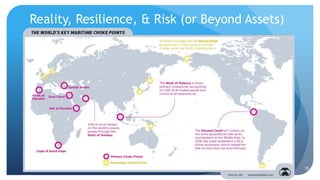
The document discusses the critical importance of supply chain management, emphasizing resilience before and after the pandemic. It highlights strategies for improving supply chain performance through technology, risk management, and alignment between upstream and downstream processes. Key considerations include adapting to logistics challenges, enhancing visibility, and redefining inventory management to respond to changes in demand.