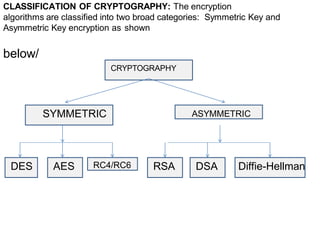
This document discusses basic concepts in cryptography including plaintext, ciphertext, ciphers, keys, encryption, decryption, cryptanalysis, and cryptology. It defines these terms and explains symmetric encryption uses one key for both encryption and decryption while asymmetric encryption uses public and private key pairs, with the public key used for encryption and private key for decryption. Symmetric encryption requires secure key exchange while asymmetric addresses this issue but is slower. Cryptography algorithms can be classified as symmetric using algorithms like DES, AES, RC4 and RC6, or asymmetric using RSA, DSA and Diffie-Hellman public key encryption.








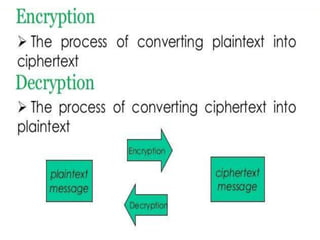




![• A. Symmetric Encryption- This type of cryptography
uses a single key, which is used for encryption and
decryption. The sender uses the key to encrypt the
plaintext and sends the cipher text to the receiver. At
the receiver side, same key will be used to decrypt
the message and get the plaintext. Because there is
common key used for encryption and decryption
process, the secret key cryptography is also known as
symmetric encryption. This was the only type of
encryption method widely known until June 1976.
There are various symmetric key algorithms such as
DES, TRIPLE DES, AES, RC4, RC6, and BLOWFISH
[2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/encryption-200409164024/85/Encryption-14-320.jpg)