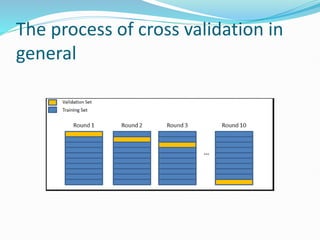
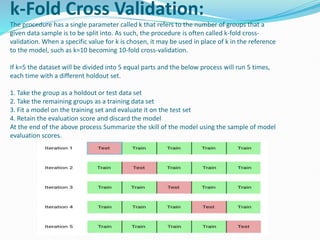
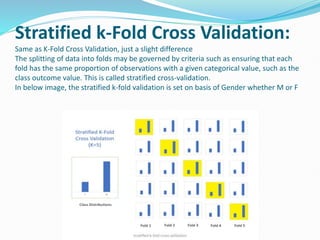
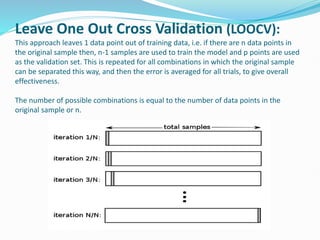
The document discusses the concepts of underfitting and overfitting in machine learning, explaining that overfitting occurs when a model captures noise in the data, leading to poor performance on new data, while underfitting arises when a model is too simple to capture underlying trends. It emphasizes the importance of cross-validation as a technique to mitigate overfitting by evaluating models on different subsets of data, with methods such as k-fold and stratified k-fold cross-validation highlighted. The document provides guidance on how to select the value of k and explains leave one out cross-validation (LOOCV) as a method to assess model performance more rigorously.