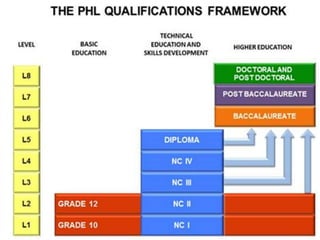
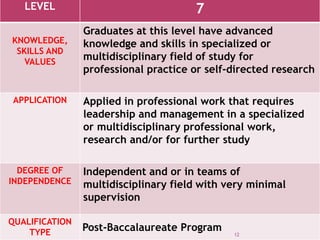
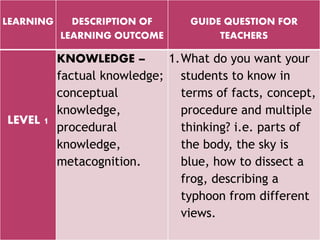
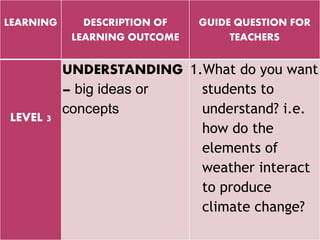
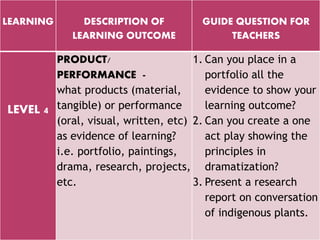
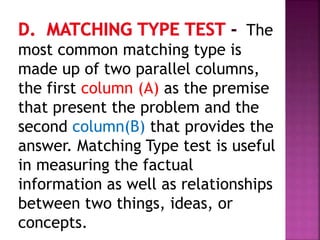
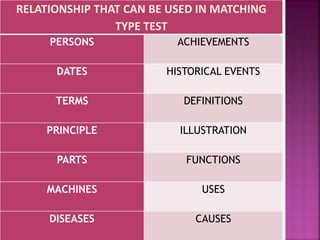
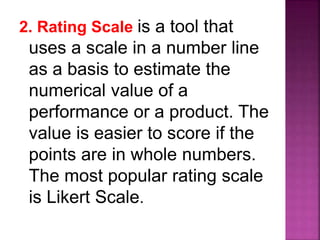
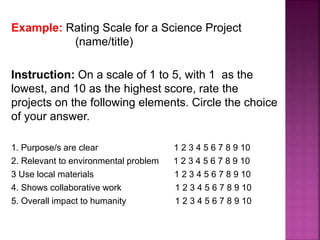
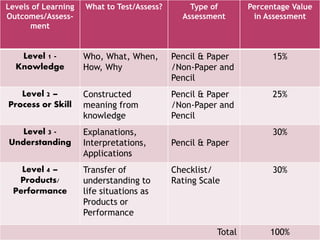
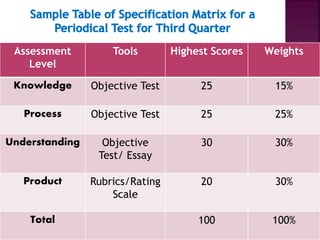
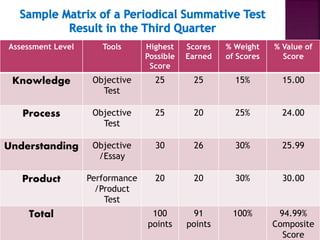
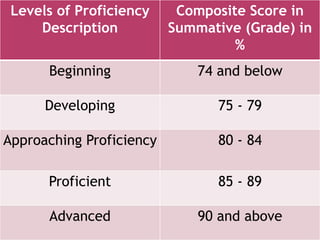
The document outlines a framework for outcome-based education that categorizes various knowledge, skills, and values into a hierarchy of levels, ranging from practical skills at Level 1 to advanced, specialized knowledge at Level 8. It describes assessment methods, including objective tests and authentic evaluation, emphasizing the importance of measuring learning outcomes across different levels of complexity. Finally, it provides guidelines for teachers on how to construct assessments that align with desired learning outcomes, ensuring accurate evaluation of student performance.