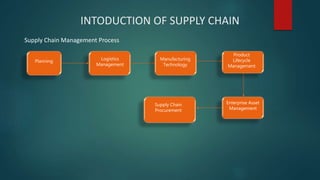
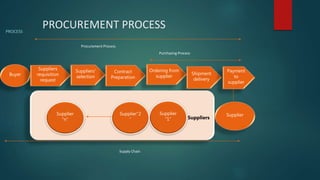
The document discusses supply chain management and procurement. It defines supply chain management as overseeing the flow of materials, information, and finances between suppliers and manufacturers. Procurement involves acquiring goods and services and managing supplier relationships. Key aspects of procurement management in the supply chain include supplier selection and contract negotiation, ensuring compliance, and overseeing the purchasing process. The document also outlines several issues procurement managers must address like risk management, sustainability, diversity, and digital transformation.