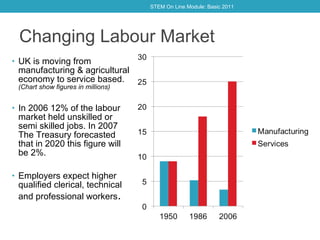
The document outlines current and future trends impacting the demand for STEM skills, including a shift from manufacturing to a service-based economy, an ageing population increasing the need for health and medical services, and a rising STEM skills shortage among UK employers. It highlights specific opportunities within biomedical engineering, bioinformatics, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy technology driven by climate change initiatives and global economic competition, particularly from BRIC nations. A strong emphasis is placed on the necessity of educating the next generation in STEM fields to ensure the UK remains competitive internationally.