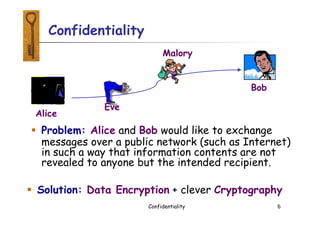
This document provides an introduction to symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. Symmetric cryptography uses the same key for encryption and decryption, while asymmetric cryptography uses public and private key pairs. Symmetric cryptography is faster but requires secure key exchange, while asymmetric cryptography allows secure communication between parties who have not previously shared a key. Examples of symmetric algorithms discussed include AES and DES, while asymmetric or public key cryptography is illustrated using Diffie-Hellman key exchange. Both types are still widely used with increasingly large key sizes providing greater security.