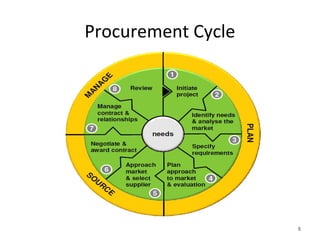
Procurement involves identifying, sourcing, and managing the external resources an organization needs to achieve its strategic objectives. It deals with sourcing activities, negotiating, and strategically selecting goods and services. The objectives of procurement are to secure high quality supplies and materials at the right time and from the right sources at the lowest possible cost.
Strategic procurement involves long-range planning to ensure a timely supply of critical goods and services. It requires considering organizational goals and needs to target achieving them over time. While traditional procurement focuses on administrative buying functions, strategic procurement emphasizes developing supplier relationships through information sharing and collaboration to reduce total ownership costs.
Effective procurement requires skills in identifying needs, negotiating contracts, managing supplier relationships, monitoring