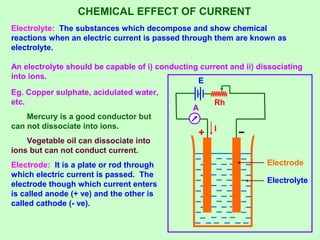
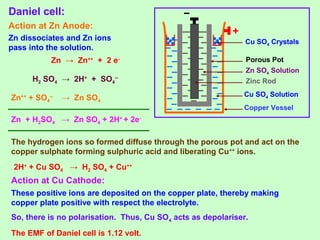
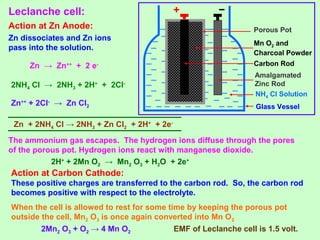
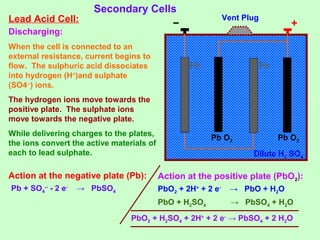
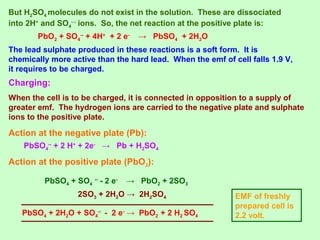
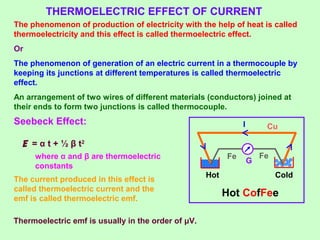
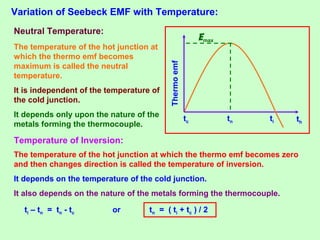
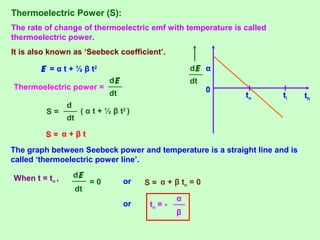
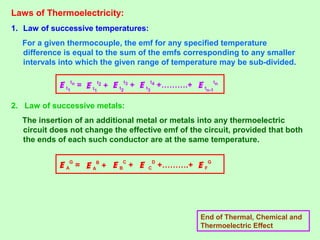
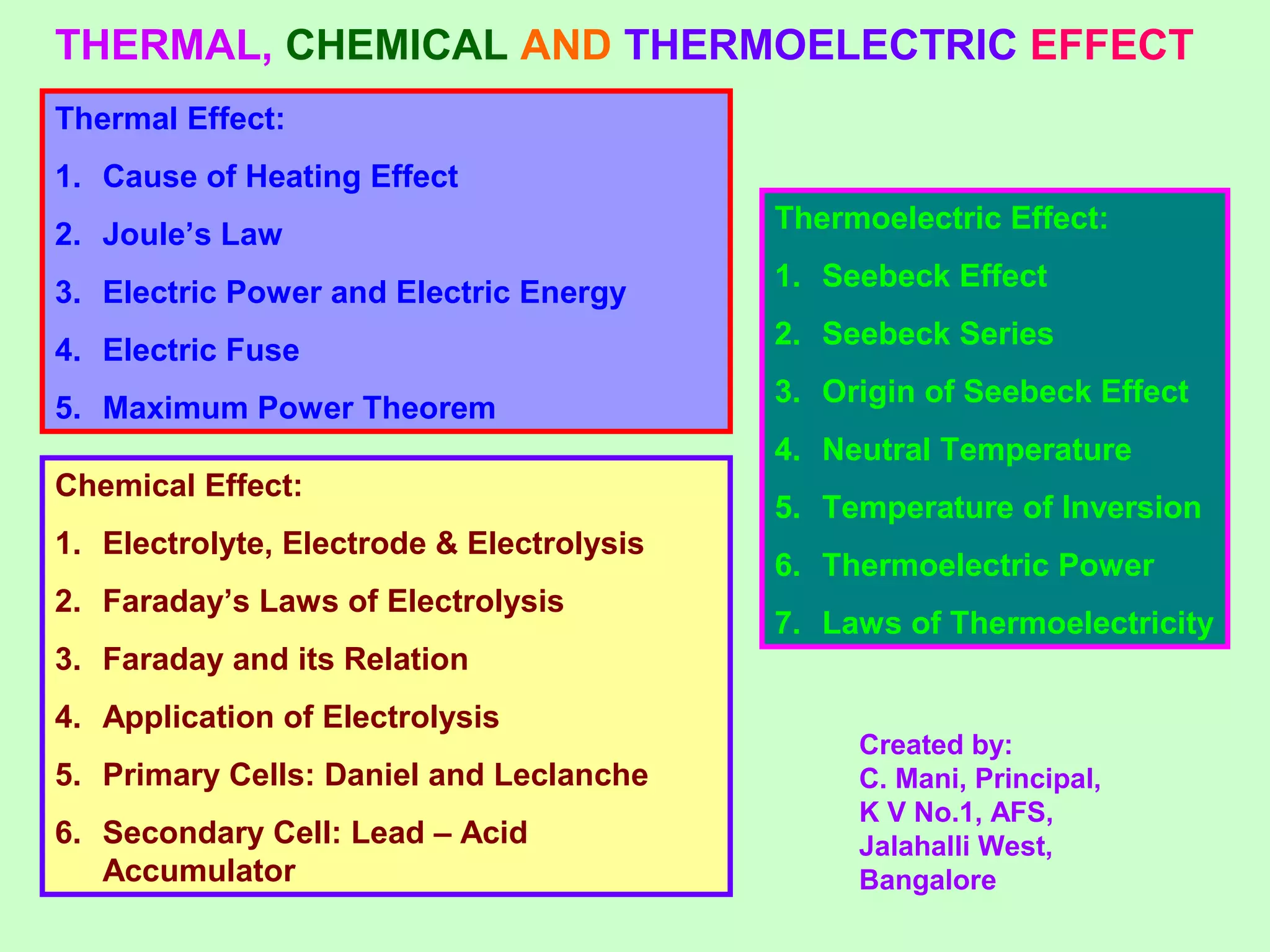
This document discusses three effects of electricity: thermal, chemical, and thermoelectric. The thermal effect explains how an electric current produces heat due to the collision of electrons with atoms in a conductor. Joule's law quantifies this relationship. The chemical effect discusses electrolysis and Faraday's laws of electrolysis. Electrolysis is the process of using a direct current to cause a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. The thermoelectric effect explains how a temperature difference across junctions of two different conductors can produce an electric current, as described by Seebeck's discovery of the thermoelectric effect. Key concepts covered include Seebeck series, neutral temperature, and temperature of inversion.
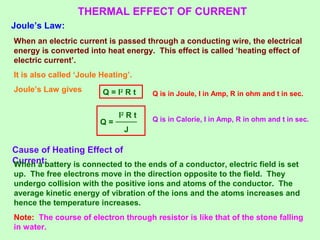

![Electric Heating Appliances use Nichrome wire (alloy of Ni and Cr).
It is used because:
i) It has high specific resistance ii) It has high melting point
iii) It has high malleability iv) It is not easily oxidised.
For given V, P α I P α 1 / R
i.e. i) Higher the power of the appliance, more is the current drawn
ii) Higher the power of the appliance, less is the resistance.
Maximum Power Theorem:
R
II
V
rE
vR + r
E
I =
Output power of source of emf, P = I2
R
R + r
E
P = [ ]2
R
For output power to be maximum,
dR
dP
= 0
Manipulating, we get R = r Maximum Power =
4R
E2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2thermalchemicaleffect-140315123639-phpapp01/85/Current-Electricity-Class-12-Part-3-4-320.jpg)