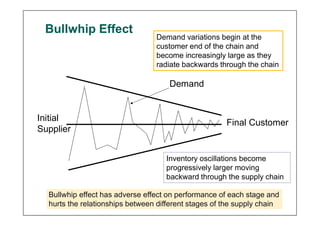
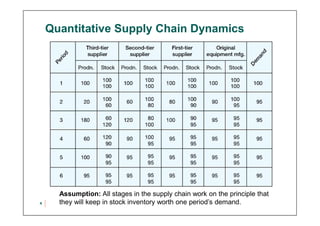
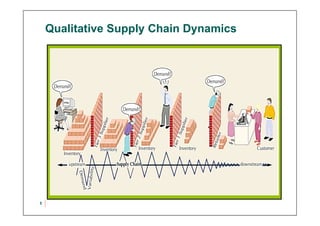
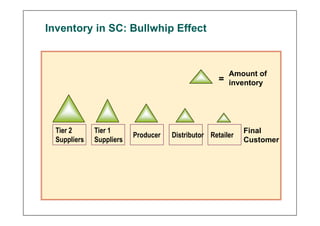
This document discusses supply chain dynamics and the bullwhip effect. It explains that small changes in customer demand can cause larger fluctuations in orders as they move up the supply chain. This disrupts supply chain performance. The causes of unstable supply chains include demand forecasting, order batching, price fluctuations, and lack of coordination. Managing these dynamics requires supply chain coordination through information sharing and alignment, as well as strategies like strategic buffering of inventory and improving operational performance.