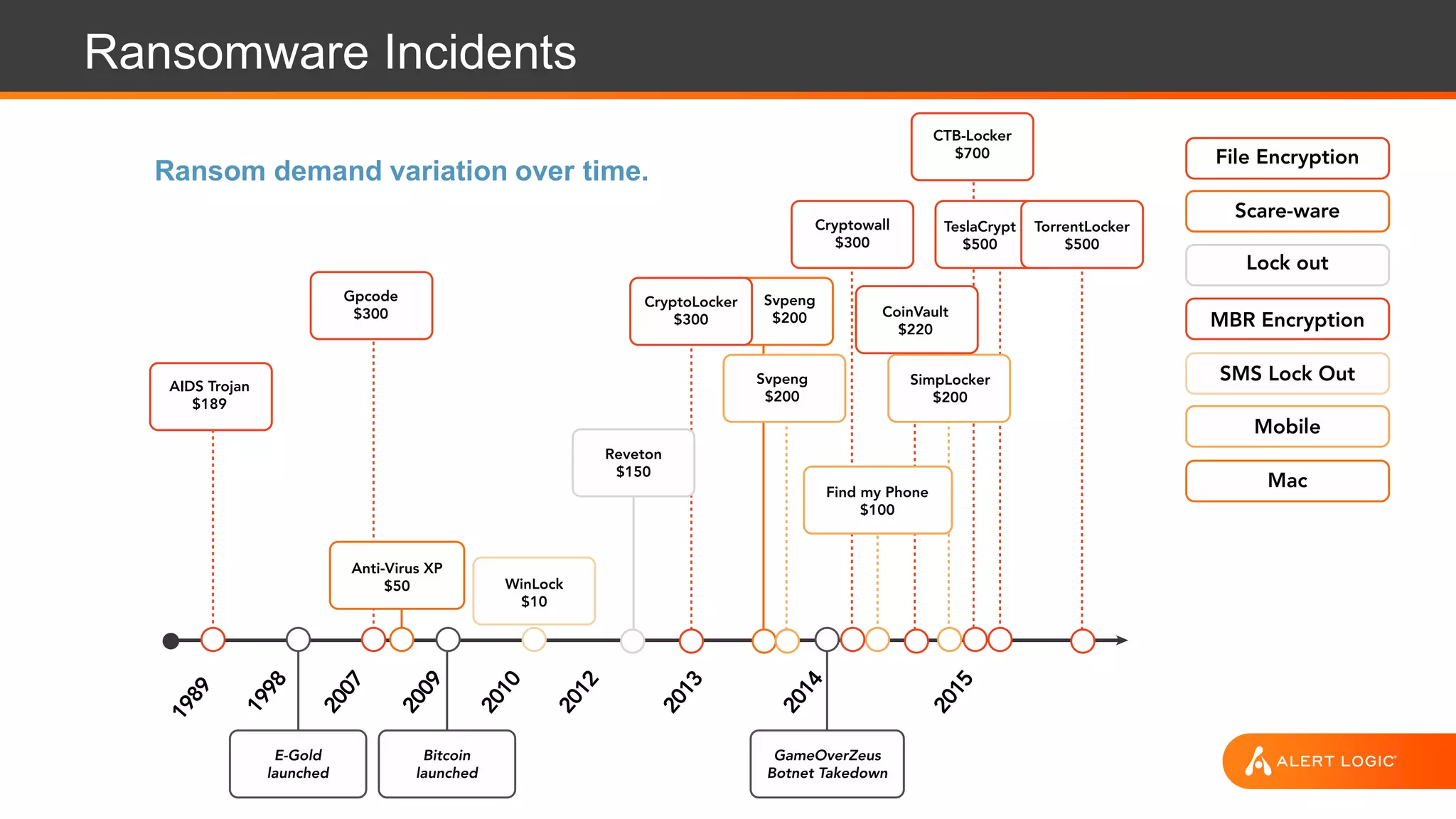
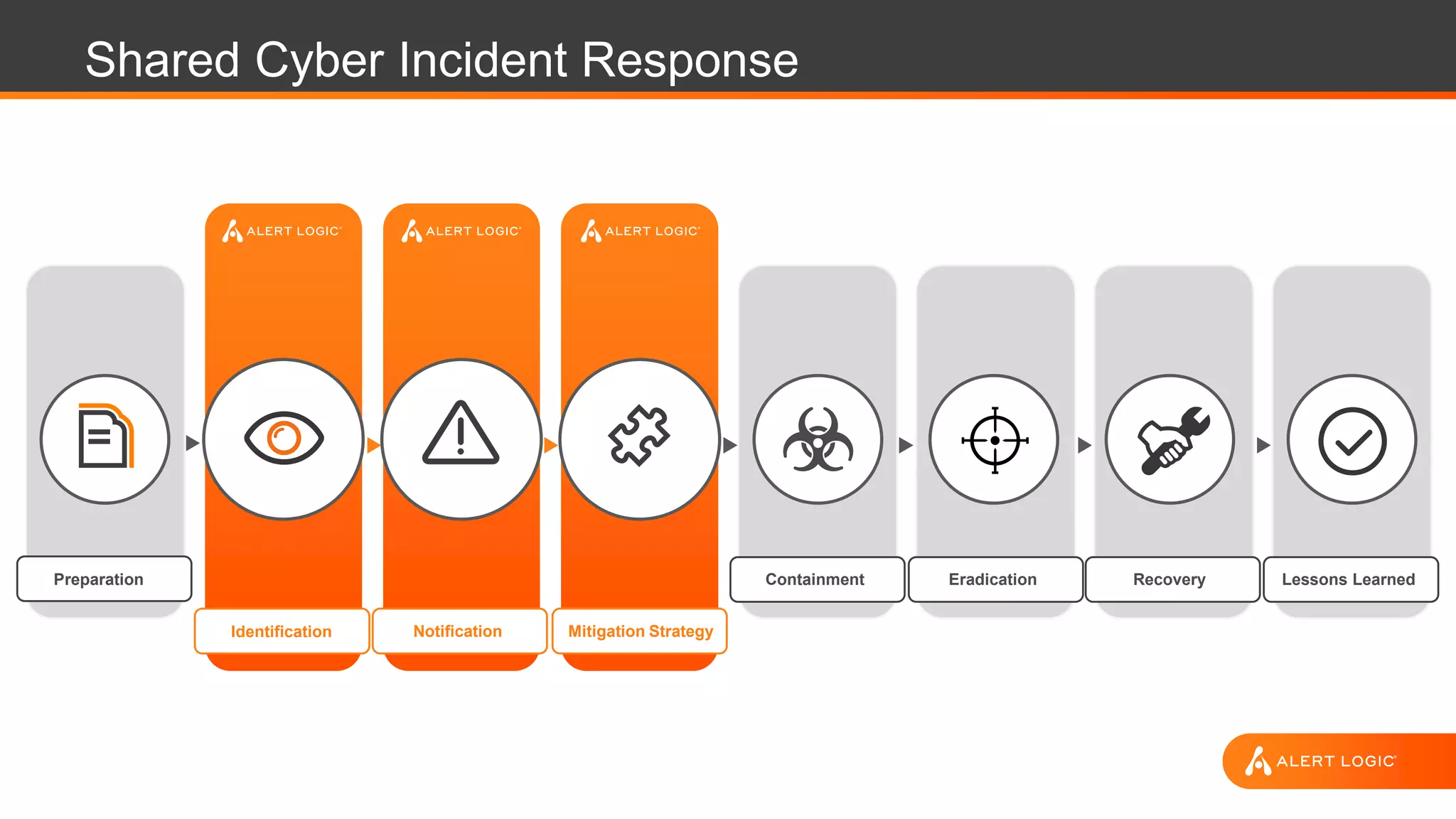
The document outlines key strategies and best practices for cyber incident response, emphasizing the importance of preparation, identification, notification, and effective mitigation strategies. It cites a case study on a ransomware attack affecting the Tewksbury Police Department, illustrating the disruptive impact of such incidents and the need for structured cyber incident response plans. The document highlights various roles and responsibilities within incident response teams and encourages regular testing and training to enhance preparedness and confidence.