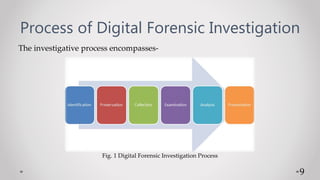
The document outlines the key aspects of digital forensics, including its definition, branches, objectives, and rules for handling digital evidence. It details the steps involved in a digital forensic investigation, which consists of identification, preservation, collection, examination, analysis, and reporting. Emphasis is placed on the importance of maintaining the integrity of evidence throughout the investigation process.