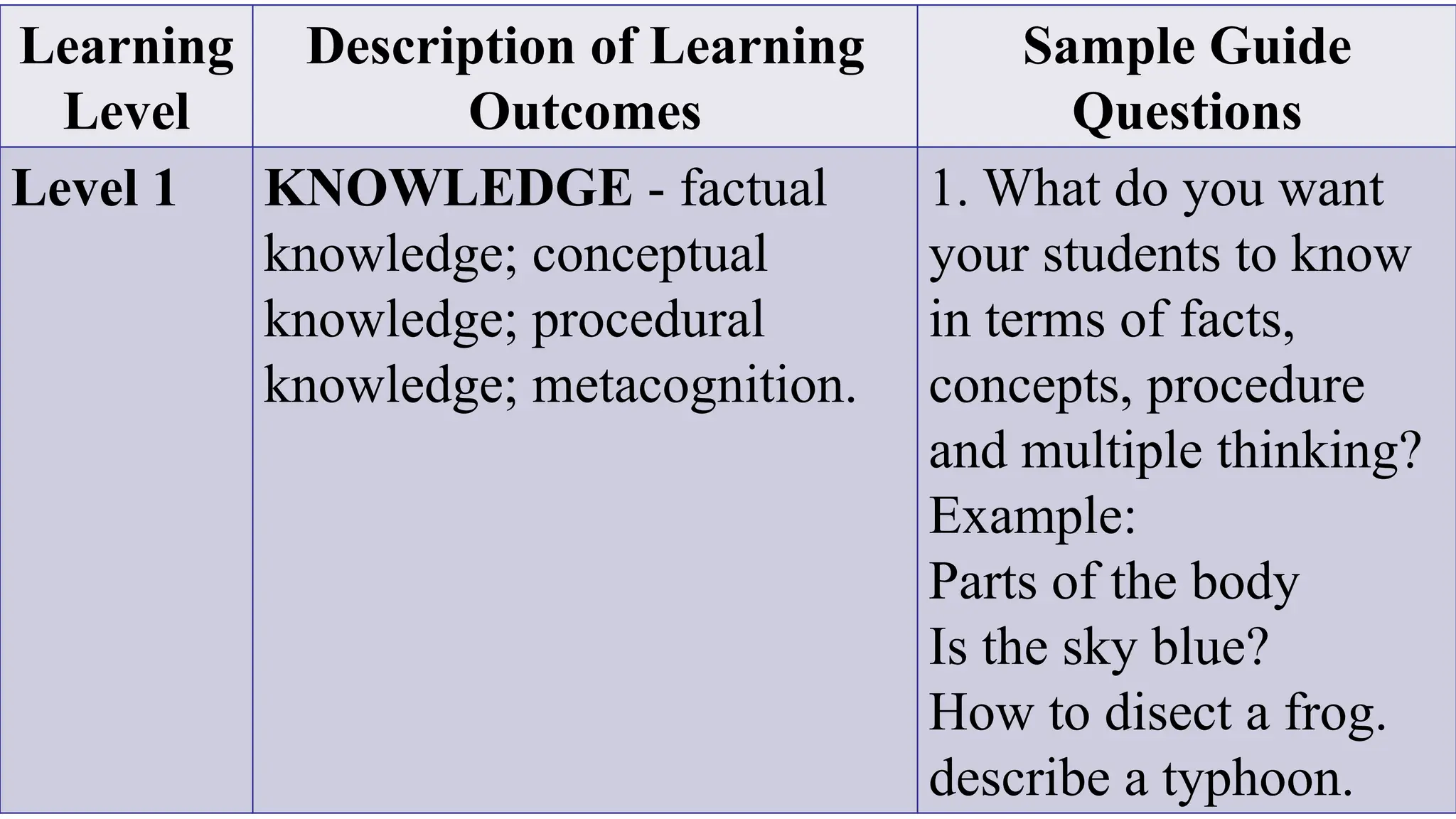
The document discusses curriculum evaluation through learning assessment in the Philippines. It provides information on the Philippines Qualification Framework (PQF) which establishes national standards for qualifications based on education and training levels. It also discusses matching competencies and learning outcomes to the PQF levels through assessment. Finally, it outlines various tools that can be used to measure different learning domains, such as objective and subjective tests, performance assessments, rubrics, and portfolios. The tools are matched to assess knowledge, processes, understanding, and performance/products as defined in the KPUP grading system.