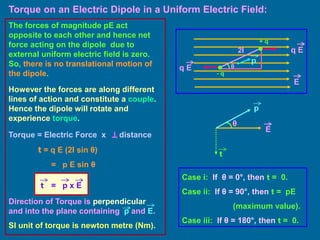
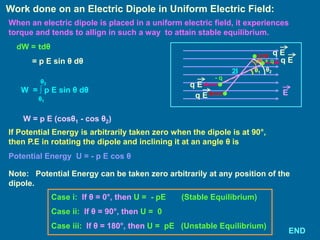
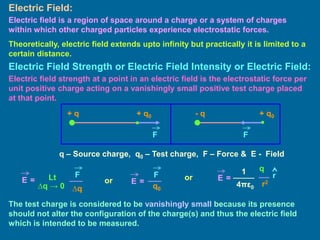
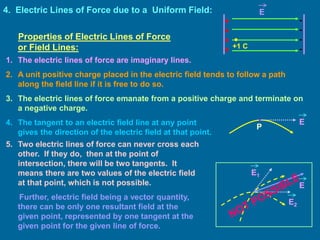
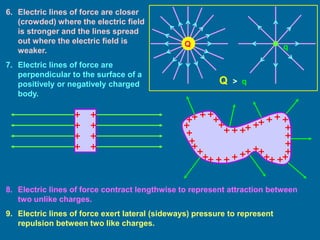
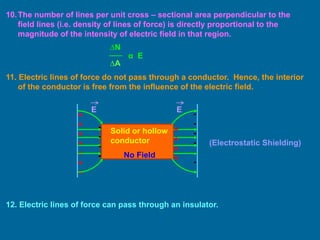
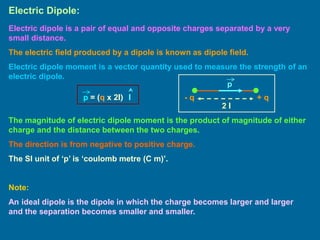
The document covers the principles of electrostatics, focusing on electric fields, electric field intensity due to point charges, and the behavior of electric dipoles. It explains the concept of electric lines of force, their properties, and the superposition principle in electrostatics. Additionally, it discusses the torque and potential energy of electric dipoles in uniform electric fields.



![Electric Field Intensity due to an Electric Dipole:
i) At a point on the axial line:
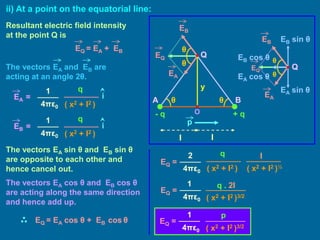
Resultant electric field intensity
at the point P is
EP = EA + EB
The vectors EA and EB are
collinear and opposite.
1
4πε0
i
EA =
q
(x + l)2
q
(x - l)2
1
4πε0
i
EB =
│EP │ = │EB│ - │EA│
│EP │ =
q
(x + l)2
q
(x - l)2
1
4πε0
]
[ -
│EP │ =
1
4πε0
2 (q . 2l) x
(x2 – l2)2
│EP │ =
1
4πε0
2 p x
(x2 – l2)2
If l << x, then
EP ≈
2 p
4πε0 x3
The direction of electric field intensity
at a point on the axial line due to a
dipole is always along the direction of
the dipole moment.
l
l
x
P
EP = EB - EA
+ q
- q
p
A B EA EB
O
EP =
1
4πε0
2 p x
(x2 – l2)2
i](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electrostatics2-240512043834-e1f6d69c/85/chapter-1-electric-charge-and-electric-field-13-320.jpg)